Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis: Insights into the Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Introduction:
Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis (EKC) stands as a notable eye infection, capturing attention for its highly contagious nature and impact on ocular health. This article aims to delve into the various facets of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Understanding EKC:
- Viral Culprit:
- Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis is primarily caused by adenoviruses, particularly types 8, 19, and 37. Adenoviruses are notorious for their ability to cause a spectrum of respiratory and ocular infections, with EKC being a distinctive ocular manifestation.
- Highly Contagious:
- Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis is infamous for its contagious nature, often spreading through direct contact with infected ocular secretions. Crowded places, such as schools, hospitals, and swimming pools, serve as fertile grounds for transmission.
Symptoms of EKC:
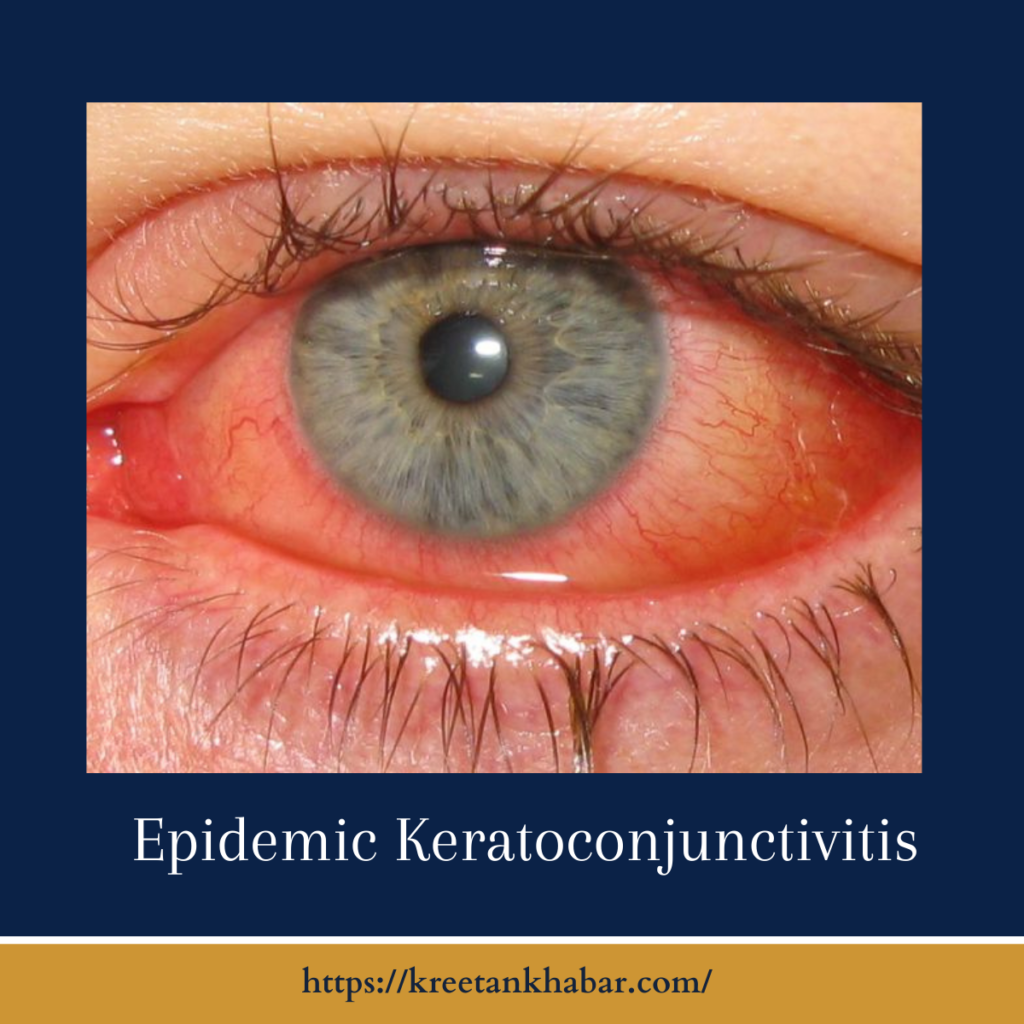
Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis (EKC) manifests a distinctive set of symptoms that can significantly impact ocular health. Individuals with EKC often experience sudden redness and irritation in the eyes, a hallmark sign of the infection. The eyes may produce a watery discharge, contributing to the contagious nature of the virus. Photophobia, or sensitivity to light, is another common symptom, prompting affected individuals to seek relief in dimly lit environments.
A pervasive sensation of having a foreign body in the eye, accompanied by itching or a gritty feeling, adds to the discomfort associated with EKC. These symptoms can escalate rapidly, and individuals may find relief through supportive measures such as cool compresses and lubricating eye drops. As EKC is highly contagious, practicing good hygiene and taking precautionary measures to avoid spreading the virus are crucial aspects of managing and mitigating the impact of this eye infection.
- Redness and Irritation:
- One of the hallmark symptoms of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis is the sudden onset of redness and irritation in the eyes. This can progress rapidly, leading to significant discomfort.
- Watery Discharge:
- Watery discharge from the eyes is a common symptom, contributing to the contagiousness of the infection. The virus thrives in the fluid produced by the eyes, facilitating its spread.
- Photophobia:
- Individuals with Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis often experience sensitivity to light, known as photophobia. This adds to the discomfort and prompts affected individuals to seek relief in dimly lit environments.
- Foreign Body Sensation:
- A pervasive sensation of having a foreign body in the eye is characteristic of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis. This sensation may be accompanied by itching or a gritty feeling.
Points of symptoms:
- Redness and Irritation:
- One of the primary symptoms of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis (EKC) is the sudden onset of redness in the eyes, accompanied by noticeable irritation.
- Watery Discharge:
- Individuals with EKC often experience a watery discharge from the eyes, contributing to the contagious nature of the infection as the virus thrives in ocular secretions.
- Photophobia (Light Sensitivity):
- Photophobia, or sensitivity to light, is a common symptom of EKC, prompting affected individuals to seek relief in dimly lit environments.
- Foreign Body Sensation:
- A prevalent and uncomfortable symptom is the sensation of having a foreign body in the eye, often accompanied by itching or a gritty feeling.
- Gritty Feeling:
- Individuals may describe a gritty feeling in the eyes, further adding to the discomfort associated with EKC.
- Rapid Onset:
- The symptoms of EKC can escalate rapidly, with individuals experiencing a sudden onset of redness, irritation, and other associated discomfort.
- Tearing:
- Excessive tearing or tearing unrelated to emotional responses is a common symptom, contributing to the contagious spread of the virus.
- Itching:
- Itching of the eyes is another symptom that individuals with EKC may experience, intensifying the overall discomfort.
- Conjunctival Swelling:
- Swelling of the conjunctiva, the thin membrane covering the white part of the eye, can occur, further contributing to redness and discomfort.
- Discomfort in Bright Light:
- Bright light exacerbates the discomfort associated with EKC, emphasizing the need for individuals to seek relief in subdued lighting conditions.
- Blurred Vision (in severe cases):
- In severe cases, EKC may lead to blurred vision, necessitating prompt medical attention to manage complications and prevent further impairment.
- Symptoms Vary in Intensity:
- It’s important to note that the intensity of symptoms can vary among individuals, ranging from mild irritation to more severe discomfort and vision issues, underscoring the diversity in the clinical presentation of EKC.
Management and Treatment:
- Supportive Care:
- As EKC is viral in nature, no specific antiviral medications target the adenovirus causing the infection. Management primarily involves supportive care to alleviate symptoms.
- Cool Compresses:
- Cool compresses can provide relief from the warmth and discomfort associated with Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis. Applying a clean, cool cloth to the eyes can soothe inflammation.
- Artificial Tears:
- Lubricating eye drops or artificial tears help alleviate dryness and maintain eye moisture. This is particularly important in managing the irritation caused by Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis.
- Avoidance of Contact Lenses:
- Individuals with EKC are often advised to discontinue the use of contact lenses during the infection. This helps prevent further irritation and facilitates the healing process.
- Hygiene Practices:
- Practicing good hygiene is paramount in controlling the spread of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis. Frequent handwashing, avoiding shared towels, and refraining from touching the eyes can help contain the virus.
- Isolation Measures:
- Infected individuals should exercise caution to prevent spreading the virus. Isolation measures, such as avoiding close contact with others, especially in communal settings, are essential.
Conclusion:
Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis, with its swift transmission and impact on ocular health, warrants a combination of preventive measures, supportive care, and vigilance. As researchers continue to explore potential antiviral treatments, the emphasis remains on public awareness, hygiene practices, and prompt management to curb the contagious spread of EKC and protect ocular well-being.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023