Ectopic Pregnancy: Understanding the Risks and Challenges
Introduction
Ectopic pregnancy (also known as extrauterine pregnancy) is a medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This condition poses significant risks to a woman’s health and requires prompt medical attention. In this article, we will explore ectopic pregnancy in detail, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and potential complications.
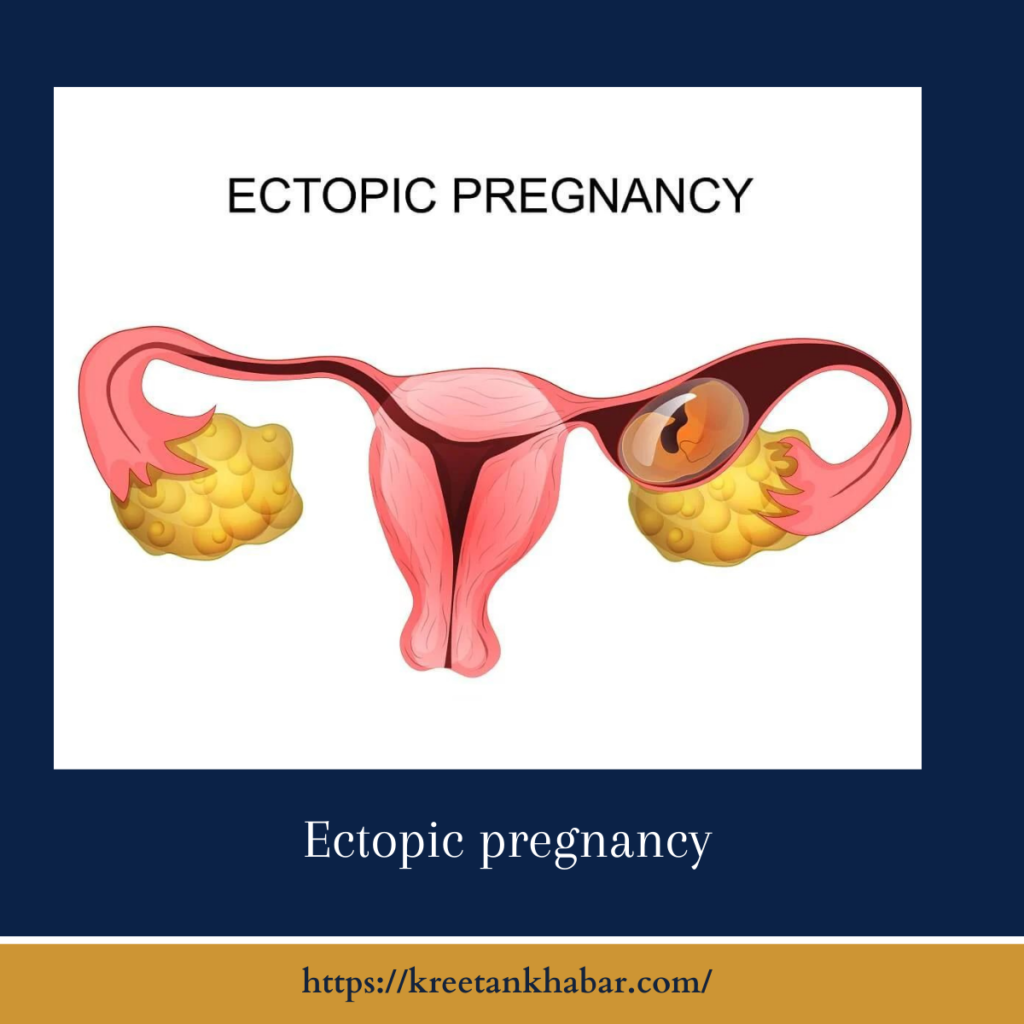
Understanding Ectopic Pregnancy
In a healthy pregnancy, a fertilized egg travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it implants and develops. However, in an extrauterine pregnancy, this process goes awry, and the embryo implants outside the uterus. While ectopic pregnancies can occur in other locations, over 95% of them occur in the fallopian tubes, earning the condition the name “tubal pregnancy.”
Causes
The exact cause of ectopic pregnancy is often unclear, but several risk factors increase the likelihood of its occurrence, including:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): Infections of the reproductive organs, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, can lead to scarring and narrowing of the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of extrauterine pregnancy.
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Women who have had an extrauterine pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of experiencing another.
- Abnormal Fallopian Tubes: Structural issues with the fallopian tubes, such as scarring or deformities, can impede the normal movement of the fertilized egg.
- Intrauterine Device (IUD) Use: While rare, IUDs can increase the risk of extrauterine pregnancy.
- Smoking: Smoking tobacco may raise the risk of extrauterine pregnancy.
Symptoms
Ectopic pregnancies often present with symptoms similar to those of a normal pregnancy, such as missed periods, breast tenderness, and nausea. However, additional warning signs include:
- Abdominal or Pelvic Pain: Sharp, severe, or persistent pain on one side of the abdomen or pelvis is a common symptom.
- Vaginal Bleeding: Light to heavy vaginal bleeding, often darker in color than regular menstruation, can occur.
- Shoulder Pain: In some cases, the fertilized egg may rupture the fallopian tube, causing internal bleeding. This can lead to referred pain in the shoulder area.
Diagnosis
extrauterine pregnancy can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This imaging technique can help visualize the location of the gestational sac and embryo.
- Blood Tests: Monitoring levels of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) can reveal whether a pregnancy is progressing normally.
- Laparoscopy: In cases of diagnostic uncertainty or when immediate treatment is required, a laparoscopic procedure may be performed to directly visualize the fallopian tubes and diagnose extrauterine pregnancy.
Treatment
Prompt treatment is crucial to prevent complications such as rupture and severe bleeding. Treatment options include:
- Methotrexate: In cases where the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and has not ruptured, a medication called methotrexate can be administered to stop the embryo’s growth and facilitate its absorption by the body.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: If the ectopic pregnancy has not ruptured and is located within the fallopian tube, minimally invasive surgery can be performed to remove the pregnancy while preserving the tube.
- Emergency Surgery: In cases of rupture or severe bleeding, emergency surgery may be necessary to remove the extrauterine pregnancy and repair any damage to the fallopian tube or nearby organs.
here are key points about the treatment of ectopic pregnancy:
- Early Detection is Vital: Detecting and treating extrauterine pregnancy early is crucial to prevent complications like fallopian tube rupture, severe bleeding, and damage to nearby organs.
- Medical Management:
- Methotrexate: In cases where the ectopic pregnancy is detected early and is not ruptured, methotrexate, a medication that stops the embryo’s growth, may be administered.
- Monitoring: After methotrexate treatment, regular monitoring of hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) hormone levels is essential to ensure the pregnancy is resolving.
- Surgical Interventions:
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery is often the preferred method when the extrauterine pregnancy is not ruptured. It involves removing the pregnancy and, if possible, preserving the fallopian tube.
- Emergency Surgery: If the ectopic pregnancy has ruptured, emergency surgery may be necessary to stop internal bleeding, remove the pregnancy, and repair damaged tissues. In some cases, the affected fallopian tube may need to be removed.
- Fertility Considerations:
- Surgery that removes the affected fallopian tube may reduce fertility, but many women can still conceive naturally with their remaining tube.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) may be an option for women with bilateral tubal damage or a history of multiple ectopic pregnancies.
- Psychological Support: Coping with the emotional and psychological impact of ectopic pregnancy is important. Women and their partners may benefit from counseling and support groups.
- Follow-Up Care: After treatment, regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor recovery and ensure there are no residual pregnancy tissues.
- Future Pregnancy Planning: Women who have had an ectopic pregnancy may be advised to wait for a certain period before trying to conceive again. Discussing family planning with a healthcare provider is crucial.
- Contraception: It’s important to discuss contraception options with a healthcare provider to prevent future ectopic pregnancies and manage family planning.
- Emotional Support: Coping with the emotional aftermath of an ectopic pregnancy can be challenging. Seeking support from mental health professionals or support groups can be beneficial.
- Risks and Complications: While treatment is generally successful, there are risks involved, including infection, bleeding, and potential damage to the remaining fallopian tube in cases where surgery is necessary.
In summary, the treatment of ectopic pregnancy depends on factors like the location of the pregnancy, its size, and whether it has ruptured. Early detection and intervention are crucial for preserving a woman’s health and fertility. Healthcare providers work closely with affected individuals to determine the most appropriate treatment plan and provide the necessary support throughout the process.
Complications
Untreated ectopic pregnancy can lead to life-threatening complications, including severe bleeding, shock, and damage to the reproductive organs. It can also impact future fertility, especially if the affected fallopian tube is removed.
Conclusion
Ectopic pregnancy is a challenging and potentially dangerous condition that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and diagnostic methods is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. Early intervention not only protects a woman’s health but also preserves her chances of having a healthy pregnancy in the future. If you suspect an ectopic pregnancy or experience its symptoms, seeking prompt medical care is essential for a safe and successful outcome.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023