Bursitis of the Knee: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Bursitis of the knee is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can cause discomfort and limit mobility. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for effectively managing this condition and improving quality of life.
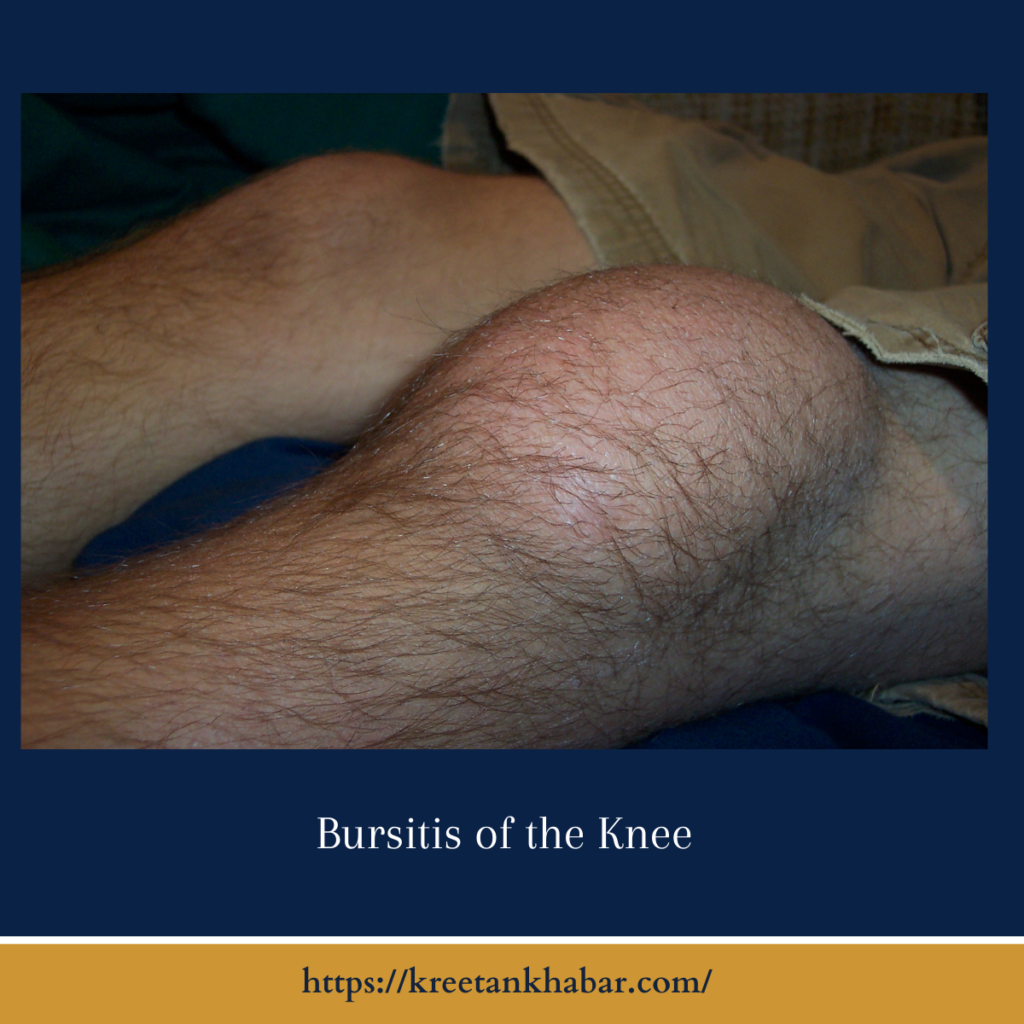
What is Bursitis of the Knee?
Bursitis of the knee refers to inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that act as cushions between bones, tendons, and muscles around the knee joint. These bursae help reduce friction and provide cushioning during movement, but when they become inflamed, they can cause pain and swelling.
Causes of Bursitis of the Knee:
Several factors can contribute to the development of knee bursitis, including:
- Repetitive Pressure or Overuse: Activities that involve repetitive bending or kneeling, such as gardening, cleaning, or certain sports, can irritate the bursae and lead to inflammation.
- Direct Trauma: A fall or blow to the knee can cause trauma to the bursae, triggering an inflammatory response.
- Poor Posture or Biomechanics: Incorrect posture or biomechanics during activities can place excessive stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of bursitis.
- Infection: In rare cases, bacteria can enter the bursae, causing an infection known as septic bursitis.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or osteoarthritis can predispose individuals to develop knee bursitis.
Symptoms of Bursitis of the Knee:
The symptoms of knee bursitis can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of inflammation. Common symptoms include:
- Pain, tenderness, or swelling around the knee joint.
- Difficulty bending or straightening the knee.
- Warmth or redness over the affected area.
- Pain that worsens with movement or pressure on the knee.
- Limited range of motion in the knee joint.
Diagnosing Bursitis of the Knee:
Diagnosing knee bursitis typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging studies. A healthcare provider will perform a thorough examination of the knee, checking for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion. They may also inquire about any recent injuries or activities that could have contributed to the development of bursitis. Imaging tests such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of knee pain.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for knee bursitis aims to reduce pain and inflammation, improve mobility, and address any underlying factors contributing to the condition. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms and allowing the knee time to rest and heal.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter or prescription NSAIDs can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve flexibility, and correct biomechanical issues.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the bursae can provide significant relief from pain and inflammation.
- Supportive Devices: Using knee braces or orthotic inserts to provide support and reduce pressure on the affected area.
- Aspiration: In cases of septic bursitis, the fluid may need to be drained from the bursa to remove the infection.
Conclusion:
Bursitis of the knee can be a painful and debilitating condition, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, most individuals can experience significant improvement in symptoms and regain function in the affected knee. If you’re experiencing persistent knee pain or swelling, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. By addressing the underlying causes and implementing appropriate interventions, individuals can effectively manage knee bursitis and return to their daily activities with minimal discomfort.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023