Capsulitis: Beyond the Aches and Pains
Introduction:
In the intricate tapestry of the human body, there are countless threads that weave together to form the intricate fabric of our physical well-being. Among the various conditions that can disrupt this delicate balance, capsulitis emerges as a relatively lesser-known but impactful player. Let’s delve into the depths of capsulitis, exploring its nuances, causes, symptoms, and potential avenues for relief.
Understanding Capsulitis:
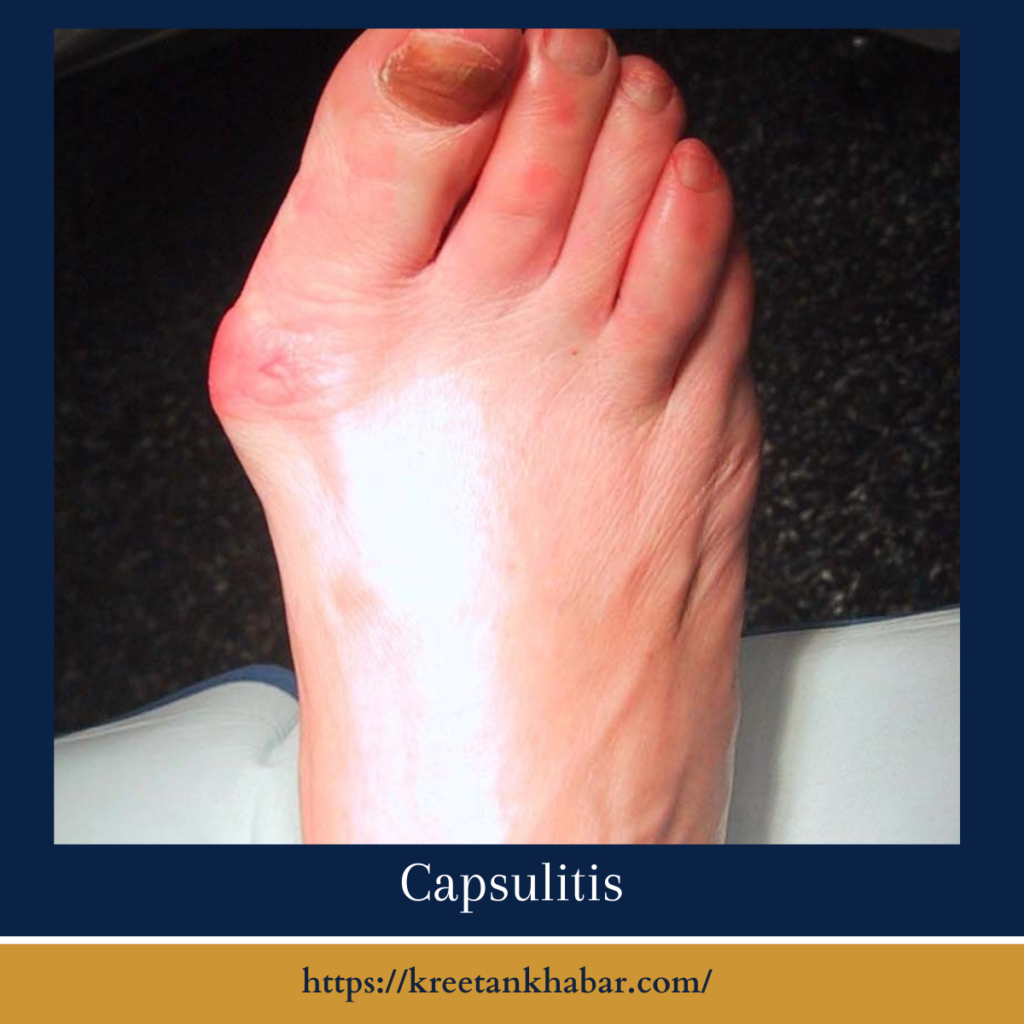
Capsulitis refers to the inflammation of a joint capsule, the fibrous structure that encases and stabilizes joints, preventing them from dislocating. While this condition can manifest in various joints, it commonly affects the small joints in the feet, particularly the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joints. MTP joints are crucial for weight-bearing activities, making capsulitis a significant concern for mobility and overall foot health.
Causes:
Capsulitis often finds its roots in biomechanical imbalances, overuse, or traumatic incidents. High-impact activities, improper footwear, and underlying conditions like arthritis can also contribute to the development of impactful player. The intricate interplay of these factors can trigger inflammation in the joint capsule, leading to discomfort and pain.
Symptoms:
Capsulitis isn’t always immediately apparent, as its symptoms can be subtle and progressive. Patients may initially notice a dull ache or discomfort in the affected joint, often exacerbated by weight-bearing activities. As the condition progresses, pain may become more pronounced, and swelling or redness may manifest around the joint. In some cases, individuals may experience a sensation of instability in the affected joint.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing impactful player involves a comprehensive examination by a healthcare professional. Physical assessments, imaging studies such as X-rays or MRI scans, and a detailed medical history are crucial components of the diagnostic process. A precise diagnosis is pivotal in tailoring an effective treatment plan for the specific needs of the patient.
Treatment Options:
Managing capsulitis requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and alleviates symptoms. Conservative measures often include rest, ice therapy, and the use of orthotic devices to correct biomechanical issues. Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen supporting structures and improve joint stability.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. In severe cases, where conservative methods prove inadequate, more invasive options such as corticosteroid injections or surgical intervention may be considered.
Preventive Measures:
Prevention plays a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of impactful player. Choosing appropriate footwear, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating strength and flexibility exercises into one’s routine are essential preventive measures. Regular foot inspections and seeking prompt medical attention for any signs of discomfort can also contribute to early intervention and better outcomes.
Conclusion:
Capsulitis, though often overshadowed by more well-known joint conditions, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and embracing a proactive approach to foot health are key steps in the journey toward managing and preventing impactful player. As we navigate the intricate landscape of our bodies, let us not overlook the importance of each joint and the role it plays in our overall well-being.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023