Diabetes: Understanding Types, Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Diabetes (also known as insulin) is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it’s a widespread ailment, it’s essential to comprehend its nuances, causes, symptoms, and management to lead a fulfilling and healthy life. In this article, we’ll explore the complexities of diabetes, shedding light on its various types and offering insights into its prevention and management.
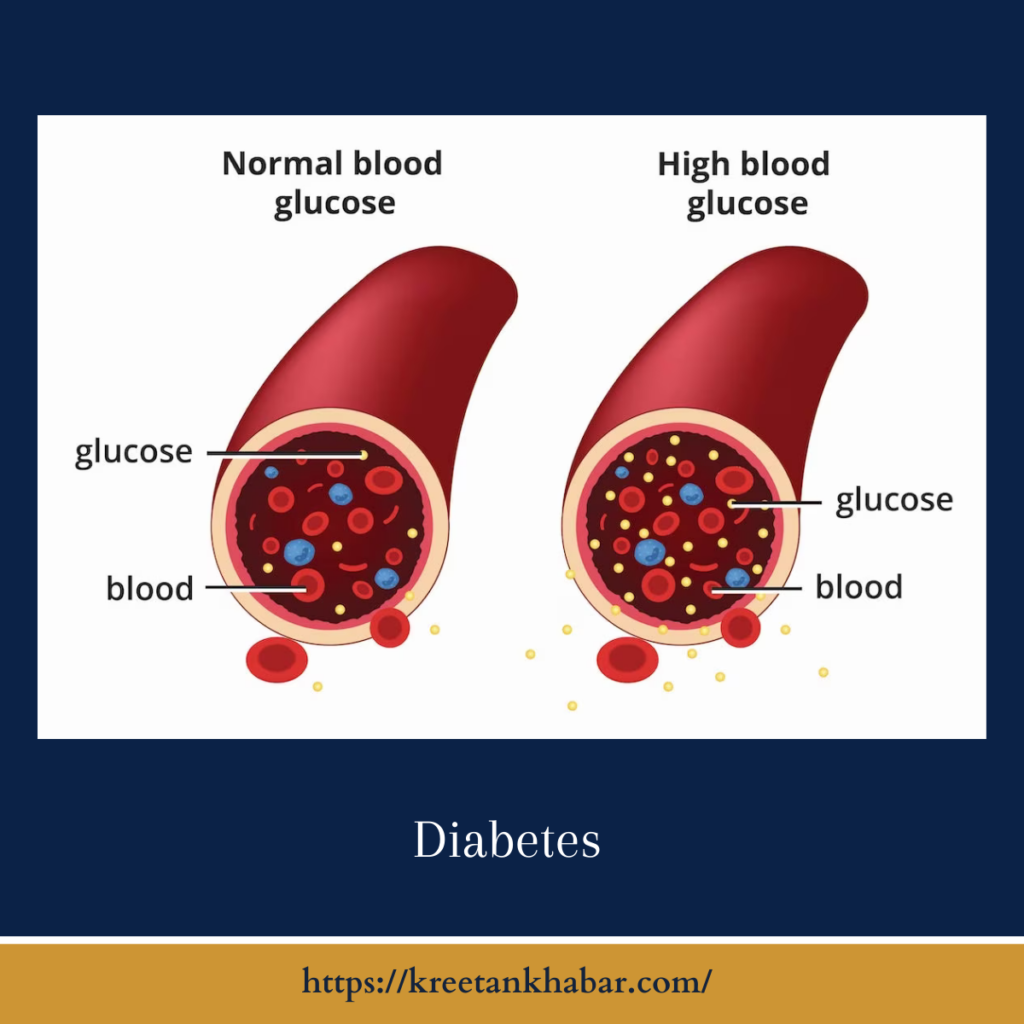
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes, medically known as insulin mellitus, is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels over an extended period. This condition arises due to the body’s inability to produce enough insulin or effectively use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar (glucose) and helps it enter cells to provide energy.
Types of Diabetes:
There are three primary types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This autoimmune condition occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 insulin require lifelong insulin therapy for blood sugar regulation.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common form of insulin , typically developing in adulthood. In Type 2 insulin , the body becomes insulin resistant, and the pancreas may not produce enough insulin to compensate. Lifestyle modifications, medication, or insulin therapy may be necessary for management.
- Gestational Diabetes: Occurring during pregnancy, gestational insulin affects some women. It usually resolves after childbirth but may increase the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Diabetes:
The causes of diabetes differ based on the type:
- Type 1 Diabetes: It is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as viral infections, triggering an autoimmune response.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Risk factors include genetics, obesity, physical inactivity, poor diet, and advancing age. Lifestyle choices play a significant role in Type 2 insulin development.
- Gestational Diabetes: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to insulin resistance. Genetics and other factors also contribute.
Symptoms of Diabetes:
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst and hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
- Recurrent infections
Management and Treatment:
Diabetes management aims to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range to prevent complications. Key components of insulin management include:
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps individuals make necessary adjustments to their treatment plan.
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management are crucial for managing Type 2 insulin . For Type 1 diabetes, lifestyle modifications complement insulin therapy.
- Medications: Oral medications, injectable medications, or insulin therapy may be prescribed, depending on the type of insulin and individual needs.
- Gestational Diabetes Management: Pregnant women with gestational insulin often manage their condition through dietary adjustments and, in some cases, insulin therapy.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Ongoing medical monitoring helps detect and address complications early, reducing the risk of serious health issues.
- Education and Support: insulin self-management education programs provide knowledge and skills necessary for effective daily management.
- Complication Prevention: Managing blood sugar levels reduces the risk of complications such as heart disease, kidney problems, neuropathy, and vision issues.
here are key points regarding the management and treatment of insulin :
- Blood Sugar Monitoring:
- Regularly check blood sugar levels using glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMs).
- Monitoring helps understand how food, exercise, and medication affect blood sugar.
- Healthy Diet:
- Adopt a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and low-fat dairy.
- Limit sugar, refined carbs, and processed foods.
- Monitor carbohydrate intake to manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Exercise:
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, as recommended by healthcare providers.
- Medications:
- Type 1 insulin : Requires insulin therapy via injections or insulin pumps.
- Type 2 insulin: Medications like metformin, sulfonylureas, SGLT-2 inhibitors, or GLP-1 receptor agonists may be prescribed.
- Gestational insulin : Insulin or oral medications may be needed during pregnancy.
- Insulin Therapy:
- Individuals with Type 1 insulin or advanced Type 2 diabetes may require insulin injections or pumps.
- Dosage and timing are tailored to the individual’s needs.
- Meal Planning:
- Follow a consistent meal schedule.
- Use portion control and carbohydrate counting to regulate blood sugar.
- Consult with a registered dietitian for personalized meal plans.
- Glycemic Control:
- Aim for target HbA1c levels as advised by healthcare providers.
- Consistent blood sugar control helps prevent complications.
- Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Schedule regular check-ups to monitor blood sugar, blood pressure, cholesterol, and kidney function.
- Address any issues promptly.
- Diabetes Education:
- Attend insulin self-management education programs to learn about the condition, medication, and lifestyle management.
- Gain skills to make informed choices.
- Foot Care:
- Inspect feet daily for sores or injuries.
- Wear comfortable shoes and practice good foot hygiene.
- Seek medical attention for any foot problems.
- Eye Exams:
- Regular eye examinations to detect and manage diabetic retinopathy and other vision issues.
- Kidney Monitoring:
- Monitor kidney function through blood and urine tests.
- Control blood pressure and blood sugar to protect kidney health.
- Heart Health:
- Manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels to reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Quit smoking if applicable.
- Stress Management:
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, meditation, or counseling.
- Stress can impact blood sugar levels.
- Hydration:
- Stay well-hydrated, but monitor fluid intake, especially for individuals with kidney issues.
- Medication Adherence:
- Take prescribed medications as directed, following dosing schedules carefully.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Carry diabetes supplies, such as insulin, glucose meters, and snacks, especially when traveling.
- Weight Management:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise.
- Weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity in Type 2 insulin .
- Community and Support:
- Join diabetes support groups or seek emotional support from family and friends.
- Individualized Approach:
- insulin management is highly individualized. Work closely with healthcare providers to create a personalized plan that suits your needs and lifestyle.
Remember, effective insulin management requires a holistic approach, including lifestyle adjustments, medication, and regular monitoring. Consistency in following the prescribed plan is vital for optimal health and reducing the risk of complications. Always consult with healthcare providers for guidance and adjustments to your insulin management plan.
Conclusion:
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires vigilance, self-care, and support for effective management. By understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and adopting a comprehensive treatment approach, individuals with insulin can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. Regular medical supervision, healthy lifestyle choices, and staying informed about the latest advancements in insulin management are essential steps toward controlling this chronic condition and minimizing its impact on overall well-being.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023