Arterial Insufficiency: A Closer Look at Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction:
Arterial insufficiency is a medical condition that occurs when there is inadequate blood flow through the arteries, resulting in a reduced supply of oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and organs. This condition can have significant implications for a person’s health, leading to various symptoms and complications. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for arterial insufficiency.
Causes:
Arterial insufficiency is commonly caused by atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances on the walls of the arteries. Over time, these deposits can narrow and harden the arteries, restricting blood flow. Other potential causes include blood clots, inflammation of the blood vessels, and arterial dissection.
The points for causes of Artial Insuffiency:
- Atherosclerosis: The primary cause of arterial insufficiency is atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances build up on the arterial walls, leading to narrowing and hardening of the arteries.
- Blood Clots: Formation of blood clots within the arteries can impede blood flow, causing arterial insufficiency. These clots may develop locally or travel from other parts of the body.
- Inflammation: Inflammatory conditions affecting the blood vessels, such as vasculitis, can lead to arterial insufficiency by causing damage to the vessel walls and restricting blood flow.
- Arterial Dissection: A tear in the arterial wall can lead to the formation of a blood clot, reducing blood flow. Arterial dissection can result from trauma or spontaneous events.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): PAD is a common contributor to arterial insufficiency, often associated with atherosclerosis affecting the arteries supplying the legs and feet.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are at an increased risk of arterial insufficiency due to the impact of high blood sugar levels on blood vessels, leading to atherosclerosis and reduced blood flow.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains chemicals that can damage blood vessels and accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis, contributing to arterial insufficiency.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Persistent high blood pressure can damage arterial walls, promoting the development of atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of arterial insufficiency.
- Hyperlipidemia: Elevated levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood can contribute to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, narrowing the arteries and causing insufficiency.
- Genetic Factors: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to conditions that increase the likelihood of arterial insufficiency, such as certain vascular diseases or disorders affecting blood clotting.
- Age: Aging is a natural factor that can contribute to the development of arterial insufficiency as blood vessels may become less elastic and more susceptible to damage over time.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is associated with an increased risk of developing atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular conditions, contributing to arterial insufficiency.
- Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles can contribute to the development of arterial insufficiency by promoting conditions like obesity and reducing overall cardiovascular health.
Understanding these diverse causes of arterial insufficiency is crucial for both prevention and effective management. Addressing risk factors through lifestyle modifications and medical interventions can play a significant role in reducing the incidence and severity of this condition.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of arterial insufficiency often manifest in the extremities, such as the legs and feet, where blood flow may be most affected. Common symptoms include:
- Claudication: This refers to pain or cramping in the muscles, typically in the legs, during physical activity. The discomfort usually subsides with rest.
- Coolness and paleness: The affected extremity may feel cooler to the touch and appear paler than usual due to reduced blood flow.
- Weak or absent pulses: In severe cases, the pulses in the affected arteries may be weak or even absent.
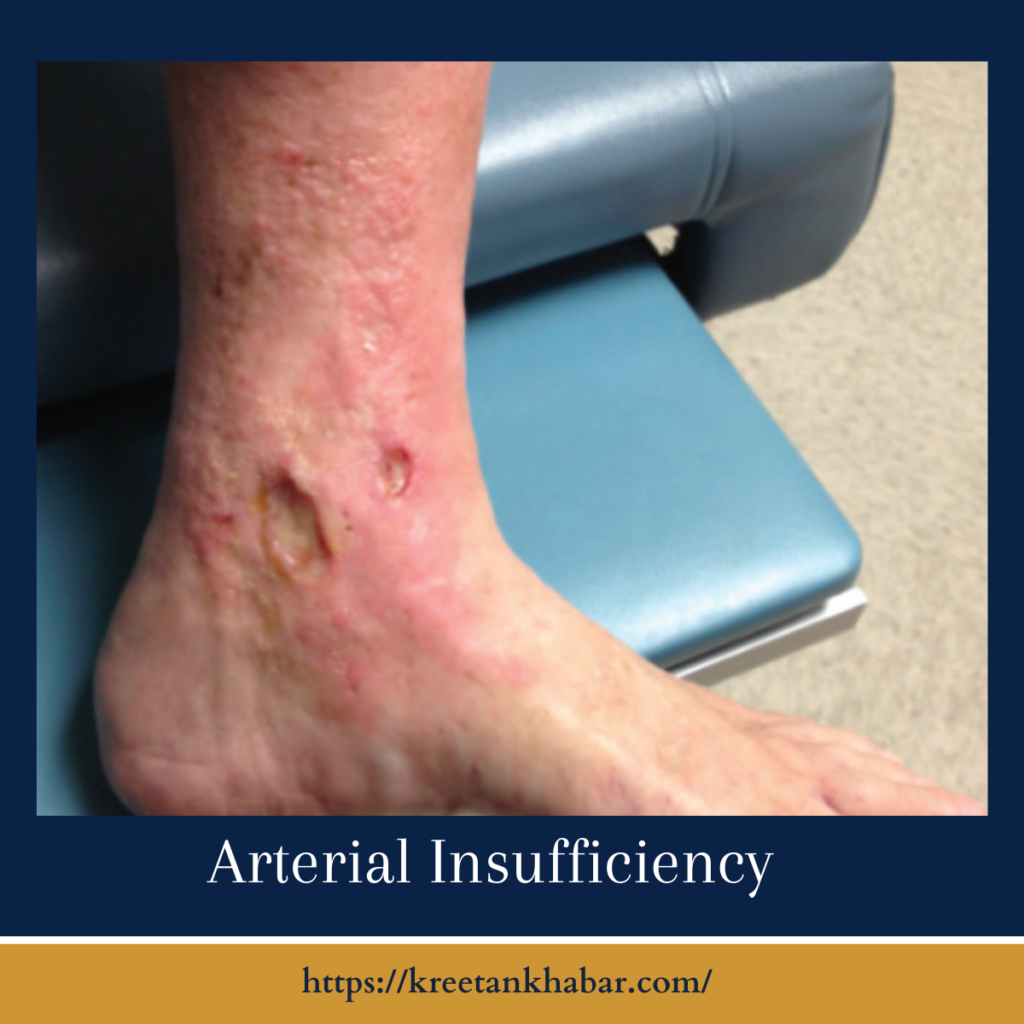
- Non-healing wounds: Reduced blood flow can impair the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow-healing or non-healing wounds, especially on the feet.
- Gangrene: In advanced stages, severe arterial insufficiency can lead to tissue death, resulting in gangrene, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
More points of symptoms:
- Claudication: One of the hallmark symptoms of arterial insufficiency is claudication, which refers to pain or cramping in the muscles, particularly in the legs, during physical activity. The discomfort usually subsides with rest.
- Coolness and Paleness: The affected extremity, often the legs or feet, may feel cooler to the touch than usual. Additionally, the skin may appear paler due to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply.
- Weak or Absent Pulses: In cases of arterial insufficiency, pulses in the affected arteries may be weak or even absent. This reflects the impaired blood flow through the narrowed or blocked vessels.
- Non-healing Wounds: Reduced blood flow hinders the body’s ability to heal, leading to slow-healing or non-healing wounds, especially in the lower extremities. These wounds may be prone to infection.
- Gangrene: In advanced stages, severe arterial insufficiency can result in tissue death, leading to gangrene. This is a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention and may be characterized by blackened or discolored skin.
- Hair Loss and Shiny Skin: Insufficient blood supply can affect the health of the skin and hair on the affected limb. Hair loss and a shiny appearance of the skin may be noticeable.
- Numbness or Weakness: Some individuals with arterial insufficiency may experience numbness or weakness in the affected extremity due to compromised nerve function resulting from reduced blood flow.
- Erectile Dysfunction: In men, arterial insufficiency affecting blood flow to the pelvic region may contribute to erectile dysfunction.
- Pain at Rest: In severe cases, individuals may experience pain even at rest, particularly during the night. This could indicate advanced arterial insufficiency with inadequate blood flow even when the body is at rest.
- Skin Ulcers: Chronic insufficient blood supply can lead to the development of skin ulcers, particularly on the feet. These ulcers may be painful and prone to infection.
- Thickened Toenails: Changes in the texture and thickness of toenails may occur due to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the nail beds.
- Pallor Upon Elevation: Elevating the affected limb may result in pallor, as the already limited blood flow is further compromised.
- Difficulty Walking: As arterial insufficiency progresses, individuals may find it increasingly difficult to walk, especially longer distances, due to pain and discomfort.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention. Individuals experiencing any of these signs should seek prompt medical attention to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment:
Managing arterial insufficiency involves addressing the underlying causes and alleviating symptoms. Here are some common treatment approaches:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, and smoking cessation, can help manage risk factors associated with arterial insufficiency.
- Medications: Blood-thinning medications, such as aspirin or antiplatelet drugs, may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clots and improve blood flow.
- Angioplasty and stenting: In some cases, minimally invasive procedures like angioplasty and stenting may be performed to open narrowed or blocked arteries.
- Bypass surgery: In severe cases, bypass surgery may be recommended to reroute blood flow around blocked arteries, improving circulation.
- Wound care: Proper care of wounds and ulcers is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. This may involve regular cleaning, dressing changes, and offloading pressure from affected areas.
Conclusion:
Arterial insufficiency is a serious condition that requires prompt diagnosis and management. Recognizing the symptoms and addressing underlying risk factors can significantly improve outcomes. If you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms of arterial insufficiency, it is crucial to seek medical attention to determine the appropriate course of action for your individual case. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing this condition and improving overall quality of life.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023