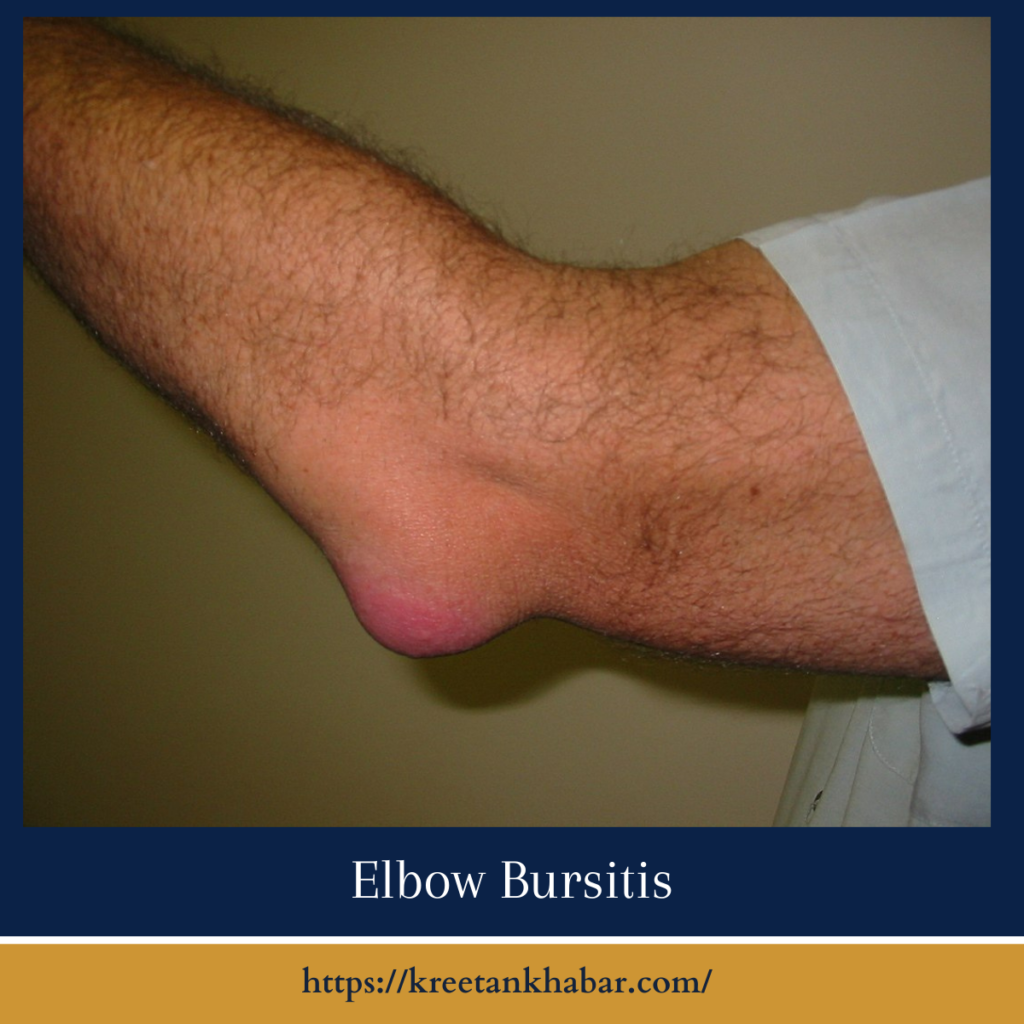
Elbow Bursitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Elbow bursitis, often referred to as olecranon bursitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the bursa located at the tip of the elbow. While it may not be as commonly discussed as other joint-related ailments, elbow bursitis can cause discomfort and restrict movement, impacting daily activities. Let’s delve into this condition, exploring its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
What Causes Elbow Bursitis?
The bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between bones, tendons, and muscles, reducing friction and allowing smooth movement of joints. Elbow bursitis occurs when this sac becomes inflamed, usually due to repetitive pressure or trauma to the elbow. Some common causes include:
- Repetitive Movements: Activities that involve repetitive motions of the elbow, such as leaning on hard surfaces for extended periods, can irritate the bursa and lead to inflammation.
- Direct Trauma: A sudden impact or blow to the elbow can cause swelling and inflammation of the bursa.
- Infection: In rare cases, elbow bursitis may be caused by an infection, resulting in increased fluid production within the bursa and subsequent inflammation.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can predispose individuals to developing elbow bursitis.
Symptoms of Elbow Bursitis
The most common symptom of elbow bursitis is swelling at the tip of the elbow, often resembling a small lump or bump. Other symptoms may include:
- Pain: Discomfort or tenderness around the affected area, especially when pressure is applied or during movement.
- Redness and Warmth: The skin over the swollen bursa may appear red and feel warm to the touch.
- Limited Range of Motion: Inflammation of the bursa can restrict movement of the elbow, making it difficult to fully extend or bend the arm.
- Fluid Build-Up: In some cases, fluid may accumulate within the bursa, causing it to feel soft and squishy.
Treatment Options for Elbow Bursitis
When it comes to treating elbow bursitis, there’s a range of options available tailored to the severity and underlying cause of the condition. Typically, initial treatment focuses on reducing inflammation and alleviating discomfort. This may involve a combination of rest, ice therapy, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications to ease pain and swelling. In more persistent cases, a healthcare provider might recommend steroid injections directly into the affected area for targeted relief.
Physical therapy can also play a crucial role, helping to restore range of motion and strengthen the muscles surrounding the elbow joint. For cases where infection is suspected, antibiotic therapy may be necessary to clear the underlying cause. In rare instances where conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical intervention to remove the inflamed bursa may be considered as a last resort. Ultimately, the best course of treatment depends on individual factors, and consulting with a healthcare professional can guide towards the most effective approach for managing elbow bursitis.
The treatment approach for elbow bursitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Rest and Immobilization: Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition and resting the affected arm can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. Immobilizing the elbow with a splint or brace may also be recommended to prevent further irritation.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area several times a day can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Steroid Injections: In cases of severe inflammation, a corticosteroid injection directly into the bursa can provide rapid relief of symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: A structured rehabilitation program involving stretching and strengthening exercises may be prescribed to improve range of motion and prevent recurrence of elbow bursitis.
- Aspiration: If there is significant fluid buildup within the bursa, a procedure called aspiration may be performed to drain the excess fluid and alleviate pressure on the joint.
- Antibiotic Therapy: If elbow bursitis is caused by an underlying infection, a course of antibiotics may be necessary to treat the infection effectively.
In rare instances where conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there is evidence of an underlying infection, surgical intervention may be required to remove the inflamed bursa (bursectomy).
Prevention
Preventing elbow bursitis involves adopting proactive measures to minimize the risk of inflammation and injury to the bursa. One key aspect is avoiding activities that place repetitive strain on the elbow joint, such as prolonged leaning on hard surfaces or repetitive motions that stress the area. Using protective gear, like elbow pads or cushions during activities that pose a risk of trauma, such as contact sports or manual labor, can also provide an added layer of protection.
Maintaining good posture and ergonomic practices can help distribute weight evenly and reduce unnecessary strain on the elbow. Additionally, gradually progressing in new exercises or activities allows the body to adapt and build strength without overtaxing the joints. By incorporating these preventive strategies into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing elbow bursitis and maintain optimal joint health.
While elbow bursitis may not always be preventable, certain measures can help reduce the risk of developing this condition:
- Avoid Repetitive Strain: Take frequent breaks from activities that involve repetitive movements of the elbow, such as leaning on hard surfaces or resting the elbow on a desk for prolonged periods.
- Protective Gear: Wear elbow pads or cushioned supports during activities that pose a risk of elbow injury, such as contact sports or manual labor.
- Maintain Proper Posture: Practice good ergonomics and maintain proper posture to minimize stress on the elbow joint.
- Gradual Progression: When starting a new exercise or activity, gradually increase intensity and duration to allow the body to adapt and avoid overuse injuries.
In conclusion,
elbow bursitis is a common yet often overlooked condition that can cause significant discomfort and limit function of the affected arm. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage this condition effectively and prevent its recurrence. If you experience persistent elbow pain or swelling, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023