Metacarpal Fractures: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Metacarpal fractures, though commonly overlooked compared to more prominent bone injuries, can significantly impact hand function and daily activities. These fractures, affecting the long bones of the hand connecting the wrist bones to the finger bones, require careful assessment and management to ensure optimal recovery. Let’s delve into the intricacies of metacarpal fractures, exploring their causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
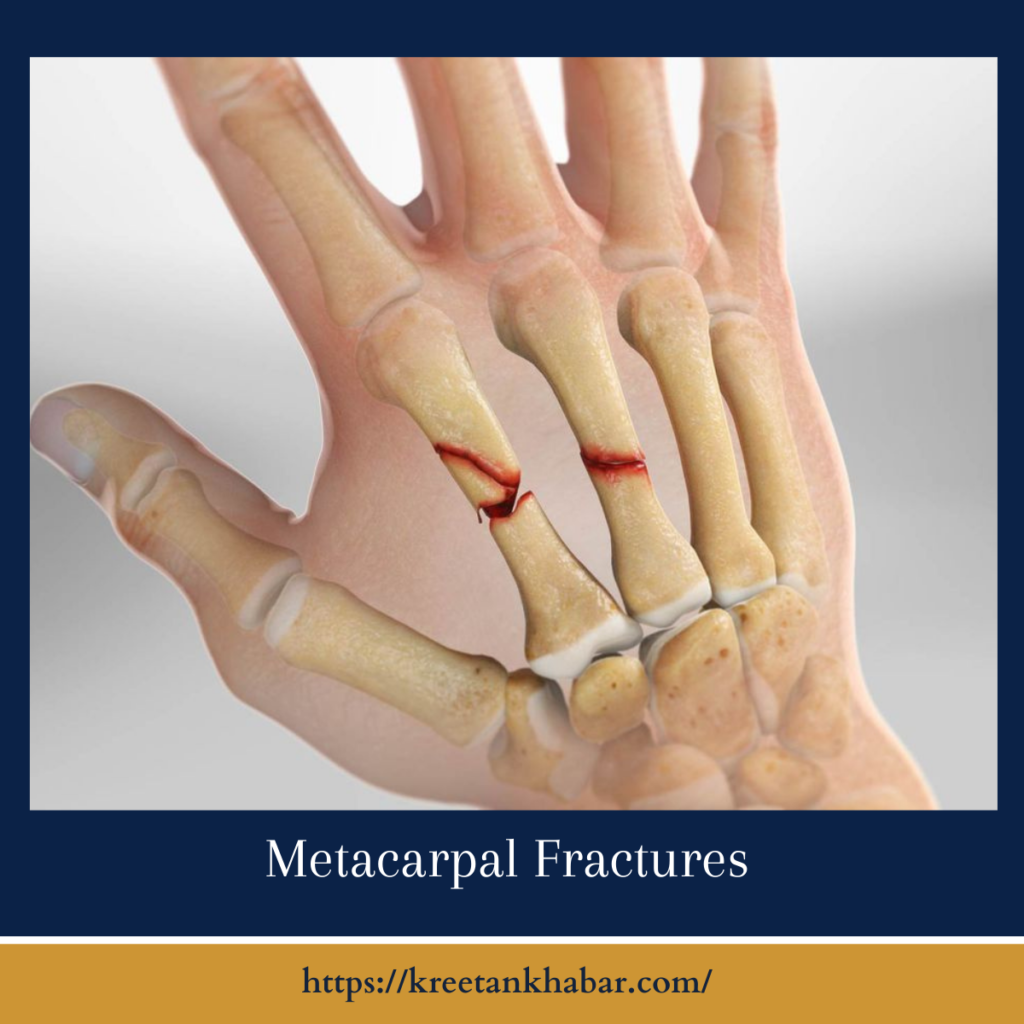
The Anatomy of Metacarpal Bones
The metacarpal bones form the framework of the hand, extending from the base of the fingers to the wrist. Each hand contains five metacarpal bones, labeled numerically from one to five, corresponding to the thumb to the little finger. These long, slender bones provide structural support and stability to the hand while allowing for a wide range of motion and dexterity. Fractures in any of these metacarpal bones can disrupt hand function and impair daily activities.
Common Causes of Metacarpal Fractures
Metacarpal fractures can occur due to various causes, including direct trauma to the hand from falls, sports injuries, or motor vehicle accidents. The most common mechanism of injury involves striking a hard object with a closed fist, resulting in a forceful impact transmitted to the metacarpal bones. Additionally, fractures may occur as a result of crushing injuries, repetitive stress or overuse, or pathological conditions such as osteoporosis or bone tumors.
- Direct Trauma: One of the most common causes of metacarpal fractures is direct trauma to the hand. This can occur from various sources such as falls, sports injuries, workplace accidents, or motor vehicle collisions. The forceful impact on the hand can result in fractures of the metacarpal bones, particularly if the hand is clenched into a fist upon impact.
- Punching or Striking Objects: Fractures of the metacarpal bones often occur when an individual punches a hard object or strikes something forcefully with a closed fist. This mechanism of injury transmits significant force through the hand, leading to fractures in the metacarpal bones closest to the point of impact.
- Crushing Injuries: Metacarpal fractures can also result from crushing injuries, where the hand gets caught or compressed between two heavy objects. This type of injury can cause multiple fractures or comminuted fractures of the metacarpal bones, particularly if the force is applied over a broad area of the hand.
- Sports Injuries: Participation in high-impact or contact sports, such as football, basketball, or martial arts, can increase the risk of metacarpal fractures. Injuries may occur from direct blows to the hand during gameplay or from falls onto an outstretched hand, leading to fractures in the metacarpal bones.
- Repetitive Stress or Overuse: Overuse injuries from repetitive activities involving the hands, such as typing, writing, or using hand tools, can contribute to metacarpal fractures over time. Prolonged or repetitive stress on the hand can weaken the bones and predispose them to fractures, particularly in individuals with underlying bone conditions or poor biomechanics.
- Occupational Hazards: Certain occupations that involve manual labor or heavy lifting may pose an increased risk of metacarpal fractures due to the potential for workplace accidents or repetitive strain injuries. Workers in industries such as construction, manufacturing, or agriculture may be at higher risk of sustaining hand injuries that lead to metacarpal fractures.
- Pathological Conditions: Underlying medical conditions such as osteoporosis, bone tumors, or metabolic disorders can weaken the bones and increase the risk of fractures, including metacarpal fractures. Individuals with compromised bone health may be more susceptible to fractures from minor trauma or falls, highlighting the importance of early detection and management of underlying conditions.
Understanding the diverse array of causes of metacarpal fractures is essential for implementing preventive measures, promoting safety practices, and reducing the risk of hand injuries in various settings. By addressing potential risk factors and promoting hand safety awareness, individuals can minimize the likelihood of sustaining metacarpal fractures and maintain optimal hand health and function.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of a metacarpal fracture may vary depending on the location and severity of the injury. Common signs and symptoms include pain, swelling, and tenderness over the injured area. Individuals may also experience difficulty moving the affected finger or hand, as well as visible deformity or misalignment of the finger. In some cases, there may be bruising or discoloration of the skin around the fracture site, indicating soft tissue injury or bleeding.
- Localized Pain and Tenderness: Individuals with metacarpal fractures commonly experience localized pain and tenderness at the site of the injury. The pain may be sharp or throbbing and typically worsens with movement or pressure applied to the affected area. Tenderness to touch over the fractured metacarpal bone is often a prominent symptom, indicating inflammation and injury to surrounding tissues.
- Swelling and Bruising: Swelling and bruising of the hand are hallmark symptoms of metacarpal fractures. The injured area may appear swollen, puffy, or inflamed due to soft tissue trauma and bleeding beneath the skin. Bruising, or discoloration of the skin, may also develop around the fracture site, ranging from mild to severe depending on the extent of tissue damage.
- Visible Deformity or Misalignment: In cases of severe or displaced metacarpal fractures, individuals may exhibit visible deformity or misalignment of the affected finger or hand. The injured finger may appear crooked, angulated, or shortened compared to adjacent fingers, indicating displacement or malalignment of the fractured bone fragments.
- Restricted Range of Motion: Metacarpal fractures can significantly impair hand function and mobility, leading to a restricted range of motion in the affected finger or hand. Individuals may experience difficulty moving the injured finger, making it challenging to perform activities such as grasping, gripping, or manipulating objects. Reduced range of motion may be accompanied by stiffness or discomfort with movement.
- Pain with Hand Movement: Pain exacerbated by hand movement is a common symptom of metacarpal fractures. Activities that involve flexing or extending the fingers, gripping objects, or applying pressure to the hand may elicit sharp or shooting pain at the site of the fracture. Individuals may also experience pain with activities that place stress on the injured hand, such as typing, writing, or lifting.
- Numbness or Tingling Sensation: In some cases, metacarpal fractures may be associated with nerve compression or injury, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or altered sensation in the fingers or hand. These sensory disturbances may indicate nerve involvement and should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out complications and ensure appropriate management.
- Difficulty Performing Activities of Daily Living: Metacarpal fractures can significantly impact the ability to perform activities of daily living, such as dressing, grooming, cooking, or working. Individuals may struggle with tasks that require fine motor skills or manual dexterity, leading to frustration, dependency, or decreased productivity. Difficulty using the affected hand may necessitate modifications to daily routines or assistive devices to facilitate independence and function.
Diagnosis and Imaging Studies
Diagnosing a metacarpal fracture typically involves a thorough physical examination, assessment of the mechanism of injury, and imaging studies to confirm the diagnosis. X-rays are the primary imaging modality used to visualize fractures and assess for any associated injuries, such as dislocations or soft tissue damage. In some cases, additional imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI scans may be ordered to further evaluate complex fractures or assess for underlying ligament or tendon injuries.
Treatment Options
Treatment for metacarpal fractures depends on various factors, including the location and severity of the fracture, degree of displacement, and functional demands of the individual. Non-displaced or minimally displaced fractures may be managed conservatively with immobilization using a splint or cast to allow for adequate healing. Physical therapy exercises focusing on hand mobility and strengthening may be initiated once the fracture begins to heal to prevent stiffness and promote functional recovery.
For more complex or displaced fractures, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the bone fragments and stabilize the fracture. Surgical techniques such as open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF), external fixation, or percutaneous pinning may be employed to achieve anatomical alignment and facilitate optimal healing. Post-operative rehabilitation and physical therapy are essential for restoring hand function and mobility following surgical treatment.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Regardless of the treatment approach, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process for metacarpal fractures. Physical therapy exercises focusing on hand mobility, strengthening, and coordination are essential for restoring function, improving range of motion, and preventing stiffness and muscle weakness. Gradual progression of activities and functional exercises under the guidance of a skilled therapist is necessary to ensure a safe and successful return to pre-injury levels of activity.
Conclusion: Restoring Hand Function and Mobility
In conclusion, metacarpal fractures can significantly impact hand function and daily activities. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for these fractures is essential for proper diagnosis and management. With prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and comprehensive rehabilitation, individuals with metacarpal fractures can achieve successful outcomes and regain optimal hand function and mobility.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023