Testicular Cancer: Early Detection and Empowering Awareness
Introduction
Testicular cancer, though relatively rare compared to other types of cancer, is a significant health concern affecting primarily young and middle-aged men. This article delves into the world of testicular cancer, exploring its risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of early detection.
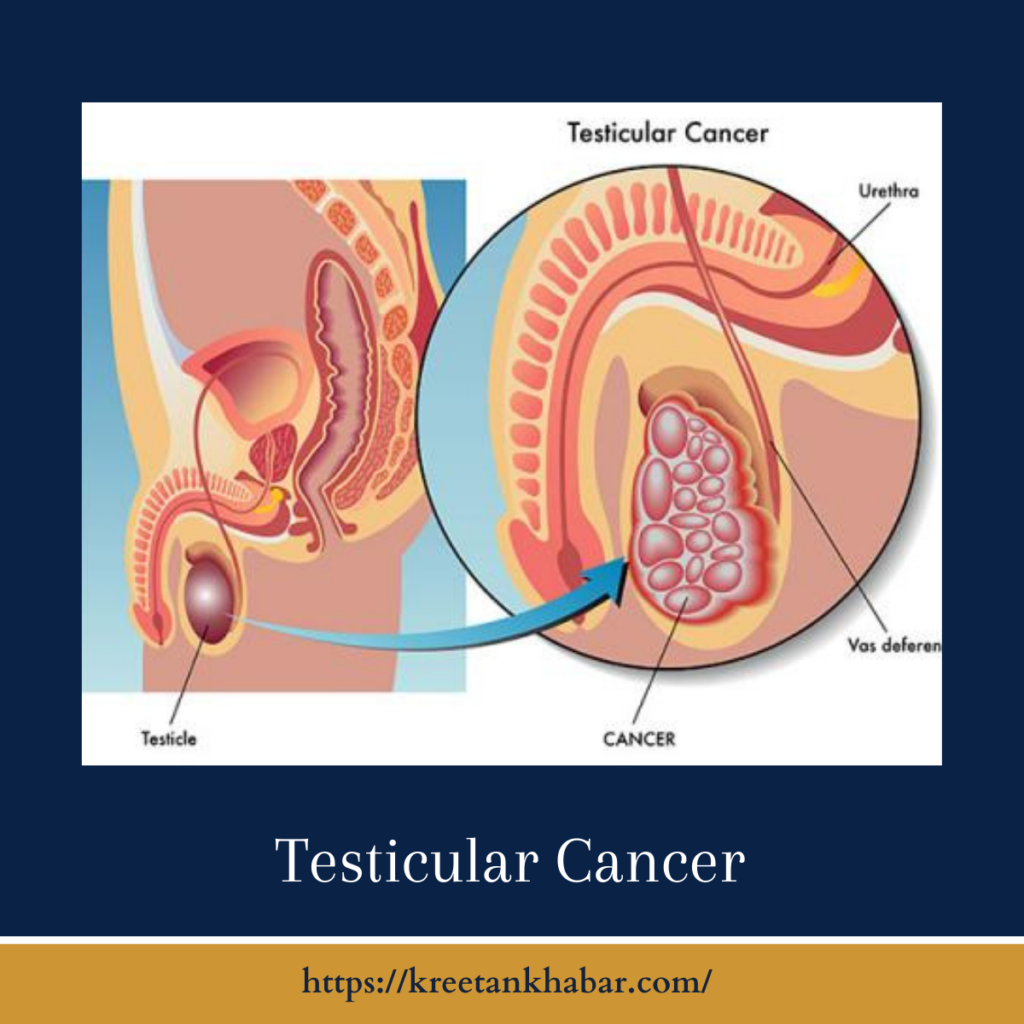
Understanding Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer originates in the testicles, the male reproductive glands responsible for producing sperm and testosterone. It typically begins as an abnormal growth of cells within the testicle, which can become cancerous over time.
Risk Factors
While the exact cause of testicular cancer remains unclear, several risk factors have been identified:
- Age: Testicular cancer is most common in men between the ages of 15 and 35, although it can occur at any age.
- Undescended Testicle (Cryptorchidism): Men born with one or both testicles not descending into the scrotum have a higher risk of developing testicular cancer.
- Family History: A family history of testicular cancer increases the risk for an individual.
- Race and Ethnicity: Testicular cancer is more common in white men than in men of other racial or ethnic groups.
- HIV Infection: Men with HIV/AIDS have a slightly elevated risk of testicular cancer.
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of testicular cancer is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment:
- Lump or Enlargement: The most common sign is a painless lump or swelling in one of the testicles.
- Pain or Discomfort: Some men may experience a dull ache or heaviness in the lower abdomen or scrotum.
- Changes in Testicle Size or Shape: Any noticeable change in the size or shape of the testicles should be evaluated.
- Pain or Discomfort in the Scrotum: Persistent pain or discomfort in the scrotum or testicles should not be ignored.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing testicular cancer typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. Key diagnostic procedures include:
- Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves create detailed images of the testicles to identify any abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Blood markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-HCG), are measured to help diagnose and classify the cancer.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a surgical procedure may be required to remove a portion or the entire affected testicle for examination.
Treatment Options
Testicular cancer is one of the most treatable forms of cancer, with high cure rates, especially when diagnosed at an early stage. Treatment options depend on the type and stage of cancer and may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the affected testicle, known as radical inguinal orchiectomy, is the primary treatment. It is often curative, even for advanced cases.
- Radiation Therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be recommended to target residual cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be administered to treat more aggressive forms of testicular cancer or to prevent recurrence.
- Surveillance: For certain early-stage cancers, active surveillance with regular follow-up is an option to monitor the condition.
here are 30 points outlining the treatment options for testicular cancer:
- Orchiectomy: Surgical removal of the affected testicle, which is the primary treatment for most cases of testicular cancer.
- Radical Inguinal Orchiectomy: The standard surgical procedure, involving the removal of the entire testicle through an incision in the groin.
- Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection (RPLND): A surgical procedure to remove lymph nodes in the abdomen, typically used for specific types and stages of testicular cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy beams of radiation target and destroy cancer cells, often used after surgery or as an alternative to chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy: Medications are administered intravenously or orally to kill cancer cells throughout the body, frequently used for advanced or aggressive forms of testicular cancer.
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy administered after surgery to prevent cancer recurrence.
- Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Administered before surgery to shrink large tumors or cancer that has spread to lymph nodes.
- High-Dose Chemotherapy with Stem Cell Transplant: For refractory or relapsed testicular cancer, high-dose chemotherapy is followed by the infusion of healthy stem cells to rebuild the bone marrow.
- Targeted Therapies: Emerging treatments that target specific proteins or genetic mutations in cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Boosting the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, an option under investigation for testicular cancer treatment.
- Active Surveillance: A strategy for low-risk or stage 1 cancer where patients are closely monitored but not immediately treated, preserving fertility.
- Testosterone Replacement Therapy: After orchiectomy, hormone therapy may be needed to maintain normal testosterone levels.
- Fertility Preservation: Options such as sperm banking can help men preserve their fertility before cancer treatment.
- Palliative Care: For advanced or incurable cases, palliative care focuses on symptom management and improving quality of life.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to innovative treatments and therapies under investigation.
- Chemotherapy Regimens: Different combinations of chemotherapy drugs are used, such as BEP (bleomycin, etoposide, cisplatin) and EP (etoposide, cisplatin).
- Radiation Techniques: Techniques like intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and proton therapy allow precise targeting of radiation to cancerous areas while sparing healthy tissue.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgical techniques may be used for lymph node dissection, reducing recovery time.
- Second Opinions: Seeking a second medical opinion can provide additional treatment options and clarity in decision-making.
- Psychological Support: Mental health support, counseling, and support groups help patients cope with the emotional challenges of treatment.
- Nutritional Guidance: Proper nutrition is essential to support the body during treatment and recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Rehabilitation and exercise programs help patients regain strength and mobility after surgery and treatments.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments and monitoring are essential to track progress and detect recurrence.
- Seminoma vs. Non-Seminoma: Treatment plans may vary depending on the type of testicular cancer, whether it’s seminoma or non-seminoma.
- Risk Assessment: Medical professionals consider the patient’s overall health, age, and stage of cancer when determining the most suitable treatment plan.
- Long-Term Side Effect Management: Addressing potential long-term side effects of treatments, such as infertility or cardiovascular issues.
- Multi-Disciplinary Care: Collaboration among urologists, oncologists, radiation therapists, and other specialists ensures comprehensive care.
- Patient Education: Informing patients about their condition and treatment options empowers them to make informed decisions.
- Supportive Medications: Medications may be prescribed to manage side effects, such as nausea or pain.
- Survivorship Care Plans: Developing personalized care plans for post-treatment life, including monitoring for any late effects or recurrence.
These 30 points highlight the diverse treatment options and considerations in managing testicular cancer. Tailored treatment plans, early detection, and comprehensive care are essential elements in ensuring the best possible outcomes for individuals facing this diagnosis.
Conclusion
Testicular cancer is a highly treatable cancer with a favorable prognosis, especially when detected and treated early. Empowering awareness about the risk factors, symptoms, and importance of regular self-examinations and medical check-ups is crucial. With advancements in medical science and early intervention, individuals diagnosed with testicular cancer can lead fulfilling lives and overcome this challenge with confidence.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023