Cardiac Tamponade: A Closer Look at a Critical Medical Emergency
Introduction:
Cardiac tamponade (also known as pericardial tamponade) is a medical emergency that occurs when fluid accumulates in the pericardium, the sac around the heart, and compresses the heart. This compression impedes the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, leading to a potentially life-threatening situation. While pericardial tamponade is rare, it requires immediate medical attention and intervention to prevent severe complications.
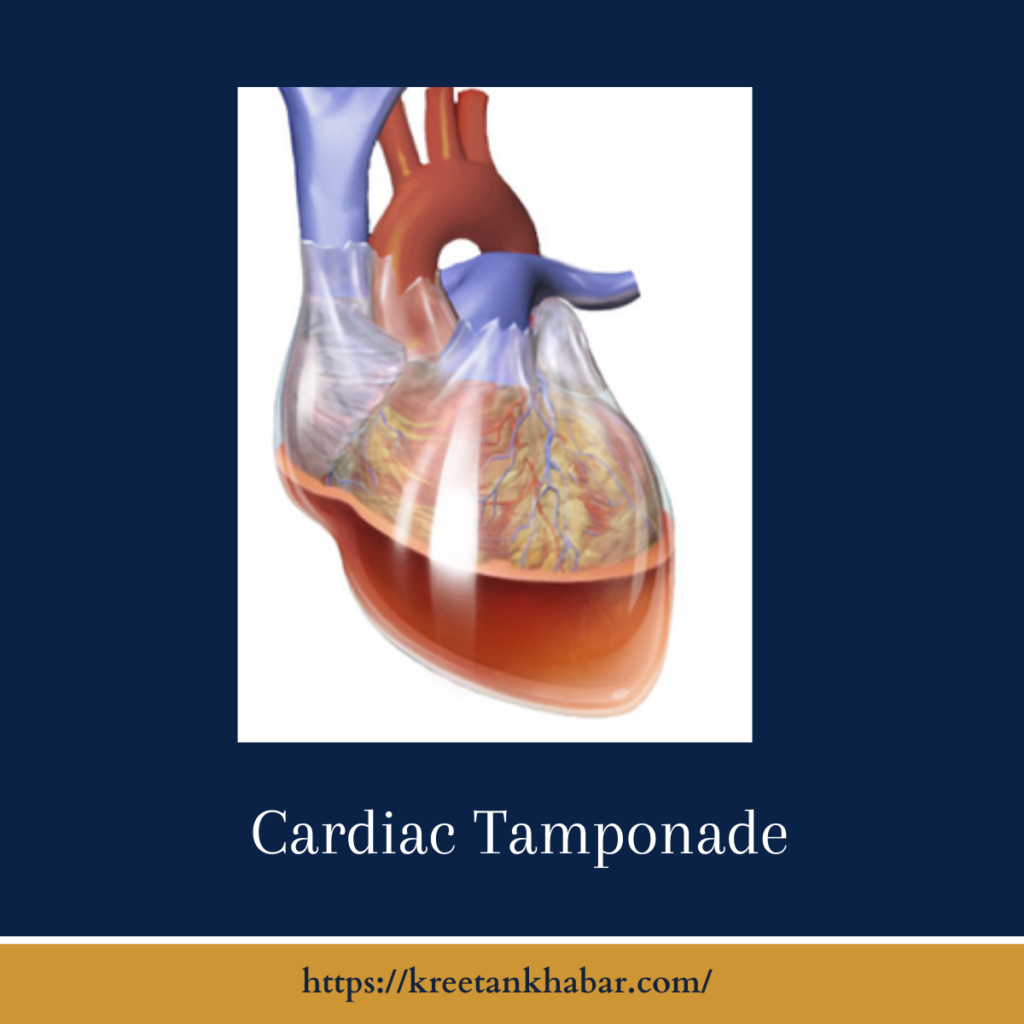
Causes:
- Trauma: One of the common causes of pericardial tamponade is trauma, such as a car accident or a severe blow to the chest, leading to rapid accumulation of blood in the pericardium.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the pericardium, known as pericarditis, can lead to the accumulation of fluid and subsequent pericardial tamponade.
- Cancer: Certain cancers, particularly those that spread to the pericardium, can cause fluid buildup and result in tamponade.
- Aortic Dissection: A tear in the inner layer of the aorta can lead to blood leaking into the pericardium, causing compression of the heart.
- Medical Procedures: Complications from medical procedures, such as heart surgery or catheter insertion, can result in pericardial tamponade.
pericardial tamponade, a life-threatening condition, can be precipitated by various underlying causes, each highlighting the complex nature of this medical emergency. Trauma, such as a severe blow to the chest or a car accident, stands as a prominent cause, leading to rapid accumulation of blood in the pericardium, the sac around the heart. Inflammation of the pericardium, known as pericarditis, can also contribute to cardiac tamponade by causing fluid buildup.
Certain cancers, particularly those that metastasize to the pericardium, pose a risk as they may induce fluid accumulation and subsequent compression of the heart. Aortic dissection, characterized by a tear in the aorta’s inner layer, can lead to blood leaking into the pericardium, exacerbating the condition. Additionally, complications arising from medical procedures such as heart surgery or catheter insertion can result in pericardial tamponade. The diverse array of causes underscores the importance of a comprehensive diagnostic approach to identify the underlying trigger and guide timely and targeted interventions for optimal patient outcomes.
Symptoms:
- Shortness of Breath: As the heart’s ability to pump blood is compromised, individuals may experience difficulty breathing or a sudden onset of shortness of breath.
- Chest Pain: Severe chest pain, often radiating to the neck, shoulders, or back, is a common symptom of cardiac tamponade.
- Rapid Heart Rate: The heart may attempt to compensate for the reduced pumping capacity by increasing its rate, leading to a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
- Hypotension: A drop in blood pressure may occur due to the heart’s compromised ability to circulate blood effectively.
- Jugular Vein Distention: Visible swelling of the jugular veins in the neck can be a sign of increased pressure in the heart.
The symptoms of cardiac tamponade are a reflection of the intense pressure exerted on the heart due to the accumulation of fluid in the pericardium. Shortness of breath is a hallmark symptom, as the compromised heart struggles to efficiently pump blood. Individuals may experience severe chest pain that can radiate to the neck, shoulders, or back, intensifying with each heartbeat. The heart, attempting to compensate, may result in a rapid or irregular heartbeat.
As the pressure builds, hypotension may occur, leading to a drop in blood pressure. Jugular vein distention, visible swelling of the jugular veins in the neck, is another characteristic sign, indicating increased pressure within the heart. Recognizing these symptoms is critical for prompt medical intervention. The causes of cardiac tamponade, whether traumatic injury, pericarditis, cancer, aortic dissection, or complications from medical procedures, underscore the urgency in understanding and addressing the condition’s diverse etiologies to optimize patient care and outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Echocardiogram: Imaging tests, such as an echocardiogram, are crucial for diagnosing cardiac tamponade by visualizing the fluid around the heart.
- Pericardiocentesis: In emergency situations, a procedure called pericardiocentesis may be performed to drain excess fluid from the pericardium.
- Surgery: In cases where the cause of tamponade is related to trauma or other underlying conditions, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the root cause and prevent recurrence.
More points of diagnosis and treatment:
Conclusion:
Cardiac tamponade is a serious medical condition that demands swift recognition and intervention. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking immediate medical attention are essential for a positive outcome. As a potentially life-threatening emergency, early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can make a significant difference in the prognosis and recovery of individuals experiencing cardiac tamponade.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023