Calcaneus Fractures
A calcaneus fractures , often referred to as a broken heel bone, is a challenging injury that can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. The calcaneus, the largest bone in the foot, plays a crucial role in supporting body weight and absorbing shock during walking and running. When fractured, whether due to a fall, automobile accident, or high-impact trauma, the intricate structure of the heel bone can be compromised, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected foot. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of calcaneus fractures , exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options to guide individuals on the road to recovery.
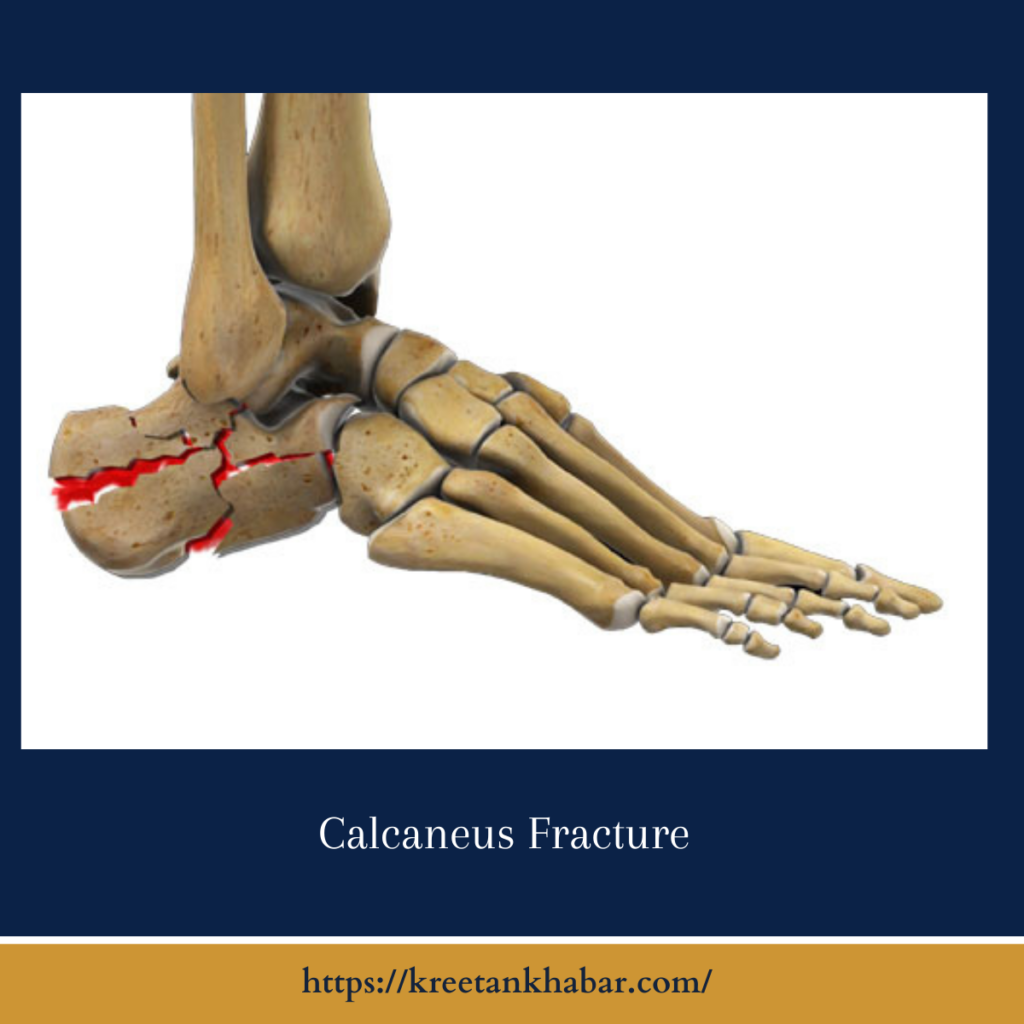
Understanding Calcaneus Fractures:
The calcaneus is a complex bone with multiple articulating surfaces and important ligament attachments. heelbone of the calcaneus typically occur as a result of significant force or trauma, such as a fall from height or a motor vehicle accident. These heelbone can vary in severity, ranging from hairline cracks to displaced or comminuted fractures where the bone breaks into multiple fragments. The location and extent of the fracture influence the symptoms experienced and the treatment approach required for optimal healing.
Signs and Symptoms:
The symptoms of a calcaneus fracture can be quite debilitating and may include:
- Pain and Swelling: Immediate pain and swelling at the back of the foot or heel area following the injury.
- Difficulty Walking: Difficulty or inability to bear weight on the affected foot due to pain and instability.
- Bruising: Bruising or discoloration around the heel and ankle area as a result of internal bleeding and tissue damage.
- Visible Deformity: In severe cases, a visible deformity or misalignment of the heel bone may be noticeable, especially in displaced fractures.
- Tenderness to Touch: Tenderness and sensitivity to touch over the injured area, indicating inflammation and tissue damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosing a calcaneus fracture typically involves a thorough physical examination, evaluation of the injury mechanism, and imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to assess the extent and severity of the fracture. Treatment options may vary depending on the specific characteristics of the fracture but often include:
- Immobilization: In cases of non-displaced or minimally displaced heelbone, immobilization with a cast or walking boot may be sufficient to promote healing and stability.
- Reduction and Fixation: For displaced or comminuted heelbone, surgical intervention may be necessary to realign the fractured fragments and stabilize the bone using screws, plates, or wires.
- Physical Therapy: Following immobilization or surgical treatment, physical therapy plays a crucial role in restoring strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected foot and ankle.
- Pain Management: Pain medications, anti-inflammatory drugs, and icing the affected area can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during the healing process.
Rehabilitation and Recovery:
Recovery from a calcaneus fracture can be a lengthy and challenging process, requiring patience, dedication, and adherence to prescribed treatment protocols. While immobilization and surgical intervention are essential for stabilizing the fracture, rehabilitation and physical therapy are equally important for restoring function and mobility. Gradual weight-bearing exercises, gait training, and strengthening exercises targeting the muscles of the foot, ankle, and lower leg can help individuals regain mobility and return to their daily activities.
Preventive Measures:
While calcaneus fractures often occur as a result of accidents or trauma, there are certain preventive measures individuals can take to minimize the risk of injury:
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Choose supportive footwear with adequate cushioning and stability to reduce the risk of falls and impact-related injuries.
- Practice Safety Precautions: Take precautions when engaging in high-risk activities such as sports or activities involving heights to minimize the risk of traumatic injuries.
- Maintain Bone Health: Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D through a balanced diet or supplements to promote bone strength and resilience.
- Exercise Caution: Be mindful of uneven surfaces, slippery floors, and other environmental hazards that can increase the risk of falls and injuries.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a calcaneus fracture is a significant injury that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to achieve optimal outcomes. Whether managed conservatively with immobilization or surgically repaired with internal fixation, the goal of treatment is to restore stability, function, and mobility to the affected foot. Rehabilitation and physical therapy play a crucial role in the recovery process, helping individuals regain strength and independence. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for calcaneus fractures , individuals can take proactive steps to prevent injury and navigate the road to recovery with confidence.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023