Corticobasal Syndrome: A Comprehensive Exploration
Introduction:
Corticobasal Syndrome (CBS) is a rare neurodegenerative disorder that presents a myriad of clinical features, making it a complex challenge in the realm of neurology. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of Corticobasal Syndrome, shedding light on its clinical manifestations, potential causes, diagnostic approaches, and the evolving landscape of treatment options for individuals grappling with this enigmatic condition.
Clinical Manifestations:
CBS is characterized by a diverse array of symptoms that affect both motor and cognitive functions. Common motor symptoms include progressive limb stiffness, akinetic-rigidity (resembling Parkinson’s disease), and apraxia—the impaired ability to execute purposeful movements despite intact motor abilities. Cognitive impairments may involve difficulties with language, memory, and executive functions, adding a layer of complexity to the clinical presentation. As CBS progresses, it often leads to a profound impact on daily activities and independence.
Potential Causes and Pathophysiology:
The exact cause of Corticobasal Syndrome remains elusive, and the disorder is often considered a part of the broader spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases. Some studies suggest an accumulation of abnormal tau protein in the brain, a hallmark seen in other neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. However, the precise pathophysiological mechanisms triggering CBS are still under investigation, emphasizing the need for further research to unravel its underlying causes.
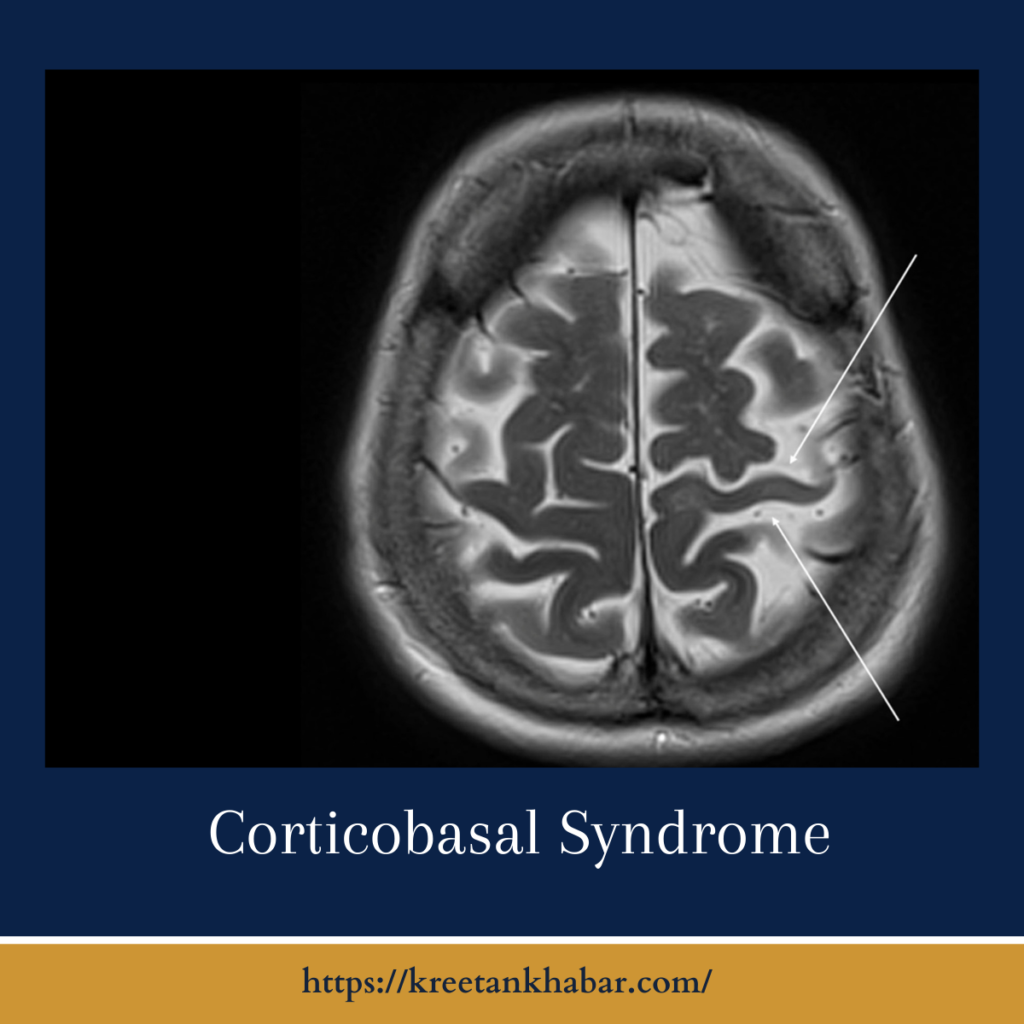
Diagnostic Approaches:
Diagnosing Corticobasal Syndrome is inherently challenging due to the variability of symptoms and the overlap with other neurodegenerative disorders. Clinical assessments, neuroimaging studies (such as MRI and PET scans), and neuropsychological testing play crucial roles in the diagnostic process. Additionally, the identification of specific biomarkers associated with CBS is an area of active research, offering potential avenues for more accurate and timely diagnosis.
Treatment Landscape:
Managing Corticobasal Syndrome is complex and often involves a multidisciplinary approach. While there is no cure for CBS, symptomatic treatments aim to alleviate specific manifestations. Medications targeting movement symptoms, physical therapy to enhance mobility, and speech therapy to address language difficulties may be components of the treatment plan. Moreover, ongoing research into disease-modifying therapies and potential interventions to target underlying pathological processes brings hope for future advancements in CBS management.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Corticobasal Syndrome poses several challenges, including the variability of clinical presentations, the absence of definitive diagnostic markers, and limited treatment options. The rarity of the condition further complicates large-scale clinical trials and comprehensive understanding. As researchers delve deeper into the molecular and genetic underpinnings of CBS, there is optimism that targeted therapies and more refined diagnostic tools will emerge, providing improved avenues for both early detection and intervention.
Conclusion:
Corticobasal Syndrome stands as a complex and often perplexing neurodegenerative disorder, necessitating ongoing collaboration between healthcare professionals, researchers, and caregivers. Enhancing our understanding of its clinical nuances, unraveling its underlying causes, and developing effective treatment strategies remain crucial goals. As the field of neurology advances, there is hope for more comprehensive care and support for individuals navigating the challenges presented by Corticobasal Syndrome.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023