Bunionette Deformity: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Bunionette deformity, also known as tailor’s bunion, is a common foot condition characterized by the protrusion of the bone on the outside of the foot at the base of the fifth toe. Despite being less prevalent than traditional bunions, bunionettes can cause significant discomfort and affect mobility. Here, we explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for tailor’s bunion to provide insight into this often-overlooked foot ailment.
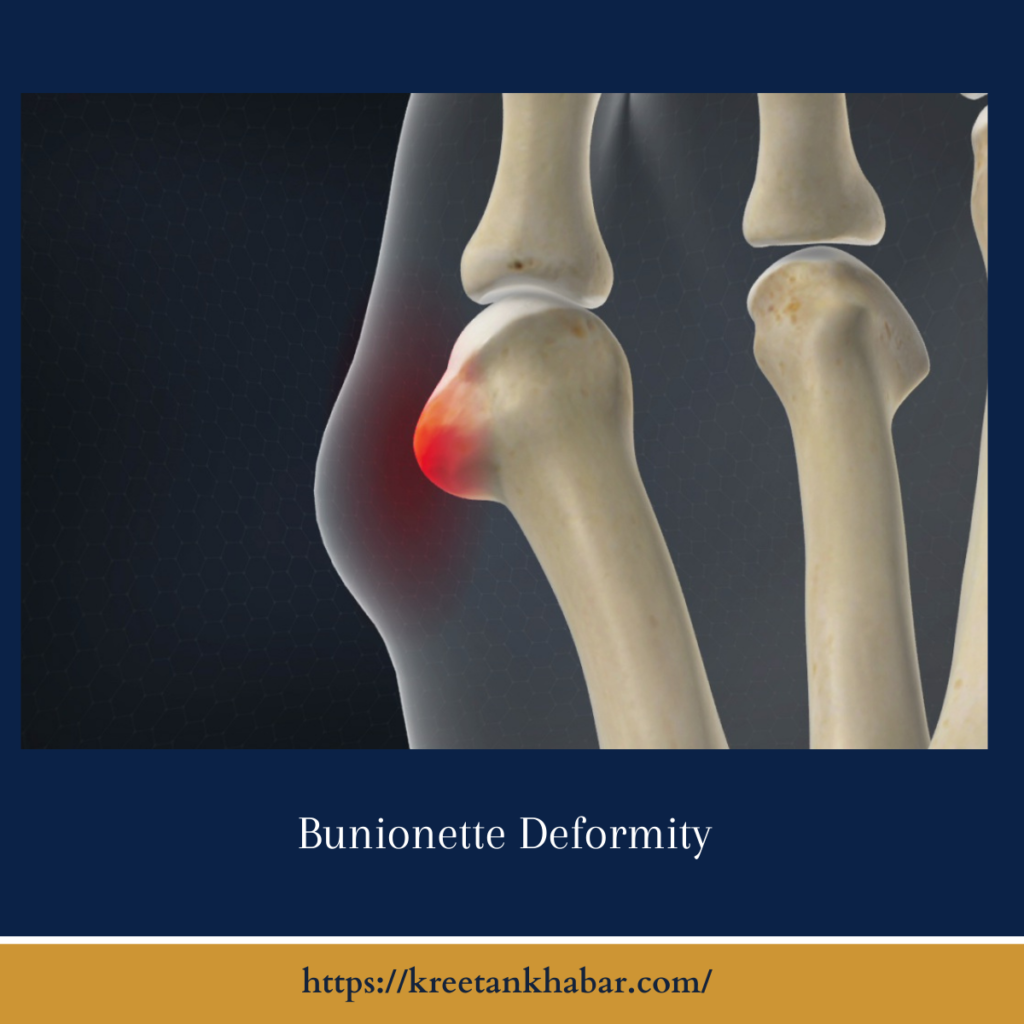
What is Bunionette Deformity?
tailor’s bunion occurs when the fifth metatarsal bone, located on the outer edge of the foot, protrudes outward, causing a visible bump and misalignment of the fifth toe. This deformity can result in pain, swelling, and difficulty wearing certain footwear, particularly shoes with narrow or pointed toes.
Causes of Bunionette Deformity:
Several factors can contribute to the development of tailor’s bunion:
- Genetics: Individuals with a family history of bunions or bunionettes may be more predisposed to developing this condition due to inherited foot structure and biomechanics.
- Footwear: Wearing shoes that are too tight or narrow can place excessive pressure on the fifth metatarsal bone, leading to irritation and inflammation.
- Foot Structure: Certain foot abnormalities, such as a prominent fifth metatarsal bone or a high arch, can increase the risk of tailor’s bunion by altering foot mechanics and redistributing pressure across the foot.
- Overpronation: Individuals who overpronate, or roll their feet inward excessively while walking, may be at higher risk of developing tailor’s bunion due to the uneven distribution of weight across the foot.
- Repetitive Stress: Activities that involve repetitive movements or pressure on the outer edge of the foot, such as ballet dancing or wearing high heels, can contribute to the development of tailor’s bunion over time.
Symptoms of Bunionette Deformity:
The symptoms oftailor’s bunion can vary from person to person but often include:
- Pain and tenderness at the base of the fifth toe, particularly when wearing shoes or walking.
- Swelling and inflammation around the bunionette bump.
- Redness or irritation over the affected area.
- Difficulty wearing shoes, especially those with narrow or pointed toes.
- Corns or calluses may develop over the bunionette bump due to friction from footwear.
Diagnosing Bunionette Deformity:
Diagnosing bunionette deformity typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging studies. A healthcare provider will inquire about the onset and duration of symptoms, as well as any factors that may exacerbate discomfort. Physical examination may reveal a visible bump on the outer edge of the foot, along with assessing foot structure and range of motion. X-rays may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of tailor’s bunion.
- Visual Inspection: Healthcare providers visually examine the affected foot, looking for a protrusion or bump on the outer edge at the base of the fifth toe, indicative of bunionette deformity.
- Medical History: A comprehensive medical history is taken, focusing on the onset and duration of symptoms, previous foot injuries, and any activities that may exacerbate discomfort, providing valuable context for diagnosis.
- Physical Examination: A hands-on examination is conducted, assessing foot structure, range of motion, and alignment. Healthcare providers palpate the bunionette area to evaluate tenderness and assess for associated inflammation.
- Footwear Assessment: Healthcare providers inquire about the types of footwear typically worn, as shoes with narrow or pointed toes can aggravate bunionette deformity. Examining the individual’s footwear may reveal contributing factors.
- X-ray Imaging: X-ray imaging may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of bunionette deformity. This allows healthcare providers to visualize the bony structures of the foot and identify any underlying structural abnormalities.
- Differential Diagnosis: Other potential causes of foot pain and deformity, such as arthritis or stress fractures, are considered during diagnosis to ensure an accurate assessment and appropriate treatment plan.
- Assessment of Symptoms: The individual’s reported symptoms, such as pain, swelling, or difficulty wearing certain shoes, are carefully evaluated to corroborate the diagnosis of bunionette deformity and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options:
Treatment options for bunionette deformity encompass a range of conservative and surgical interventions tailored to the severity of the condition and the individual’s needs. Conservative approaches typically focus on alleviating symptoms and preventing further progression of the deformity. These may include wearing shoes with a wider toe box to reduce pressure on the affected area, using padding or orthotic devices to cushion the bunionette bump and provide support to the foot, and implementing footwear modifications to avoid high heels or shoes with narrow or pointed toes.
Additionally, physical therapy exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles of the foot and improving foot mechanics may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrence. In cases where conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief or the deformity is severe, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options for bunionette deformity include procedures to realign the fifth metatarsal bone, remove the bunionette bump, and correct any associated structural abnormalities. By tailoring treatment to the individual’s specific needs and preferences, healthcare providers can effectively manage bunionette deformity and improve foot function and comfort.
Treatment for bunionette deformity aims to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and correct foot alignment. Common treatment options include:
- Footwear Modifications: Wearing shoes with a wider toe box can help reduce pressure on the bunionette bump and alleviate discomfort. Avoiding high heels or shoes with narrow or pointed toes is also recommended.
- Padding and Orthotics: Using padding or orthotic devices can help cushion the bunionette bump and provide support to the foot, reducing friction and discomfort.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help alleviate pain and inflammation associated with bunionette deformity.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles of the foot and improve foot mechanics can help alleviate symptoms and prevent progression of bunionette deformity.
- Injection Therapy: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce pain and inflammation around the bunionette bump, providing temporary relief.
- Surgical Intervention: For severe or persistent cases of bunionette deformity that do not respond to conservative treatments, surgical correction may be considered to realign the fifth metatarsal bone and remove the bunionette bump.
Conclusion:
Bunionette deformity may not receive as much attention as traditional bunions, but its impact on foot health and quality of life should not be underestimated. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options for bunionette deformity, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this condition and alleviate discomfort. If you’re experiencing symptoms of bunionette deformity, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. With the right approach, individuals can effectively manage bunionette deformity and maintain optimal foot health for years to come.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023