Cavernous Malformation: Navigating the Silent Landscape of Vascular Anomalies
Introduction:
In the intricate landscape of neurological health, cavernous malformations stand as enigmatic anomalies, silently residing within the brain or spinal cord. This article aims to unravel the intricacies of cavernous malformations, exploring their characteristics, potential symptoms, diagnostic challenges, and the evolving landscape of treatment for these vascular anomalies.
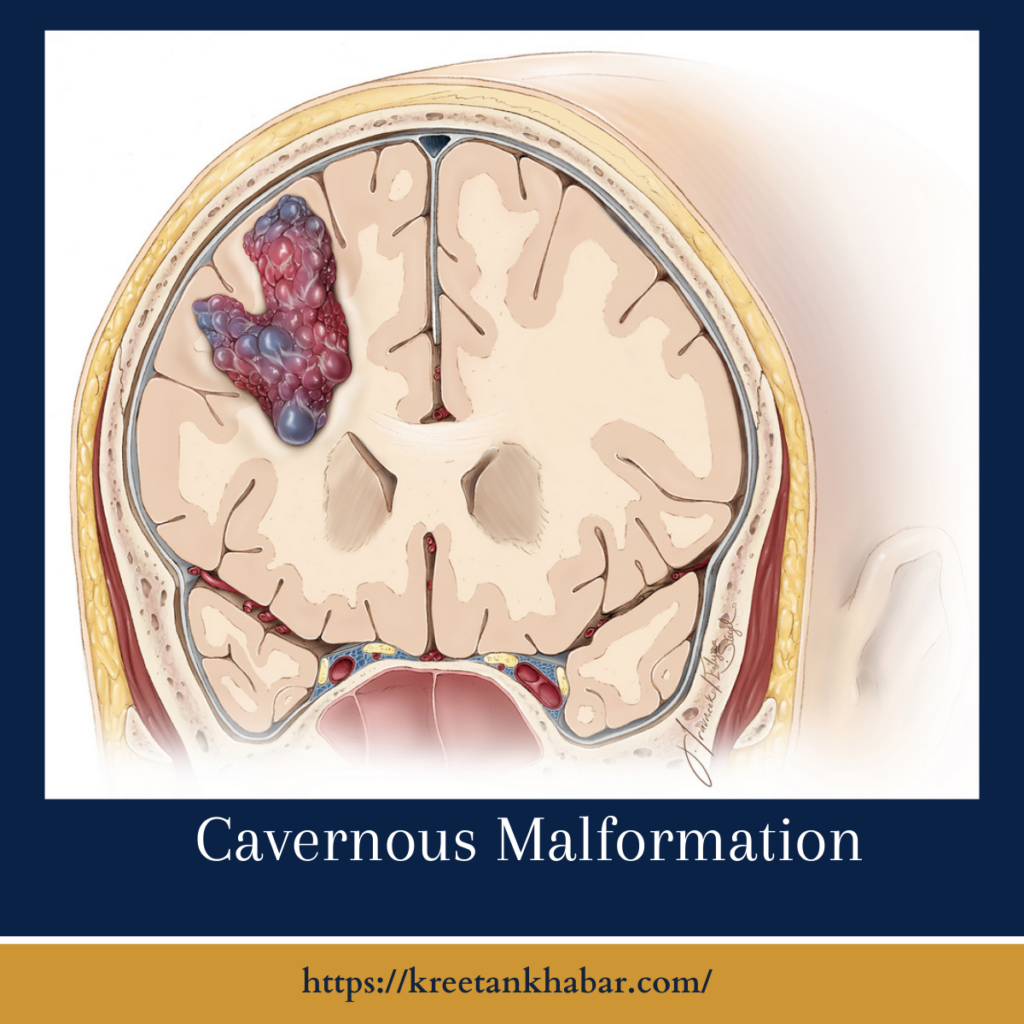
Understanding Cavernous Malformation:
Cavernous malformations, also known as cavernous angiomas or cavernomas, are vascular abnormalities characterized by clusters of dilated, thin-walled blood vessels. Unlike more robust blood vessels, these clusters lack the typical structural elements, making them prone to leakage and potential hemorrhage. While cavernous malformations can occur anywhere in the body, they most commonly manifest in the central nervous system, raising unique challenges due to the delicate nature of neural tissue.
Symptoms and Silent Nature:
Cavernous malformations often exist stealthily, causing no noticeable symptoms in many cases. However, when symptoms do arise, they can vary widely. Common manifestations include seizures, headaches, neurological deficits, and, in severe cases, hemorrhages leading to strokes. The silent nature of cavernous malformations adds an element of complexity to their diagnosis, as individuals may live with these anomalies for years before any symptoms emerge.
Diagnosis Challenges:
Diagnosing cavernous malformations presents unique challenges due to their often asymptomatic nature and the variability of symptoms when they do occur. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the primary diagnostic tool, as it provides detailed images necessary for identifying the characteristic appearance of these anomalies. However, small or deep-seated cavernomas may pose challenges in detection, requiring specialized imaging techniques and expertise.
Genetic Factors and Hereditary Cavernous Malformations:
In some cases, cavernomas may be hereditary, resulting from genetic mutations. Familial Cavernous Malformation (FCM) is a rare condition where multiple family members may develop these anomalies. Genetic testing plays a crucial role in identifying at-risk individuals and informing treatment decisions.
Treatment Strategies:
The management of cavernomas cavernous malformations is nuanced and varies based on factors such as the location, size, and symptoms. In cases where the malformation is asymptomatic or presents a low risk of hemorrhage, a conservative approach may be adopted, focusing on monitoring and symptom management. Surgical intervention may be considered for symptomatic or high-risk cases, involving the removal or resection of the malformation.
The Points of Treatment Strategies:
- Conservative Management for Asymptomatic Cases:
- Asymptomatic cavernomas may be managed conservatively, with a focus on regular monitoring through imaging studies.
- In the absence of symptoms, the potential risks associated with surgical intervention may outweigh the benefits.
- Symptomatic Relief through Medication:
- Medications may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms associated with cavernomas.
- Antiepileptic drugs can help control seizures, and pain medications may alleviate headaches or discomfort.
- Surgical Resection for Symptomatic or High-Risk Cases:
- Symptomatic cavernomas or those at high risk of bleeding may necessitate surgical intervention.
- Resection involves removing the malformation, and the decision to proceed with surgery is based on factors such as the location and size of the lesion.
- Navigating Deep-Seated Lesions with Stereotactic Radiosurgery:
- Stereotactic radiosurgery is a non-invasive treatment option that uses precisely targeted radiation to manage cavernomas.
- This approach is particularly beneficial for deep-seated or inaccessible lesions, aiming to reduce the risk of bleeding.
- Genetic Counseling and Testing for Familial Cases:
- In cases of familial cavernomas, genetic counseling is crucial to assess the risk of other family members.
- Genetic testing can identify specific mutations, informing treatment decisions and guiding surveillance strategies.
- Multi-Disciplinary Approach for Optimal Care:
- Managing cavernomas often requires a multi-disciplinary approach involving neurologists, neurosurgeons, and other specialists.
- This collaborative effort ensures comprehensive care that considers the diverse aspects of the condition.
- Regular Imaging Follow-Up for Monitoring Changes:
- Regardless of the chosen treatment strategy, regular imaging follow-up is essential to monitor any changes in the cavernous malformation.
- This allows healthcare professionals to adapt the management plan based on the evolving nature of the lesion.
- Education and Support for Individuals and Families:
- Providing education and support to individuals diagnosed with cavernomas and their families is integral.
- Understanding the condition, its potential implications, and available treatment options empowers individuals to actively participate in their care.
- Clinical Trials and Research Participation:
- Ongoing clinical trials explore novel treatment modalities and interventions for cavernomas.
- Participation in research studies may offer eligible individuals access to cutting-edge therapies and contribute to advancements in the field.
- Pain Management Strategies:
- For individuals experiencing pain associated with cavernomas, pain management strategies, including physical therapy and counseling, may be beneficial.
- Tailored approaches address the unique pain profiles of each individual.
- Individualized Treatment Plans:
- Treatment strategies for cavernomas are highly individualized, considering the specific characteristics of each lesion and the patient’s overall health.
- Tailoring interventions ensures that the chosen approach aligns with the unique needs and circumstances of the individual.
- Long-Term Follow-Up and Quality of Life Considerations:
- Long-term follow-up is essential to assess the ongoing impact of treatment and address any new developments.
- Quality of life considerations, including cognitive function and emotional well-being, play a crucial role in determining the overall success of treatment strategies.
Navigating the treatment landscape of cavernous malformations involves a comprehensive and personalized approach, addressing symptoms, minimizing risks, and optimizing the quality of life for individuals affected by these complex vascular anomalies.
Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Emerging Therapies:
Stereotactic radiosurgery, a non-invasive technique using focused radiation, is gaining prominence as a treatment option for cavernous malformations. This approach aims to reduce the risk of bleeding and alleviate symptoms without the need for surgical intervention. Ongoing research explores the potential of emerging therapies, including medications targeting angiogenesis and inflammation, offering hope for more targeted and minimally invasive treatment options.
Living with Cavernous Malformations:
For individuals diagnosed with cavernous malformations, living with the condition involves a delicate balance of vigilant monitoring and addressing symptoms as they arise. Regular follow-up with healthcare professionals, including neurologists and neurosurgeons, is essential to track any changes in the malformation and adapt the management plan accordingly.
Conclusion:
Cavernous malformations cast a silent shadow within the intricate realm of neurological health, necessitating a nuanced understanding of their characteristics, diagnostic challenges, and evolving treatment options. As research advances and technology continues to refine our ability to detect and manage these anomalies, individuals diagnosed with cavernous malformations can find hope in the ongoing efforts to unravel the mysteries and improve outcomes for those navigating the silent landscape of vascular anomalies within the central nervous system.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023