Scapula
The scapula(also known as shoulder blade), often overlooked in discussions of the shoulder complex, serves as a silent powerhouse crucial for optimal upper limb function. Positioned on the posterior thoracic wall like a guardian, this triangular bone boasts a myriad of features that contribute to the grace and versatility of our shoulder movements. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the scapula, exploring its anatomy, function, and significance in our daily lives.
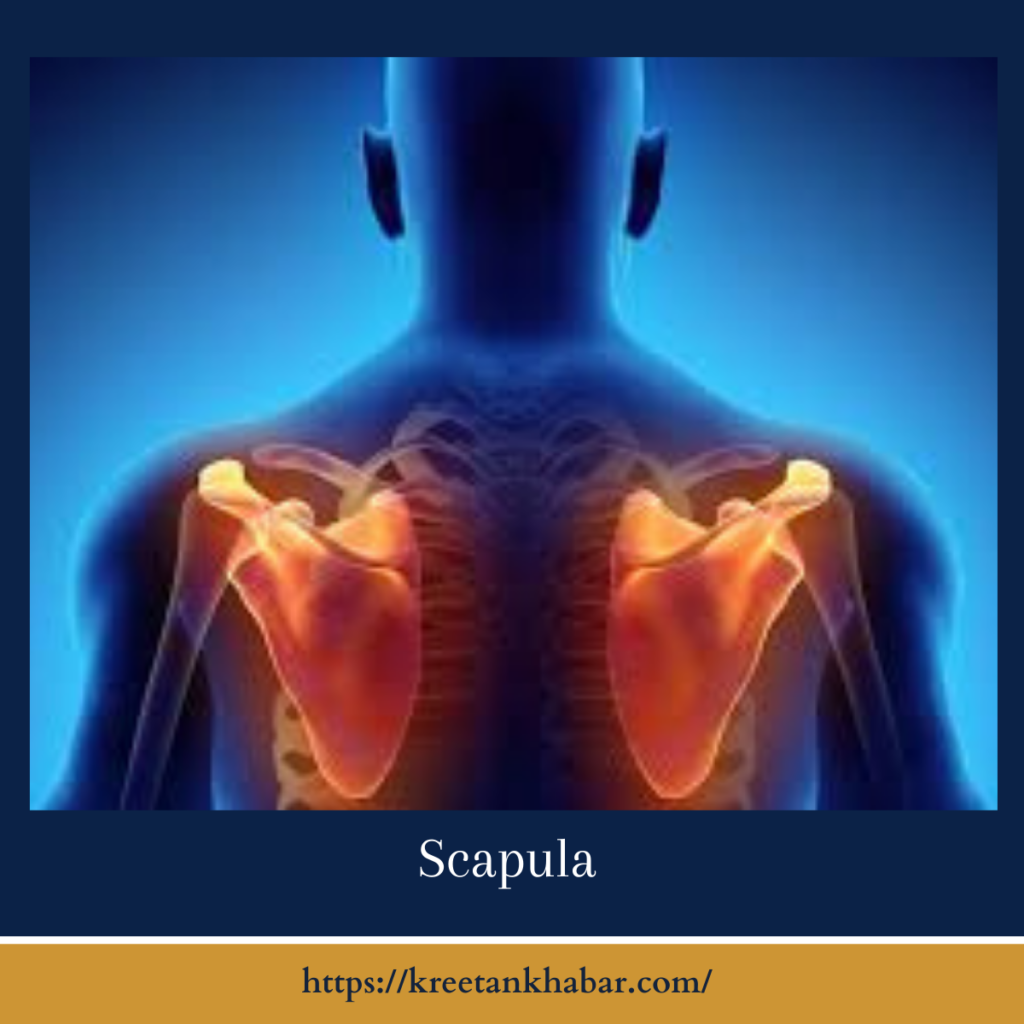
Anatomy Unveiled
The scapula’s anatomy is a testament to both elegance and functionality. It features distinctive landmarks such as the acromion process, which forms the bony roof of the shoulder joint, and the glenoid cavity, a shallow indentation that cradles the humeral head to form the shoulder joint. Additionally, the coracoid process, jutting out like a sentinel, provides attachment points for crucial shoulder muscles and ligaments. Surrounding these landmarks are various fossae and borders, each serving as anchor points for muscles essential to shoulder movement and stability.
Function in Motion
As the unsung hero of shoulder mobility, the shoulder blade orchestrates a symphony of movements essential for daily activities. It glides effortlessly along the ribcage, allowing the arm to move in multiple planes. During arm elevation, the scapula rotates upward and outward, providing clearance for the humeral head and preventing impingement. Its coordinated movements, guided by an intricate network of muscles including the trapezius, serratus anterior, and rhomboids, ensure smooth and controlled shoulder motion with every reach, lift, and rotation.
Beyond the Ordinary: Scapular Disorders
Despite its resilience, the scapula is not immune to injury and dysfunction. shoulder blade dyskinesis, characterized by abnormal movement patterns, can arise due to muscle imbalances, poor posture, or overuse injuries. This condition can lead to shoulder pain, reduced range of motion, and compromised shoulder function. Other scapular disorders, such as winging or instability, may result from trauma, nerve damage, or underlying medical conditions, further highlighting the importance of maintaining scapular health and function.
- Dynamic Stability Hub: While often seen as a static bone, the shoulder blade is a dynamic structure crucial for stabilizing the shoulder joint during complex movements. Its ability to glide, rotate, and tilt in multiple directions allows for smooth and coordinated motion of the arm, making it a dynamic stability hub rather than a passive structure.
- Bridge Between Upper Body and Core: The scapula serves as a vital link between the upper body and the core, facilitating efficient transfer of forces and energy during functional movements. Its connections to the ribcage, spine, and shoulder girdle create a seamless integration of upper body and core musculature, essential for activities like throwing, lifting, and reaching.
- Integrative Role in Movement Patterns: Beyond its role in shoulder motion, the shoulder blade plays an integrative role in various movement patterns across the body. Its position and stability influence the alignment and function of adjacent joints, including the cervical spine, thoracic spine, and shoulder complex. By optimizing scapular mechanics, we can enhance overall movement efficiency and reduce the risk of injury throughout the kinetic chain.
- Gateway to Mind-Body Connection: Exploring the movement and positioning of the shoulder blade can deepen our understanding of the mind-body connection and its impact on movement patterns. Mindful awareness of scapular position and movement can foster greater proprioception, body awareness, and motor control, enhancing movement quality and efficiency.
- Expression of Individuality: The shape, size, and movement patterns of the shoulder blade are unique to each individual, reflecting their anatomical variations, movement habits, and biomechanical predispositions. Embracing the diversity of scapular anatomy and function highlights the intricacies of human movement and celebrates the individuality of our physical expression.
- Gateway to Movement Potential: By unlocking the full potential of the shoulder blade, we can tap into a vast reservoir of movement capabilities and possibilities. Exploring novel movement patterns, variations, and challenges that engage the scapular muscles can expand our movement repertoire, enhance functional capacity, and promote overall well-being.
- Symbol of Adaptability and Resilience: The scapula’s ability to adapt and respond to changing movement demands exemplifies its resilience and adaptability. Whether in sports, rehabilitation, or daily activities, the shoulder blade adapts to accommodate varying loads, positions, and movement patterns, embodying the resilience of the human body in the face of challenges.
By delving beyond the ordinary perception of the shoulder blade, we can uncover its profound significance in movement, expression, and well-being, inviting a deeper exploration of its role in human anatomy and function.
Nurturing Shoulder Health
To nurture the health and vitality of our shoulders, it’s essential to pay homage to the shoulder blade. Incorporating exercises that target scapular stability and mobility into our fitness routines can help prevent injuries and enhance overall shoulder performance. Additionally, maintaining good posture and ergonomics in daily activities can reduce the risk of scapular dysfunction and promote optimal shoulder mechanics.
- Scapular Mobility Exercises: Incorporating exercises that promote shoulder blade mobility into your fitness routine can help maintain optimal shoulder health. Movements such as scapular retractions, shoulder blade squeezes, and scapular circles can help improve flexibility and mobility of the shoulder blade, reducing the risk of stiffness and dysfunction.
- Strengthening Scapular Stabilizers: Targeting the muscles that stabilize the scapula, such as the rhomboids, serratus anterior, and lower trapezius, can enhance shoulder stability and prevent injuries. Exercises like rows, scapular push-ups, and external rotation exercises with resistance bands can effectively strengthen these muscles, promoting proper scapular mechanics during shoulder movement.
- Postural Awareness: Maintaining good posture throughout the day is essential for supporting the health of the shoulder blade and preventing musculoskeletal imbalances. Practicing proper posture habits, such as sitting up straight, keeping the shoulders relaxed and down, and avoiding prolonged slouching or hunching, can reduce strain on the shoulder blade muscles and ligaments.
- Ergonomic Considerations: Paying attention to ergonomic factors in your work and daily activities can also support shoulder health and shoulder blade function. Adjusting your workspace setup, using ergonomic tools and equipment, and taking regular breaks to stretch and move can alleviate stress on the shoulders and promote optimal shoulder blade positioning.
- Balanced Strength Training: Incorporating a well-rounded strength training program that targets all muscle groups surrounding the shoulder joint, including the shoulder blade stabilizers, can promote balanced strength and muscle coordination. Avoiding overemphasis on certain muscle groups while neglecting others can help prevent muscle imbalances and reduce the risk of shoulder injuries.
- Regular Stretching and Mobility Work: Including regular stretching and mobility exercises in your routine can help maintain flexibility and range of motion in the shoulder and scapular joints. Gentle stretches for the chest, shoulders, and upper back, along with dynamic mobility drills for the shoulders and shoulder blade, can improve tissue flexibility and prevent stiffness.
- Seeking Professional Guidance: If you’re experiencing persistent shoulder pain or dysfunction, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or orthopedic specialist, can provide personalized recommendations and interventions to address your specific needs. They can assess your movement patterns, identify any underlying issues, and develop a tailored treatment plan to optimize shoulder and shoulder blade health.
Conclusion: A Tribute to the Scapula
In conclusion, the scapula stands as a cornerstone of shoulder function, silently supporting our every movement with grace and precision. From its intricate anatomy to its indispensable role in shoulder mobility, the scapula embodies the beauty of human anatomy and the marvels of biomechanics. By acknowledging its significance and nurturing its health, we can honor the unsung hero of shoulder mobility and embrace a life of strength, agility, and vitality.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023