Fractures of the Shoulder Blade: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Fractures of the shoulder blade, medically known as scapular fractures, can occur due to various traumatic incidents or underlying medical conditions. While less common than fractures of other bones in the shoulder region, such as the collarbone or humerus, Fractures of the shoulder blade can still cause significant pain and dysfunction. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for fractures of the shoulder blade is essential for proper diagnosis and management of these injuries.
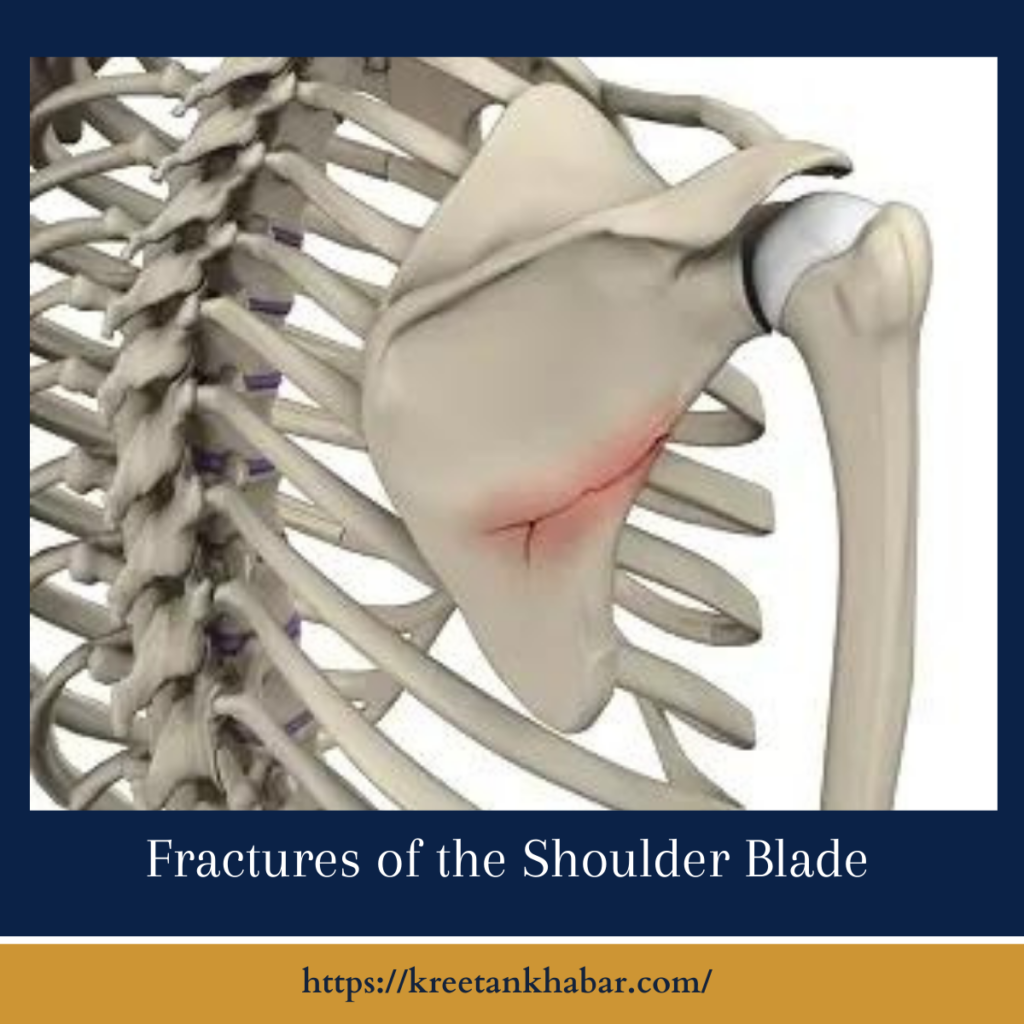
Causes of Scapular Fractures
Fractures of the shoulder blade typically result from high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle accidents, falls from height, or direct blows to the shoulder area. The force applied to the shoulder blade during these incidents can cause the bone to break in different locations, including the body, neck, or acromion and coracoid processes. In some cases, Fractures of the shoulder blademay also occur as a result of repetitive stress or overuse, particularly in athletes involved in overhead sports like baseball or swimming.
Symptoms of Scapular Fractures
The symptoms of a scapular fracture can vary depending on the location and severity of the injury. Common signs and symptoms include intense pain in the shoulder area, swelling, bruising, and difficulty moving the arm. In some cases, there may be visible deformity or asymmetry of the shoulder contour. Individuals with Fractures of the shoulder blade may also experience tenderness to touch over the affected area and pain with shoulder movements or deep breathing. Severe fractures may be associated with additional symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arm or hand, indicating nerve or blood vessel injury.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing scapular fractures typically involves a thorough physical examination, imaging studies, and assessment of the mechanism of injury. X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans may be used to visualize the extent and location of the fracture and assess for any associated injuries to surrounding structures. Treatment options for Fractures of the shoulder blade depend on various factors, including the severity of the fracture, displacement of bone fragments, and presence of associated injuries.
Conservative management, such as immobilization with a sling or shoulder brace, is often sufficient for stable Fractures of the shoulder blade that are not significantly displaced. Physical therapy may be prescribed to promote shoulder mobility and prevent stiffness during the healing process. However, for more complex or displaced fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the bone fragments and restore normal shoulder anatomy. Surgical techniques such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) or minimally invasive procedures using plates, screws, or wires may be employed to stabilize the fracture and facilitate optimal healing.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Diagnosing fractures of the shoulder blade typically involves imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. These imaging modalities help visualize the extent and location of the fracture, assess for displacement of bone fragments, and identify any associated injuries to surrounding structures such as nerves or blood vessels.
- Classification of Fractures: Scapular fractures can vary widely in their location, severity, and complexity. They may be classified based on the specific region of the scapula involved, such as fractures of the body, neck, acromion process, or coracoid process. Additionally, fractures may be categorized as stable or unstable, depending on the degree of displacement and potential for associated injuries.
- Conservative Management: Stable Fractures of the shoulder blade that are minimally displaced or non-displaced may be managed conservatively with immobilization using a sling or shoulder brace. Rest, ice, and over-the-counter pain medications may also be recommended to alleviate pain and inflammation during the initial stages of healing.
- Surgical Intervention: For more complex or displaced fractures of the shoulder blade, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the bone fragments and restore normal shoulder anatomy. Surgical techniques such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) or minimally invasive procedures using plates, screws, or wires may be employed to stabilize the fracture and facilitate optimal healing.
- Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy: Following either conservative or surgical management, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process for Fractures of the shoulder blade. Physical therapy exercises focusing on shoulder mobility, strengthening, and proprioception are essential for restoring function, improving range of motion, and preventing stiffness and muscle weakness. Gradual progression of activities and functional exercises under the guidance of a skilled therapist is necessary to ensure a safe and successful return to pre-injury levels of activity.
- Monitoring for Complications: Throughout the treatment and recovery process, close monitoring for potential complications such as nerve or blood vessel injury, delayed healing, or malunion of the fracture is essential. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers and imaging studies may be recommended to assess progress and detect any issues early on, allowing for prompt intervention if needed.
- Patient Education and Support: Providing education and support to patients and their families about the diagnosis, treatment options, and expected outcomes of scapular fractures is crucial for promoting adherence to treatment plans and facilitating recovery. Empowering patients with information about self-care strategies, activity modifications, and signs of complications can help enhance their confidence and engagement in the healing process.
By considering these unique points about the diagnosis and treatment of fractures of the shoulder blade, healthcare providers can develop comprehensive and individualized management plans tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of each patient.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Regardless of the treatment approach, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process following a scapular fracture. Physical therapy exercises focusing on shoulder mobility, strengthening, and proprioception can help restore function, improve range of motion, and prevent stiffness and muscle weakness. Gradual progression of activities and functional exercises under the guidance of a skilled therapist or healthcare provider is essential to ensure a safe and successful return to pre-injury levels of activity.
Conclusion
Fractures of the shoulder blade, while less common than other shoulder injuries, can have significant implications for shoulder function and mobility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for Fractures of the shoulder blade is essential for timely diagnosis and appropriate management of these injuries. With proper evaluation, treatment, and rehabilitation, individuals with scapular fractures can achieve successful outcomes and return to their usual activities with restored shoulder function and mobility.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023