Understanding Benign Prostate Enlargement: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Benign Prostate Enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common medical condition that affects a significant number of men as they age. While it is not life-threatening, it can cause uncomfortable and bothersome urinary symptoms. In this article, we will delve into the details of BPH, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
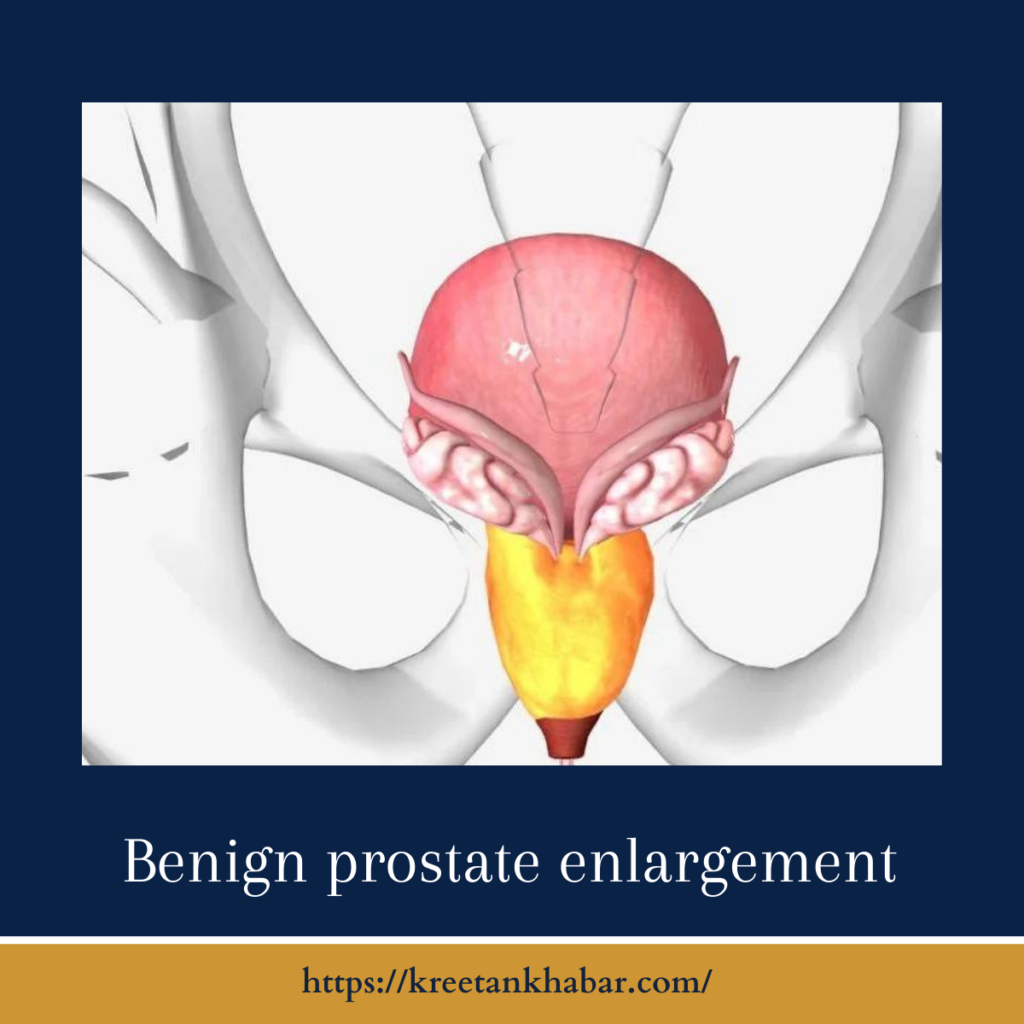
What is Benign Prostate Enlargement?
The prostate is a walnut-sized gland located just below the bladder in men. Its primary function is to produce a fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. As men age, the prostate gland can gradually enlarge, a condition known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Unlike prostate cancer, which involves the growth of malignant cells, BPH is characterized by non-cancerous growth of the prostate tissue.
Causes of Benign Prostate Enlargement
The exact cause of BPH remains unclear, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These include hormonal changes, particularly an increase in dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. Genetic predisposition may also play a role, as BPH tends to run in families. Additionally, aging is a significant risk factor, with most cases occurring in men over the age of 50.
Symptoms
The symptoms of BPH can vary in severity and may include:
- Urinary Frequency: Men with BPH often find themselves needing to urinate more frequently, especially at night (nocturia).
- Urgency: There may be a sudden and compelling urge to urinate, making it difficult to hold back.
- Weak Urine Stream: The urinary stream may become weaker, and it may take longer to empty the bladder completely.
- Difficulty Starting Urination: Some men experience difficulty initiating urination, which can be accompanied by straining.
- Incomplete Emptying: It may feel as if the bladder has not completely emptied after urination.
- Dribbling: After urination, dribbling or leaking of urine can occur.
Diagnosis
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional. To diagnose benign prostate enlargement, your doctor may perform several tests, including:
- Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): This involves the doctor feeling the prostate gland through the rectum to assess its size and check for abnormalities.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: Elevated PSA levels can indicate prostate enlargement, though it is not a definitive diagnostic tool for benign prostate enlargement.
- Urinalysis: This test checks for signs of infection or other urinary problems.
- Transrectal Ultrasound: An ultrasound probe is inserted into the rectum to provide detailed images of the prostate.
- Urodynamic Tests: These assess how well the bladder and urethra are functioning.
Treatment Options
Treatment for BPH depends on the severity of symptoms and their impact on your quality of life. Common treatment options include:
- Watchful Waiting: If symptoms are mild, your doctor may recommend regular monitoring without immediate intervention.
- Medications: Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can help relieve symptoms by relaxing the prostate and reducing its size.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser therapy can be used to remove excess prostate tissue.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective, surgical procedures like open prostatectomy may be necessary to remove the enlarged prostate tissue.
Treatment Options for Benign Prostate Enlargement
Benign prostate enlargement, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition among aging men that can cause bothersome urinary symptoms. Fortunately, there are several effective treatment options available to manage BPH, tailored to the severity of the condition and individual patient preferences. Here are the primary treatment options for BPH:
- Watchful Waiting (Active Surveillance):
- This approach is suitable for men with mild or asymptomatic benign prostate enlargement.
- It involves regular monitoring of symptoms and prostate size without immediate intervention.
- Recommended for those who have minimal or no impact on their daily life.
- Medications:
- Alpha-Blockers (e.g., Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin): These drugs relax the prostate and bladder neck muscles, improving urine flow.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors (e.g., Finasteride, Dutasteride): They reduce the size of the prostate by inhibiting the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone associated with prostate growth.
- Combination Therapy: Some patients benefit from a combination of alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
- This surgical procedure involves removing excess prostate tissue using a resectoscope passed through the urethra.
- Effective for moderate to severe benign prostate enlargement and provides rapid symptom relief.
- Laser Therapy (Laser Vaporization or Enucleation):
- Different types of laser procedures can be used to vaporize or enucleate the prostate tissue.
- These techniques are less invasive than TURP and have shorter recovery times.
- Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy (TUMT):
- A minimally invasive procedure that uses microwave energy to heat and shrink prostate tissue.
- Suitable for moderate benign prostate enlargement cases.
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP):
- UroLift System:
- A minimally invasive procedure that places small implants to lift and hold the enlarged prostate tissue away from the urethra.
- Relieves urinary symptoms without causing sexual dysfunction.
- Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE):
- A non-surgical procedure that blocks the blood supply to the prostate, causing it to shrink.
- An option for men who wish to avoid surgery or are not suitable candidates for other procedures.
- Open Prostatectomy:
- Reserved for severe cases or when other treatments are not feasible.
- Involves surgically removing the excess prostate tissue through an abdominal incision.
- Typically requires a longer hospital stay and recovery time compared to minimally invasive options.
- Combination Therapies:
- In some cases, doctors may recommend a combination of treatments to achieve the best results, such as medication alongside a minimally invasive procedure.
The choice of treatment for benign prostate enlargement depends on various factors, including the severity of symptoms, prostate size, overall health, and patient preferences. It is crucial for individuals experiencing benign prostate enlargement symptoms to consult with a healthcare provider who can assess their condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan to improve their quality of life.
Conclusion
Benign Prostate Enlargement is a common condition that affects many men as they age. While it is not a life-threatening condition, it can significantly impact one’s quality of life due to urinary symptoms. Seeking early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage the symptoms effectively, allowing men to lead a more comfortable and active life as they age. If you suspect you have BPH, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023