Chronic Lateral Ankle Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Chronic lateral ankle pain, a persistent discomfort experienced on the outer side of the ankle joint, poses a significant challenge for many individuals. Unlike acute injuries that heal with time, chronic lateral ankle pain lingers, impacting daily activities and diminishing quality of life. To effectively manage this condition, it’s essential to grasp its underlying causes, recognize its symptoms, and explore available treatment options.
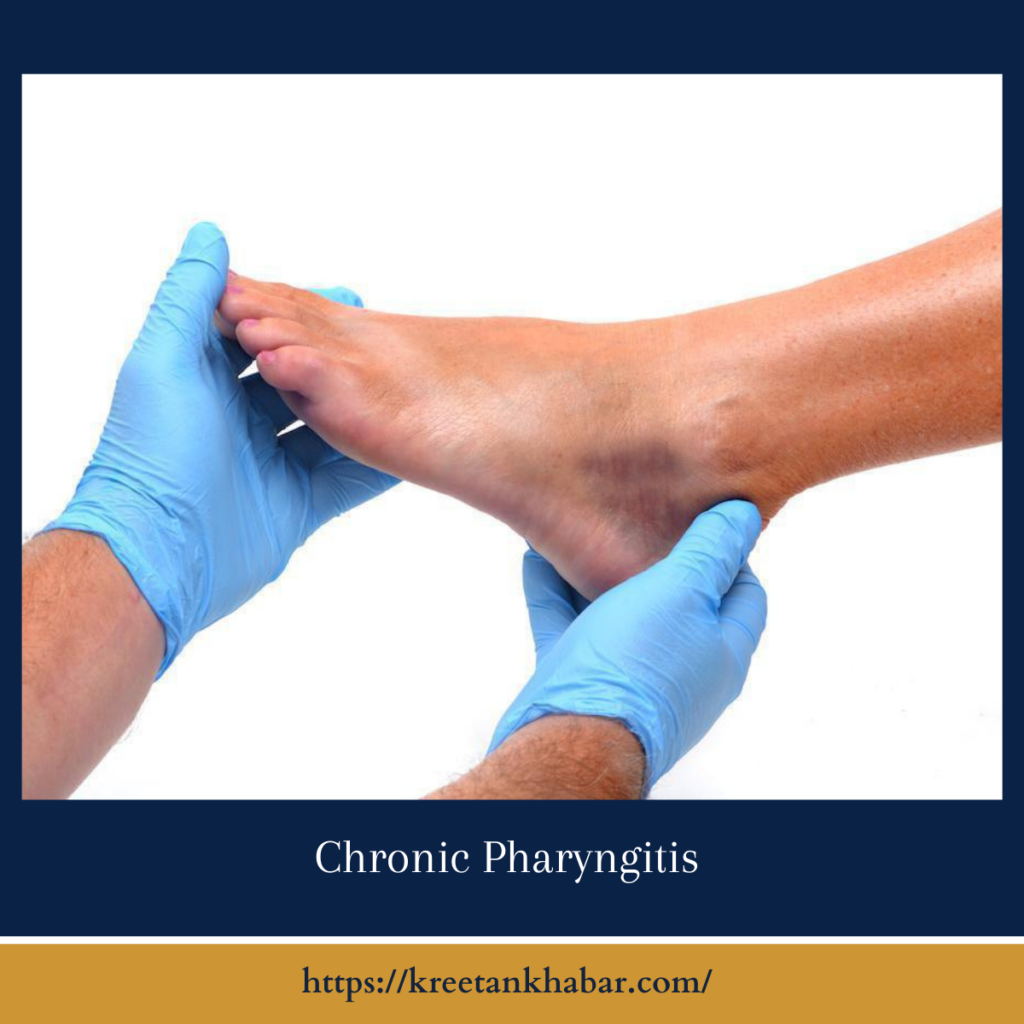
The Roots of Discomfort
Chronic lateral ankle pain often originates from previous ankle injuries, particularly sprains or strains that weren’t adequately treated or rehabilitated. These injuries can lead to instability in the ankle joint, causing repetitive microtrauma and inflammation of the surrounding ligaments and tendons. Over time, this ongoing stress results in chronic pain and discomfort.
Unveiling the Symptoms
The symptoms of chronic lateral ankle pain vary from person to person but commonly include persistent pain, tenderness, and swelling on the outer side of the ankle. Individuals may also experience instability or a feeling of giving way in the ankle joint, especially during weight-bearing activities. Stiffness and limited range of motion in the ankle joint are also common, making movements like walking, running, or climbing stairs challenging.
- Persistent Pain: Chronic lateral ankle pain is characterized by ongoing discomfort on the outer side of the ankle joint, often present even during periods of rest or inactivity.
- Tenderness: Individuals may experience tenderness to the touch along the outer aspect of the ankle, particularly over the affected ligaments and tendons.
- Swelling: Chronic inflammation in the ankle joint can lead to swelling, which may be visible or palpable around the lateral ankle area.
- Instability: Ankle instability is a common symptom of chronic lateral ankle pain, with individuals often reporting feelings of giving way or “rolling” of the ankle during weight-bearing activities.
- Stiffness: Chronic inflammation and repeated injury to the ligaments and tendons can result in stiffness in the ankle joint, limiting range of motion and making movement uncomfortable.
- Weakness: Weakness in the muscles surrounding the ankle joint may accompany chronic lateral ankle pain, contributing to feelings of instability and difficulty with activities that require balance or coordination.
- Difficulty with Weight-Bearing Activities: Pain and discomfort may worsen during activities that place stress on the ankle joint, such as walking, running, or climbing stairs.
- Pain with Specific Movements: Certain movements, such as inversion (turning the ankle inward) or dorsiflexion (bringing the foot upward), may exacerbate pain and discomfort in individuals with chronic lateral ankle pain.
- Recurrent Sprains: Individuals with chronic lateral ankle pain may have a history of recurrent ankle sprains, indicating underlying instability and susceptibility to injury.
- Functional Limitations: Chronic lateral ankle pain can significantly impact daily activities and functional abilities, affecting mobility, sports performance, and overall quality of life.
Exploring Treatment Options
Treatment for chronic lateral ankle pain aims to alleviate symptoms, improve ankle stability, and restore function. Depending on the severity of the condition, treatment options may include:
- Physical Therapy: A structured physical therapy program focusing on strengthening exercises, balance training, and proprioception exercises can help improve ankle stability and reduce pain.
- Bracing or Taping: External support in the form of ankle braces or athletic tape may be recommended to provide stability to the ankle joint during activities.
- Orthotics: Custom orthotic devices, such as shoe inserts or ankle-foot orthoses, can help correct biomechanical imbalances and provide additional support to the ankle.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation in the ankle joint.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as ligament repair, ankle arthroscopy, or ankle fusion may be performed to address underlying issues contributing to chronic lateral ankle pain.
The Road to Recovery
Recovery from chronic lateral ankle pain is often a gradual process that requires patience and dedication. Individuals undergoing treatment should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations, adhere to prescribed exercise programs, and avoid activities that exacerbate symptoms. With time and consistent effort, many individuals experience significant improvement in pain and function, allowing them to return to their desired level of activity.
Conclusion
Chronic lateral ankle pain can be a persistent and debilitating condition, but with proper understanding and management, relief is attainable. By addressing the underlying causes, recognizing symptoms early, and exploring appropriate treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps towards recovery and reclaiming their ankle health. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs and circumstances.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023