Cerebral Cavernous Malformation: A Hidden Threat in the Brain
Introduction:
Within the intricate network of the human brain lies a condition that often goes unnoticed until it manifests in unexpected ways. Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM), though relatively rare, presents a significant challenge to those affected and the medical community alike. This article aims to shed light on this often overlooked neurological condition, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the impact it has on individuals and families.
Unraveling the Mystery of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation:
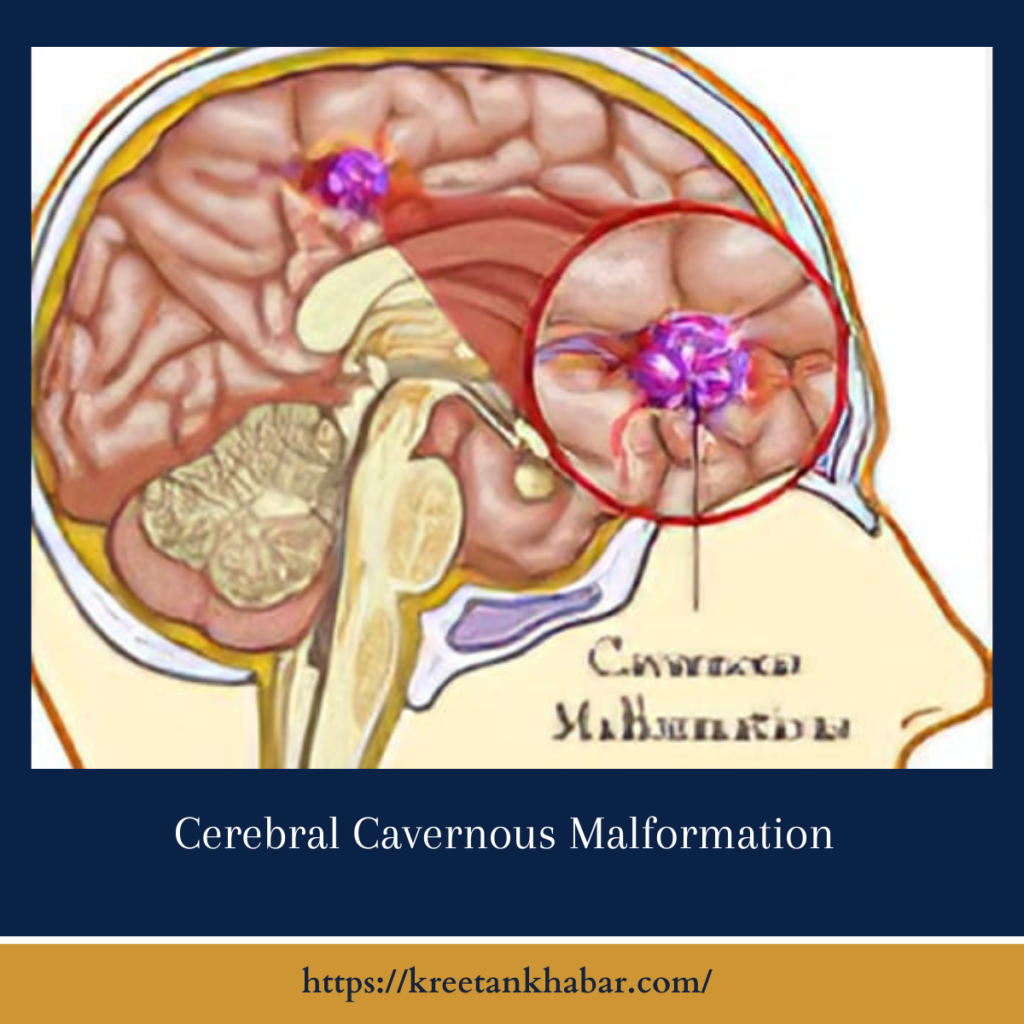
Cerebral Cavernous Malformation, also known as Cavernous Angioma or Cavernoma, is a vascular disorder characterized by the presence of abnormal clusters of dilated blood vessels in the brain or spinal cord. These clusters, resembling small mulberries, are prone to leakage and can cause a range of neurological symptoms.
Symptoms and Manifestations:
One of the challenges with CCM is its variability in symptom presentation. Some individuals may remain asymptomatic throughout their lives, while others may experience debilitating symptoms. Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, neurological deficits such as weakness or numbness, vision or hearing changes, and cognitive impairment. The severity and frequency of symptoms can vary widely among patients, making diagnosis and management complex.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing Cerebral Cavernous Malformation often involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the preferred modality for visualizing these lesions due to its ability to provide detailed images of the brain’s structures. In some cases, genetic testing may also be recommended, especially if there is a family history of CCM or suspicion of an underlying genetic mutation.
- Imaging Modalities: Diagnosis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation (CCM) heavily relies on advanced imaging modalities, primarily Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRI provides detailed images of the brain, allowing healthcare providers to visualize the characteristic clusters of dilated blood vessels associated with CCM.
- Characteristic Appearance: On MRI scans, CCM lesions typically appear as clusters of popcorn-like or mulberry-like structures with a dark rim, indicating hemosiderin deposition from previous microhemorrhages. This distinct appearance helps differentiate CCM from other vascular lesions or tumors.
- Sequencing Studies: In cases where there is a family history of CCM or suspicion of an underlying genetic predisposition, sequencing studies may be conducted to identify mutations in genes associated with CCM, such as the CCM1, CCM2, and CCM3 genes.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can provide valuable information about the risk of developing CCM and help guide treatment decisions, particularly in families with a history of the condition. Identifying specific genetic mutations can also aid in genetic counseling for affected individuals and their relatives.
- Clinical Evaluation: Alongside imaging studies and genetic testing, clinical evaluation plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of CCM. Healthcare providers assess patients for symptoms such as headaches, seizures, neurological deficits, or other signs suggestive of CCM. A thorough medical history and neurological examination help guide further diagnostic investigations.
- Differential Diagnosis: It’s essential to differentiate CCM from other vascular lesions or conditions that may present with similar symptoms. Differential diagnosis may include arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), cavernous hemangiomas, developmental venous anomalies (DVAs), or tumors such as gliomas.
- Serial Imaging: In some cases, particularly when CCM lesions are small or asymptomatic, serial imaging studies may be recommended to monitor for changes in size or appearance over time. Regular follow-up allows healthcare providers to assess disease progression and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Multi-disciplinary Approach: Diagnosis and management of CCM often require a multi-disciplinary approach involving neurologists, neurosurgeons, neuroradiologists, and genetic counselors. Collaboration between different specialties ensures comprehensive care and tailored treatment strategies for individual patients.
- Patient Education and Support: Patient education is an integral part of the diagnostic process, helping individuals understand their condition, treatment options, and potential implications for themselves and their families. Providing access to support groups and resources can also offer emotional support and practical guidance throughout the diagnostic journey.
- Research and Advancements: Ongoing research efforts continue to enhance our understanding of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation, leading to advancements in diagnostic techniques and targeted therapies. By staying abreast of the latest developments, healthcare providers can offer patients the most effective diagnostic and treatment options available.
In conclusion, the diagnosis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation involves a combination of imaging studies, genetic testing, clinical evaluation, and collaboration among healthcare professionals. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and improving outcomes for individuals affected by this complex neurological condition.
Treatment Options:
The management of CCM depends on various factors, including the location and size of the lesions, as well as the presence and severity of symptoms. In asymptomatic cases or those with mild symptoms, a conservative approach with regular monitoring may be recommended. However, for symptomatic individuals or those at risk of complications such as hemorrhage, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options include lesion resection, stereotactic radiosurgery, or endovascular embolization, each with its own risks and benefits.
Living with Cerebral Cavernous Malformation:
For those diagnosed with CCM, living with the condition can be challenging. The unpredictability of symptoms and the potential for complications can significantly impact quality of life. Managing symptoms, adhering to treatment plans, and regular follow-up with healthcare providers are essential aspects of coping with CCM. Additionally, support from family, friends, and patient advocacy groups can provide much-needed emotional and practical support.
Research and Future Directions:
Advances in medical imaging, genetics, and neurosurgical techniques have improved our understanding and management of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation. However, there is still much to learn about the underlying mechanisms of the disease, genetic factors influencing its development, and targeted therapeutic approaches. Ongoing research efforts aim to unravel the complexities of CCM and develop more effective treatments to improve outcomes for those affected.
Conclusion:
Cerebral Cavernous Malformation may be a relatively rare condition, but its impact on individuals and families can be profound. By raising awareness, promoting early diagnosis, and advancing research efforts, we can strive to improve the lives of those living with CCM. With continued collaboration between healthcare providers, researchers, and patient communities, we can work towards better understanding, management, and ultimately, finding a cure for this complex neurological disorder.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023