Ear Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction
Ear infections a(also known as labyrinthitis ) are a common ailment, particularly in children, but they can affect individuals of all ages. These infections can range from mild and temporary to severe and chronic. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for ear infections, shedding light on a condition that can be both painful and disruptive.
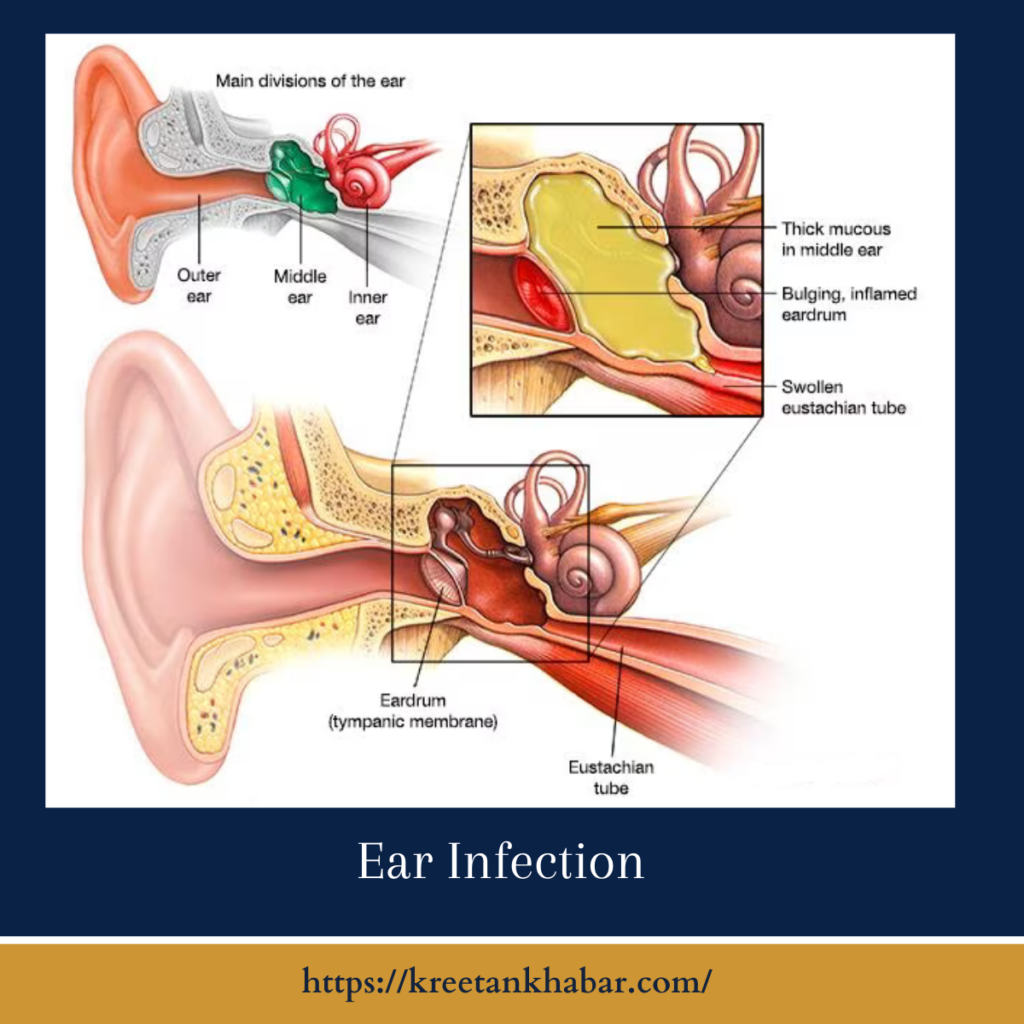
Understanding Ear Infections
Ear infections, or otitis, refer to the inflammation and infection of the ear, typically the middle or outer ear. They are often categorized into two main types:
- Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): This is the most common type of ear infection, often occurring as a result of a respiratory infection. It involves the inflammation and infection of the middle ear, which is the space behind the eardrum. Otitis media can be acute (short-term) or chronic (recurring).
- Otitis Externa (Outer Ear Infection): Otitis externa, also known as swimmer’s ear, affects the outer ear canal. It is typically caused by water remaining in the ear after swimming, creating a favorable environment for bacterial growth.
Common Causes of Ear Infections
- Bacterial and Viral Infections: Most labyrinthitis are caused by bacteria, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae, or viruses like the common cold and flu.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation in the ear and increase the risk of infection.
- Excess Earwax: A buildup of earwax can trap bacteria and create a conducive environment for infection.
- Sinus Infections: Infections in the sinuses can lead to labyrinthitis , as the ear and sinus passages are interconnected.
Symptoms of Ear Infections
The symptoms of ear infections can vary based on the type and severity but commonly include:
- Ear Pain: A sharp, throbbing, or constant earache is often the most prominent symptom.
- Hearing Difficulties: Decreased hearing or a sensation of fullness in the ear can occur due to fluid buildup.
- Fever: In cases of acute labyrinthitis , fever may be present.
- Drainage: In some cases, the infected ear may produce a discharge that can be yellow, white, or bloody.
- Irritability: Infants and young children with labyrinthitis may be fussy and have difficulty sleeping.
Treatment and Management
Treatment for ear infections may include:
- Antibiotics: If the infection is bacterial, antibiotics are often prescribed.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate ear pain and reduce fever.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can provide relief.
- Observation: In some cases, especially with mild infections, a healthcare provider may recommend observation to see if the infection resolves on its own.
Treatment and Management of Ear Infection: Key Points
- Antibiotics: Bacterial labyrinthitis are typically treated with a course of antibiotics prescribed by a healthcare provider. It’s crucial to complete the entire prescribed course, even if symptoms improve earlier.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage ear pain and reduce fever. Follow dosing instructions carefully.
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm, moist compress to the affected ear can provide relief from discomfort and may help reduce inflammation.
- Observation: In some cases, especially with mild labyrinthitis , healthcare providers may recommend observation rather than immediate antibiotic treatment. They monitor the patient’s condition to see if the infection resolves on its own.
- Prescription Medications: If the ear infection is severe or recurrent, prescription medications may be necessary. These may include stronger antibiotics or eardrops, depending on the type and location of the infection.
- Drainage: If the ear infection results in the buildup of fluid or pus within the ear, a healthcare provider may need to drain it to relieve pressure and discomfort.
- Tympanostomy Tubes: In some cases, especially for chronic labyrinthitis , healthcare providers may recommend the placement of small tubes in the eardrums. These tubes help ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid buildup.
- Hearing Tests: Hearing tests may be recommended to assess any hearing loss resulting from the ear infection. This is especially important in children to ensure timely intervention if hearing problems are detected.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all follow-up appointments as scheduled by your healthcare provider to monitor progress and ensure that the infection has cleared completely.
- Pain Management for Children: In cases involving infants and young children, especially those too young for pain relievers, comforting measures such as cuddling, offering a pacifier, or using warm bottles may help soothe the child.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is important, especially if fever is present. Encourage fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
- Ear Protection: Avoid exposing the affected ear to water, as it can exacerbate the infection. Use earplugs or cotton balls coated with petroleum jelly when showering or swimming.
- Monitor for Complications: Be vigilant for signs of complications, such as worsening pain, high fever, or the development of new symptoms, and promptly consult a healthcare provider if any concerns arise.
- Preventive Measures: Once the infection has cleared, focus on preventive measures, such as good hygiene, vaccination, and managing allergies, to reduce the risk of future labyrinthitis .
- Consult a Specialist: In cases of recurrent or chronic ear infections, consultation with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist may be necessary for further evaluation and management.
Effective treatment and management of ear infections depend on the type, severity, and individual circumstances. It’s essential to follow healthcare provider recommendations, complete prescribed medications, and seek timely medical attention when needed to ensure a full recovery and minimize complications.
Preventive Measures
To reduce the risk of ear infections:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Keep ears clean and dry, and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
- Vaccination: Staying up-to-date with vaccinations, especially the pneumococcal vaccine, can reduce the risk of infections.
- Manage Allergies: Proper management of allergies can help prevent ear infections.
- Avoid Smoking: Avoid exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can increase the risk of ear infections.
- Promptly Treat Respiratory Infections: Treating colds and respiratory infections promptly can prevent them from spreading to the ears.
Conclusion
Ear infections can be painful and disruptive, but with timely medical care and preventive measures, their impact can be minimized. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking appropriate treatment are essential steps in managing this common condition and ensuring ear health.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023