Hemorrhage: Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Hemorrhage, commonly referred to as bleeding, is a medical condition characterized by excessive or abnormal bleeding from blood vessels. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment of bleeding is crucial for effective management and timely intervention. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this condition to gain a comprehensive understanding.
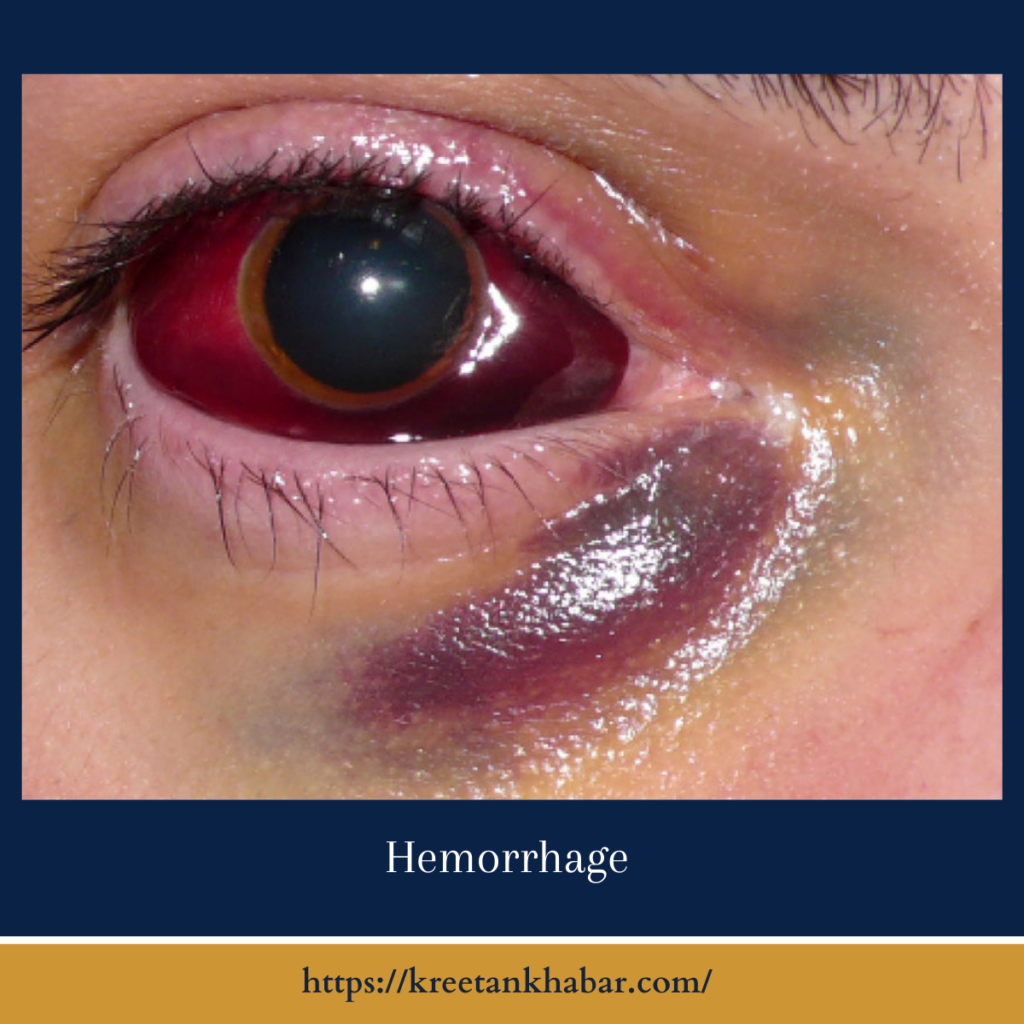
Types of Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage can occur internally or externally and may be classified into various types, including:
- Arterial Hemorrhage: Involves bleeding from an artery, characterized by bright red blood spurting or pulsating from the wound.
- Venous Hemorrhage: Involves bleeding from a vein, characterized by steady, dark red or maroon-colored blood flow.
- Capillary Hemorrhage: Involves bleeding from small capillaries, characterized by slow oozing of blood from the wound.
Causes of Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage can result from various underlying causes, including:
- Trauma: Physical injuries, such as cuts, wounds, or blunt force trauma, can damage blood vessels and lead to bleeding.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hemophilia, thrombocytopenia, or liver disease, can impair blood clotting mechanisms, increasing the risk of bleeding.
- Surgical Complications: Hemorrhage can occur as a complication of surgical procedures, particularly those involving major blood vessels or organs.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as blood thinners or antiplatelet drugs, can interfere with normal blood clotting processes, predisposing individuals to bleeding.
More points of causes of homorrhage:
Recognizing the Symptoms
Symptoms of hemorrhage may vary depending on the location, severity, and underlying cause but commonly include:
- Visible Bleeding: External bleeding from wounds, cuts, or abrasions may be apparent.
- Internal Bleeding: Symptoms of internal bleeding may include abdominal pain, lightheadedness, fainting, rapid heartbeat, or pale skin.
- Hypovolemic Shock: Severe hemorrhage can lead to hypovolemic shock, characterized by symptoms such as rapid breathing, confusion, cold and clammy skin, and decreased urine output.
Treatment of Hemorrhage
Treatment for hemorrhage aims to control bleeding, restore blood volume, and address underlying causes. Depending on the severity and location of the bleeding, treatment options may include:
- Direct Pressure: Applying direct pressure to the bleeding site can help control external bleeding and promote clot formation.
- Tourniquet: In cases of severe bleeding from limbs, applying a tourniquet proximal to the wound can help restrict blood flow and control hemorrhage.
- Fluid Resuscitation: Intravenous fluids or blood products may be administered to restore blood volume in cases of significant hemorrhage.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe or internal bleeding, surgical intervention may be necessary to identify and repair damaged blood vessels or organs.
Conclusion
Hemorrhage is a serious medical condition that requires prompt recognition and appropriate treatment to prevent complications and improve outcomes. By understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hemorrhage, healthcare professionals and individuals alike can take proactive steps to manage this condition effectively and ensure optimal patient care. Early intervention is key to successful management, and individuals experiencing symptoms of bleeding should seek immediate medical attention for timely evaluation and treatment.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023