Charcots Neuroarthropathy: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Charcot’s neuroarthropathy, also known as Charcot joint or neuropathic arthropathy, is a debilitating condition characterized by progressive degeneration and destruction of the joints, most commonly affecting the feet and ankles. While relatively rare, Charcot’s neuroarthropathy poses significant challenges in diagnosis and management, necessitating a multidisciplinary approach to address its complex underlying mechanisms and diverse clinical manifestations.
Exploring the Underlying Causes:
Charcot’s neuroarthropathy typically arises in individuals with peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage that impairs sensation and motor function. Peripheral neuropathy can result from various underlying causes, including:
- Diabetes: The most common cause of peripheral neuropathy and Charcot’s neuroarthropathy, diabetes-related nerve damage can lead to loss of sensation and proprioception, predisposing individuals to joint injury and deformity.
- Trauma: Previous trauma or repetitive microtrauma to the affected joint, often compounded by reduced pain sensation, can trigger the inflammatory cascade characteristic of Charcot’s neuroarthropathy.
- Other Neurological Conditions: Neurological disorders such as syringomyelia, tabes dorsalis, and spinal cord injury can also predispose individuals to the development of Charcot’s neuroarthropathy through disruption of sensory and motor pathways.
Recognizing Symptoms and Clinical Presentation:
The clinical presentation of Charcot’s neuroarthropathy can vary depending on the stage of the disease and the specific joints involved. Common signs and symptoms may include:
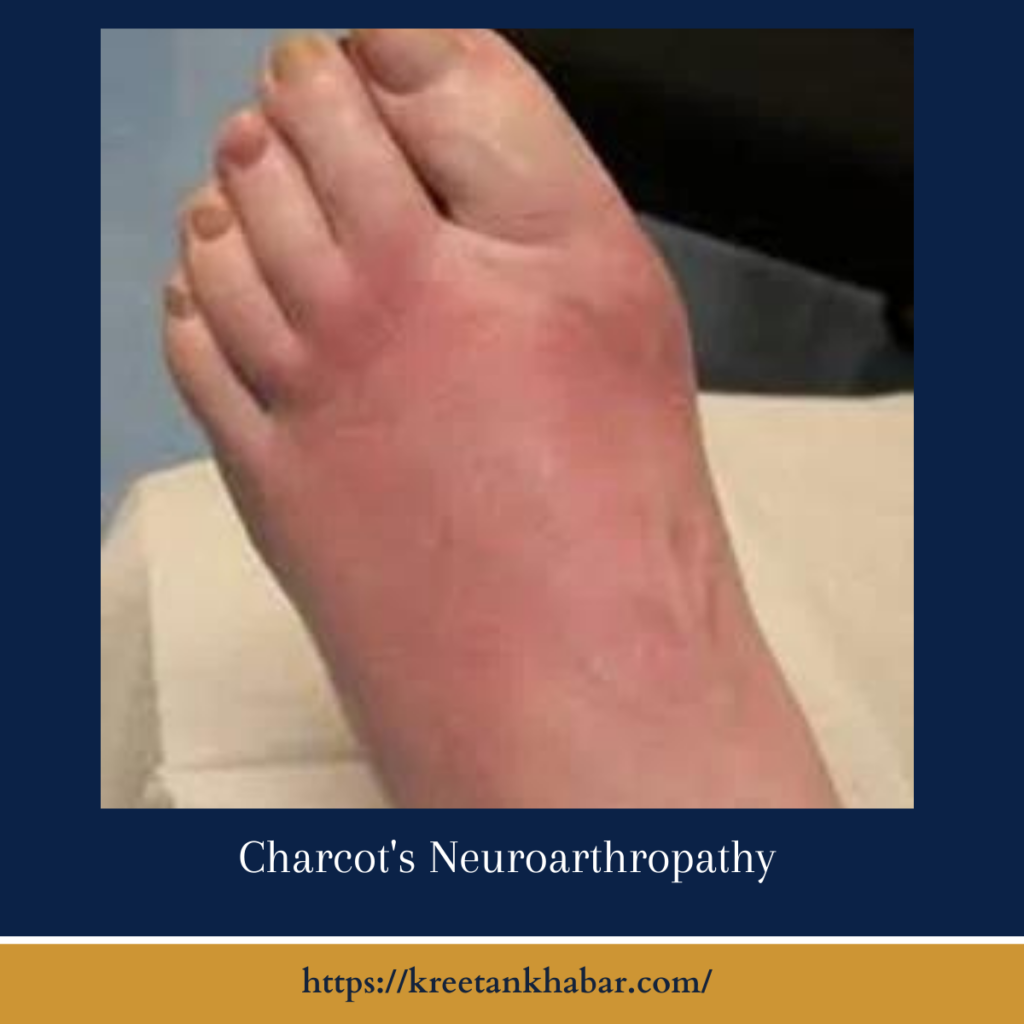
- Swelling and Redness: Acute inflammatory changes, including joint swelling, erythema, and warmth, are hallmark features of the early stage of Charcot’s neuroarthropathy.
- Joint Instability: As the condition progresses, joint instability and laxity may develop, leading to deformity, subluxation, or dislocation. Weight-bearing joints such as the ankles and midfoot are most commonly affected.
- Painlessness: One of the most striking features of Charcot’s neuroarthropathy is the relative absence of pain, despite the severity of joint deformity and destruction. This “painless charcot foot” phenomenon can delay diagnosis and exacerbate disease progression.
Diagnostic Challenges and Imaging Modalities:
Diagnosing Charcots neuroarthropathy presents a significant challenge due to its multifaceted nature and the absence of specific diagnostic tests. One of the primary obstacles is the condition’s rarity, which can lead to under-recognition and misdiagnosis, especially among healthcare professionals who may not encounter it frequently. Furthermore, Charcot’s neuroarthropathy often occurs in individuals with preexisting peripheral neuropathy, such as those with diabetes, making it challenging to differentiate from other neuropathic conditions.
The insidious onset and variable clinical presentation further complicate diagnosis, as symptoms may mimic those of other musculoskeletal disorders or infectious processes. Additionally, the hallmark feature of painlessness can delay seeking medical attention and contribute to the progression of joint deformity before diagnosis. Thus, a high index of suspicion, comprehensive clinical evaluation, and judicious use of imaging modalities are crucial for timely recognition and management of Charcots neuroarthropathy, highlighting the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration and ongoing education among healthcare providers.
Diagnosing Charcots neuroarthropathy requires a high index of suspicion, particularly in individuals with underlying neuropathy and risk factors such as diabetes. Clinical examination, supplemented by imaging studies, plays a crucial role in establishing a diagnosis. Key imaging modalities include:
- X-ray: Radiographic findings of Charcots neuroarthropathy may include joint fragmentation, dislocation, periarticular osteopenia, and bony resorption. However, these changes may not be evident in the early stages of the disease.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is highly sensitive for detecting early soft tissue and bone changes associated with Charcots neuroarthropathy, facilitating early diagnosis and intervention.
Multidisciplinary Management and Treatment Approaches:
Management of Charcots neuroarthropathy requires a multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, podiatrists, endocrinologists, and rehabilitation specialists. Treatment strategies aim to mitigate disease progression, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. Key interventions may include:
- Immobilization: Offloading the affected joint through the use of casts, braces, or orthotic devices can help stabilize the joint and promote healing.
- Temperature Control: Avoidance of extreme temperatures and temperature differentials between affected and unaffected limbs can minimize the risk of recurrent inflammation and injury.
- Footwear Modification: Custom footwear and accommodative orthoses can offload pressure points, reduce shear forces, and enhance foot biomechanics, thereby reducing the risk of ulceration and secondary complications.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe deformity or instability, surgical correction may be necessary to realign the joint, restore function, and prevent further deterioration.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes:
The prognosis of Charcots neuroarthropathy varies depending on the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis, the adequacy of treatment, and the presence of comorbidities such as diabetes. Early recognition and intervention are critical for optimizing outcomes and minimizing the risk of irreversible joint damage, ulceration, and limb loss. Long-term management focuses on preventive foot care, patient education, and regular monitoring to detect and address early signs of disease recurrence or complications.
- Variable Disease Progression: The prognosis of Charcots neuroarthropathy can vary widely among individuals, depending on factors such as the stage of the disease at diagnosis, underlying neuropathic condition, and adherence to treatment. Some patients may experience relatively mild symptoms and stable joint deformity over time, while others may progress rapidly to severe joint destruction and functional impairment.
- Risk of Complications: Left untreated or inadequately managed, Charcots neuroarthropathy can lead to a range of complications, including recurrent ulceration, chronic infection, osteomyelitis (bone infection), and lower limb amputation. These complications significantly impact patients’ quality of life and pose substantial challenges for healthcare providers in terms of wound management and limb salvage.
- Impact on Mobility and Function: As Charcots neuroarthropathy progresses, affected individuals may experience significant limitations in mobility and functional capacity, particularly if lower limb joints are involved. Joint instability, deformity, and painlessness can impair gait mechanics, balance, and weight-bearing ability, leading to reduced independence and reliance on assistive devices for ambulation.
- Challenges in Wound Healing: Charcots neuroarthropathy often coexists with peripheral vascular disease and diabetic neuropathy, further complicating wound healing and tissue repair. Chronic ulceration, impaired circulation, and neuropathic changes in skin integrity predispose patients to delayed wound healing, recurrent infections, and potential limb-threatening complications.
- Multidisciplinary Management Approach: Optimizing long-term outcomes in Charcots neuroarthropathy requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, podiatrists, endocrinologists, wound care specialists, and rehabilitation professionals. Coordination of care, patient education, and close monitoring are essential components of successful long-term management strategies.
- Preventive Foot Care: Patient education and preventive foot care play a crucial role in minimizing the risk of recurrent ulceration and complications in Charcots neuroarthropathy. Regular foot inspections, proper footwear selection, and adherence to foot hygiene practices can help mitigate the risk of skin breakdown, infection, and subsequent morbidity.
- Importance of Glycemic Control: For individuals with diabetes-related Charcots neuroarthropathy, optimizing glycemic control is paramount in preventing disease progression and minimizing the risk of diabetic complications. Tight glycemic management, alongside regular monitoring of blood glucose levels and HbA1c, can help mitigate the neurovascular complications associated with diabetes and improve long-term outcomes.
- Emphasis on Patient Engagement: Engaging patients in their own care and fostering self-management skills are critical components of achieving favorable long-term outcomes in Charcots neuroarthropathy. Empowering patients to recognize early signs of disease recurrence, adhere to prescribed treatment regimens, and adopt healthy lifestyle behaviors can enhance their overall well-being and functional independence.
- Regular Monitoring and Surveillance: Long-term follow-up and surveillance are essential in monitoring disease progression, detecting early signs of recurrence or complications, and adjusting treatment strategies accordingly. Regular clinical evaluations, imaging studies, and assessment of neuropathic symptoms facilitate timely intervention and optimize outcomes in Charcots neuroarthropathy.
- Research and Innovation: Ongoing research efforts aimed at elucidating the pathophysiology of Charcots neuroarthropathy, identifying biomarkers for disease progression, and exploring novel therapeutic interventions hold promise for improving long-term outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. Collaborative research endeavors and innovation in diagnostic modalities and treatment approaches are essential for advancing the field and addressing the unmet needs of patients with Charcots neuroarthropathy.
Conclusion:
Charcot’s neuroarthropathy poses significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges due to its complex pathophysiology and diverse clinical manifestations. By increasing awareness among healthcare providers and the general public, fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, and implementing evidence-based treatment strategies, we can improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by this debilitating condition. Early recognition, timely intervention, and comprehensive long-term management are paramount in mitigating the devastating consequences of Charcot’s neuroarthropathy and preserving limb function and mobility.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023