Gangrene: Causes, Types, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction
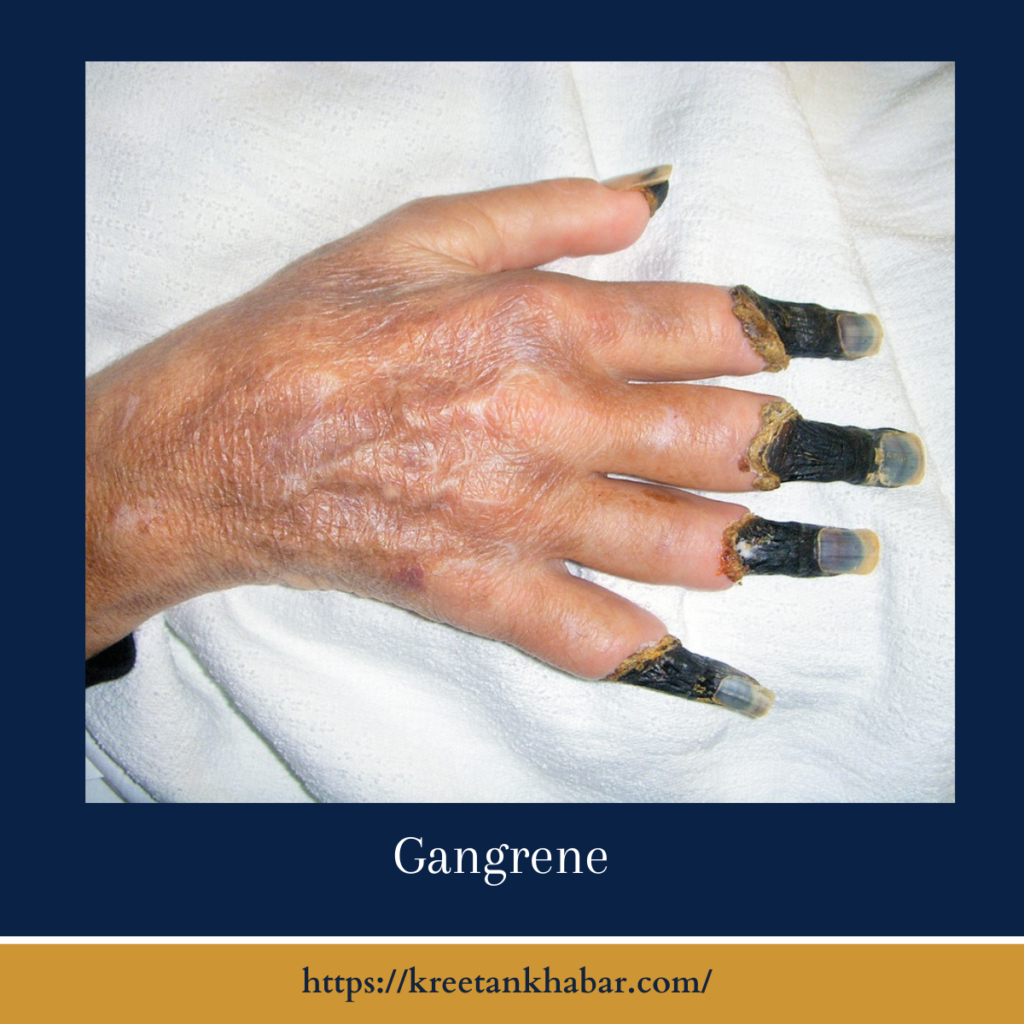
Gangrene (also known as a blight) is a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by the death of body tissue, typically as a result of insufficient blood supply or bacterial infection. It is a serious medical concern that demands immediate attention and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the causes, types, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures associated with gangrene.
Understanding Gangrene
Gangrene is often a consequence of necrosis, the premature death of cells and tissues. It can occur in various forms, each with distinct causes and characteristics. The primary types of blight include dry gangrene, wet gangrene, and gas gangrene, each with unique attributes and risks.
Common Causes of Gangrene
- Poor Circulation: Reduced blood flow, often due to underlying conditions like atherosclerosis, diabetes, or peripheral artery disease, can lead to tissue damage and blight.
- Infection: Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Clostridium perfringens (in gas gangrene) or Streptococcus (in necrotizing fasciitis), can result in blight.
- Trauma: Severe injuries, frostbite, or crushing injuries can compromise blood flow to an area, initiating the development of blight.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of blight.
- Smoking: Smoking impairs circulation and increases the risk of peripheral artery disease, which can lead to blight.
Symptoms of Gangrene
Gangrene manifests differently based on the type, but common symptoms include:
- Discoloration: Tissues affected by gangrene may change color, often becoming black, brown, or greenish.
- Pain: Initially, there may be severe pain, but as the tissue dies, the area can become numb.
- Swelling and Blisters: Swelling and the formation of fluid-filled blisters may occur in wet blight.
- Foul Odor: Gas gangrene produces a distinctive, foul odor due to the release of toxins by bacteria.
- Fever and Chills: In cases of infection-related blight, fever, chills, and a general sense of illness may be present.
Treatment Options
- Surgical Debridement: To remove dead or infected tissue, surgical debridement is performed, which can be a life-saving intervention.
- Antibiotics: In cases of infection-related blight, antibiotics are administered to combat the bacterial infection.
- Amputation: In severe cases where blight has advanced significantly, amputation may be necessary to prevent the spread of the condition.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: This therapy involves inhaling pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which can promote tissue healing by increasing oxygen delivery.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential, including cleaning, dressing changes, and keeping the area sterile to prevent infection.
Treatment Options for Gangrene: Key Points
- Surgical Debridement: Surgical debridement is a crucial treatment for blight. It involves the surgical removal of dead or infected tissue to stop the spread of the condition and promote healing.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are used to treat infection-related blight. They target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection, preventing its further spread.
- Amputation: In severe cases where gangrene has advanced extensively and there is no other viable option, amputation may be necessary. It involves the removal of the affected limb or tissue to save the patient’s life and prevent the condition from spreading.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a specialized treatment that involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber. It increases oxygen delivery to damaged tissues, promoting healing and fighting infection. HBOT is particularly beneficial for specific types of blight, such as diabetic foot ulcers.
- Wound Care: Proper wound care is essential for managing blight. This includes cleaning and dressing the affected area, keeping it sterile, and preventing further infection.
- Pain Management: Pain management may be necessary, especially in cases of significant pain associated with blight. Analgesics or other pain-relief techniques can be administered.
- Revascularization: In cases where poor blood supply is the primary cause of gangrene, revascularization procedures, such as angioplasty or bypass surgery, may be performed to restore blood flow to the affected area and promote tissue healing.
- Supportive Care: Patients with gangrene often require supportive care, including nutritional support, hydration, and addressing any underlying health conditions that contributed to the condition.
- Tissue Growth Stimulants: Certain medications or therapies may be used to stimulate tissue growth and regeneration in areas affected by blight.
- Regular Follow-Up: Patients who have undergone treatment for gangrene should maintain regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare providers to monitor the healing process and address any concerns or complications.
- Adjunct Therapies: Complementary therapies like physical therapy or occupational therapy may be necessary to help patients regain mobility and independence after treatment.
- Psychological Support: Coping with the physical and emotional challenges of gangrene can be demanding. Psychological support, including counseling or support groups, can be beneficial for patients and their families.
The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of gangrene, the patient’s overall health, and the specific circumstances. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical in managing blight and preventing its complications.
Preventive Measures
- Manage Underlying Conditions: Controlling conditions like diabetes and peripheral artery disease is crucial to reduce the risk of blight.
- Wound Care: Properly care for wounds, even minor ones, to prevent infection. Clean and dress wounds promptly.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cessation improves circulation and reduces the risk of peripheral artery disease.
- Hygiene: Practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of bacterial infections that can lead to blight.
- Regular Checkups: Regular medical checkups can help detect underlying conditions and circulatory problems early.
Preventive Measures for Gangrene: Key Points
- Manage Underlying Health Conditions: Control conditions like diabetes, peripheral artery disease, and atherosclerosis, as these are significant risk factors for gangrene. Regular medical checkups are crucial for early detection and management.
- Wound Care: Properly clean and care for any wounds, cuts, or injuries, no matter how minor. Keep them clean, dry, and covered to prevent infection.
- Hygiene: Practice good hygiene, including regular handwashing and keeping your body clean. This reduces the risk of bacterial infections that can lead to gangrene.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for peripheral artery disease and poor circulation, increasing the likelihood of gangrene. Quitting smoking improves circulation and reduces this risk.
- Foot Care: If you have diabetes, pay special attention to foot care. Check your feet daily for any signs of injury or infection, and promptly address any issues.
- Adequate Nutrition: Maintain a well-balanced diet to support overall health and tissue healing. Proper nutrition is essential for preventing gangrene.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to maintain good circulation and overall cardiovascular health. Exercise is particularly important for individuals at risk of gangrene.
- Monitor Skin Changes: Keep an eye on your skin for any color changes, unusual sensations, or the development of pressure sores, especially if you have limited mobility.
- Stay Hydrated: Ensure you are adequately hydrated, as dehydration can lead to complications, including poor circulation, which can contribute to gangrene.
- Peripheral Awareness: If you have peripheral artery disease, be aware of signs like cold extremities, pain, or numbness. Seek prompt medical attention if you notice any unusual symptoms.
Preventive measures are vital for reducing the risk of gangrene, particularly for individuals with underlying health conditions or risk factors. A combination of good hygiene, wound care, and a healthy lifestyle can go a long way in preventing this serious medical condition.
Conclusion
Gangrene is a serious medical condition that requires immediate attention and treatment. Understanding its causes, types, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for early intervention. Prevention is equally vital, particularly for individuals with underlying health issues, as it can significantly reduce the risk of gangrene and its potentially devastating consequences.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023