Emphysema: Unraveling the Impact of Chronic Lung Disease
Introduction
Emphysema,(also known as asthmatic) often referred to in the context of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), is a chronic and progressive lung condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. It’s a condition that gradually diminishes lung function and quality of life. In this article, we delve into what emphysema is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatments.
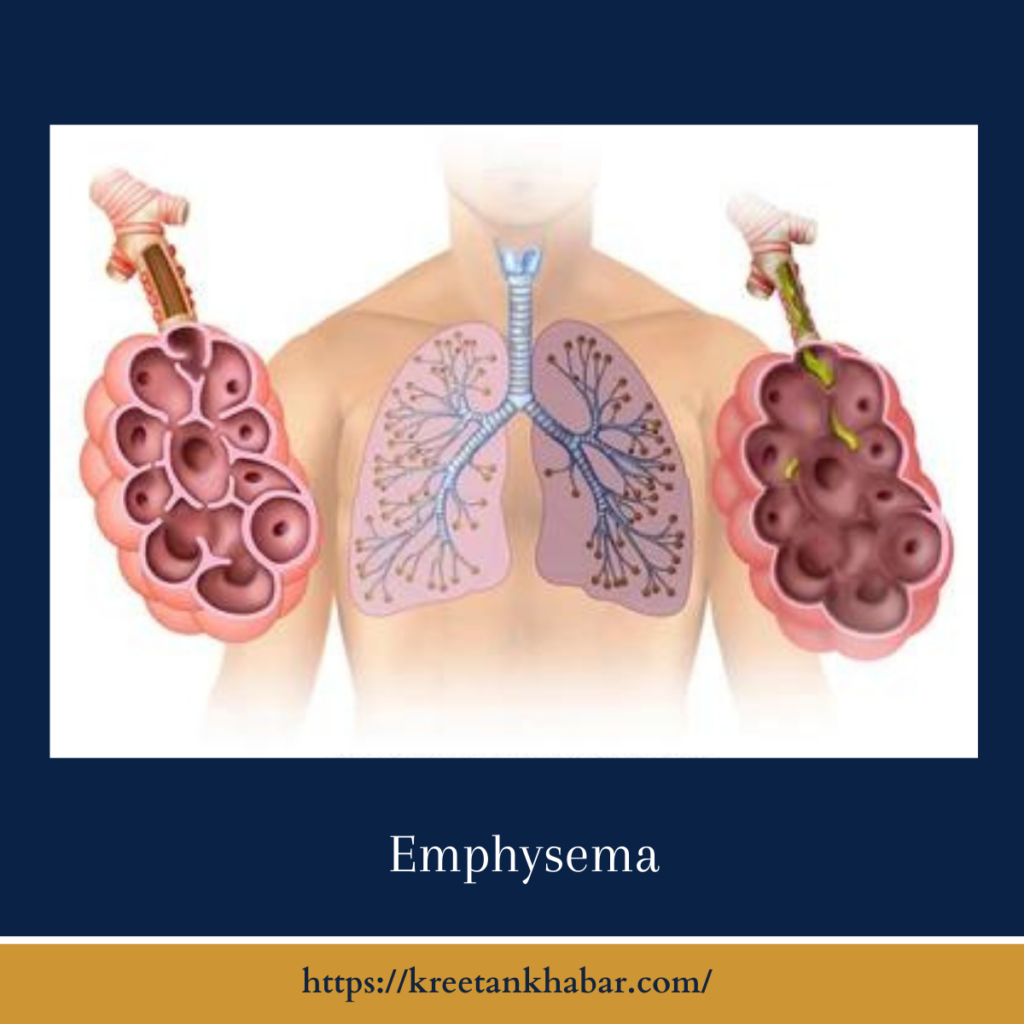
Understanding Emphysema
Emphysema is a type of COPD characterized by damage to the tiny air sacs in the lungs, known as alveoli. These air sacs play a crucial role in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body. asthmatic leads to a gradual breakdown of the alveoli, reducing the surface area for oxygen exchange and making it progressively more challenging to breathe.
Causes of Emphysema
- Smoking: The most common cause of asthmatic is cigarette smoking. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke lead to inflammation and damage in the air sacs over time.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to environmental irritants like air pollution, chemical fumes, or dust can contribute to the development of asthmatic, particularly in non-smokers.
- Genetic Factors: A rare genetic disorder known as alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can predispose individuals to asthmatic. This genetic factor accounts for a small percentage of emphysema cases.
Symptoms of Emphysema
The symptoms of emphysema usually develop gradually and become more pronounced as the disease progresses:
- Shortness of Breath: A persistent feeling of breathlessness, especially during physical activities, is one of the first noticeable symptoms.
- Chronic Cough: Individuals with asthmatic often develop a chronic cough, which may produce mucus.
- Wheezing: Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing, particularly during exhalation.
- Chest Tightness: A sense of tightness or pressure in the chest is a common discomfort in individuals with asthmatic.
- Fatigue: As the body struggles to obtain sufficient oxygen, fatigue and weakness can become pronounced.
- Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss is often seen in advanced cases of asthmatic.
Diagnosis of Emphysema
Diagnosing emphysema typically involves a combination of the following:
- Medical History: A detailed account of the patient’s medical history, including risk factors such as smoking and occupational exposures.
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may listen for abnormal breath sounds and evaluate the patient’s overall health.
- Lung Function Tests: These tests, such as spirometry, measure lung capacity and airflow. They are crucial in confirming the diagnosis and assessing disease severity.
- Imaging: Chest X-rays and CT scans can reveal characteristic signs of asthmatic, including hyperinflated lungs and damaged air sacs.
here are some key points about the diagnosis of emphysema:
- Medical History: The diagnosis of asthmatic typically begins with a thorough medical history. Patients are asked about their smoking history, exposure to environmental pollutants, and any family history of lung disease.
- Physical Examination: Healthcare providers conduct a physical examination, focusing on the patient’s respiratory system. They may listen to the patient’s chest for abnormal breath sounds, assess the patient’s overall health, and inquire about specific symptoms.
- Lung Function Tests: Lung function tests are crucial in diagnosing asthmatic. Spirometry is a common test that measures lung capacity and airflow. It assesses how well the lungs can inhale and exhale air. Patients are asked to take a deep breath and then exhale as forcefully and completely as possible into a device called a spirometer. This test helps confirm the diagnosis and assess the severity of the disease.
- Imaging: Chest X-rays and CT (computed tomography) scans are often used to visualize the lungs. They can reveal characteristic signs of asthmatic, including hyperinflated lungs and damaged air sacs.
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Test: An ABG test measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, providing valuable information about how well the lungs are oxygenating the body.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for specific biomarkers related to lung inflammation and function, such as C-reactive protein or alpha-1 antitrypsin levels.
- Differential Diagnosis: asthmatic symptoms can overlap with other respiratory conditions like chronic bronchitis, asthma, or bronchiectasis. A healthcare provider may need to differentiate asthmatic from these conditions through careful assessment and additional tests.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG may be performed to evaluate the heart’s electrical activity, as asthmatic can sometimes affect the heart due to chronic oxygen deficiencies.
- Pulmonary Function Tests (PFTs): Beyond spirometry, PFTs may include more detailed assessments of lung function, such as lung volumes and diffusing capacity. These tests can provide a comprehensive understanding of how asthmatic affects lung function.
- Consultation with a Pulmonologist: In complex cases or when a definitive diagnosis is elusive, patients may be referred to a pulmonologist, a specialist in lung diseases, who can provide expert evaluation and conduct additional diagnostic tests.
In cases of suspected asthmatic, the combination of a detailed medical history, physical examination, lung function tests, and imaging studies plays a critical role in achieving an accurate diagnosis. Early diagnosis is vital in managing emphysema and preventing further lung damage.
Treatment Options for Emphysema
While emphysema is a chronic condition with no cure, several treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Smoking Cessation: If the individual smokes, quitting is the most crucial step to slow the progression of asthmatic.
- Medications: Bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids can help open the airways and reduce inflammation, making breathing easier.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen can improve oxygen levels in the blood, alleviating shortness of breath.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: These programs include exercise, breathing techniques, and education to help individuals manage their condition and improve physical endurance.
- Surgery: In severe cases, lung volume reduction surgery or lung transplantation may be considered.
here are some key points about the treatment of asthmatic:
- Smoking Cessation: The most critical step in managing asthmatic is quitting smoking. Smoking is the leading cause of the condition, and stopping can significantly slow its progression.
- Medications: Several types of medications are used to manage asthmatic symptoms:
- Bronchodilators: These drugs help relax the airway muscles and open the air passages, making it easier to breathe. They come in short-acting and long-acting forms.
- Inhaled Corticosteroids: These medications reduce airway inflammation and may be prescribed in combination with bronchodilators.
- Phosphodiesterase-4 Inhibitors: These drugs can reduce inflammation and relax the airways.
- Oxygen Therapy: In cases of severe emphysema and low blood oxygen levels, supplemental oxygen therapy is often prescribed. Oxygen is provided through nasal cannulas or masks to improve oxygen saturation in the blood and alleviate breathlessness.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Pulmonary rehabilitation programs are designed to improve the patient’s overall well-being. These programs typically include:
- Exercise training to increase physical endurance.
- Breathing exercises to improve lung function.
- Education on disease management, medications, and nutrition.
- Psychological support and counseling to cope with the emotional aspects of the disease.
- Surgery: In select cases, surgical interventions may be considered for severe emphysema:
- Lung Volume Reduction Surgery (LVRS): This procedure removes damaged lung tissue to improve the function of the remaining healthier lung tissue. It can enhance lung function and overall quality of life.
- Lung Transplant: For individuals with end-stage emphysema, a lung transplant may be necessary.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed when emphysema exacerbations are triggered by bacterial infections.
- Vaccinations: Patients with emphysema are encouraged to stay up-to-date with vaccinations, particularly the annual influenza vaccine and the pneumococcal vaccine. These vaccinations can help prevent respiratory infections that can exacerbate emphysema symptoms.
- Nutritional Support: Maintaining a healthy diet can help individuals with emphysema manage their condition. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to develop a dietary plan that meets specific needs.
- Supportive Care: Managing emphysema often requires lifestyle adjustments, including:
- Avoiding exposure to environmental pollutants and irritants.
- Implementing energy-saving techniques to conserve energy and reduce fatigue.
- Employing breathing techniques, such as pursed-lip breathing, to make exhalation more effective.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to monitor the progression of emphysema, assess treatment effectiveness, and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Treatment of emphysema is a comprehensive approach that combines medications, therapies, lifestyle changes, and support to improve symptoms, enhance lung function, and provide a better quality of life for individuals living with this chronic lung condition.
Conclusion
Emphysema is a debilitating lung disease that impacts the lives of countless individuals. While there is no cure, early diagnosis, lifestyle modifications, and medical treatments can significantly slow down its progression and improve the quality of life for those affected. Awareness of risk factors, particularly smoking, is vital in preventing the development of this condition, and timely medical intervention is key to managing its effects.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023