Glenoid Labrum Tears: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
The shoulder joint is a marvel of intricate structures that enable a wide range of motion and functionality. Among these structures, the glenoid labrum plays a crucial role in stabilizing the shoulder and facilitating smooth movement. However, injuries such as glenoid labrum tears can significantly impact shoulder function and quality of life. Let’s delve into the details of this condition, from its causes and symptoms to available treatment options.
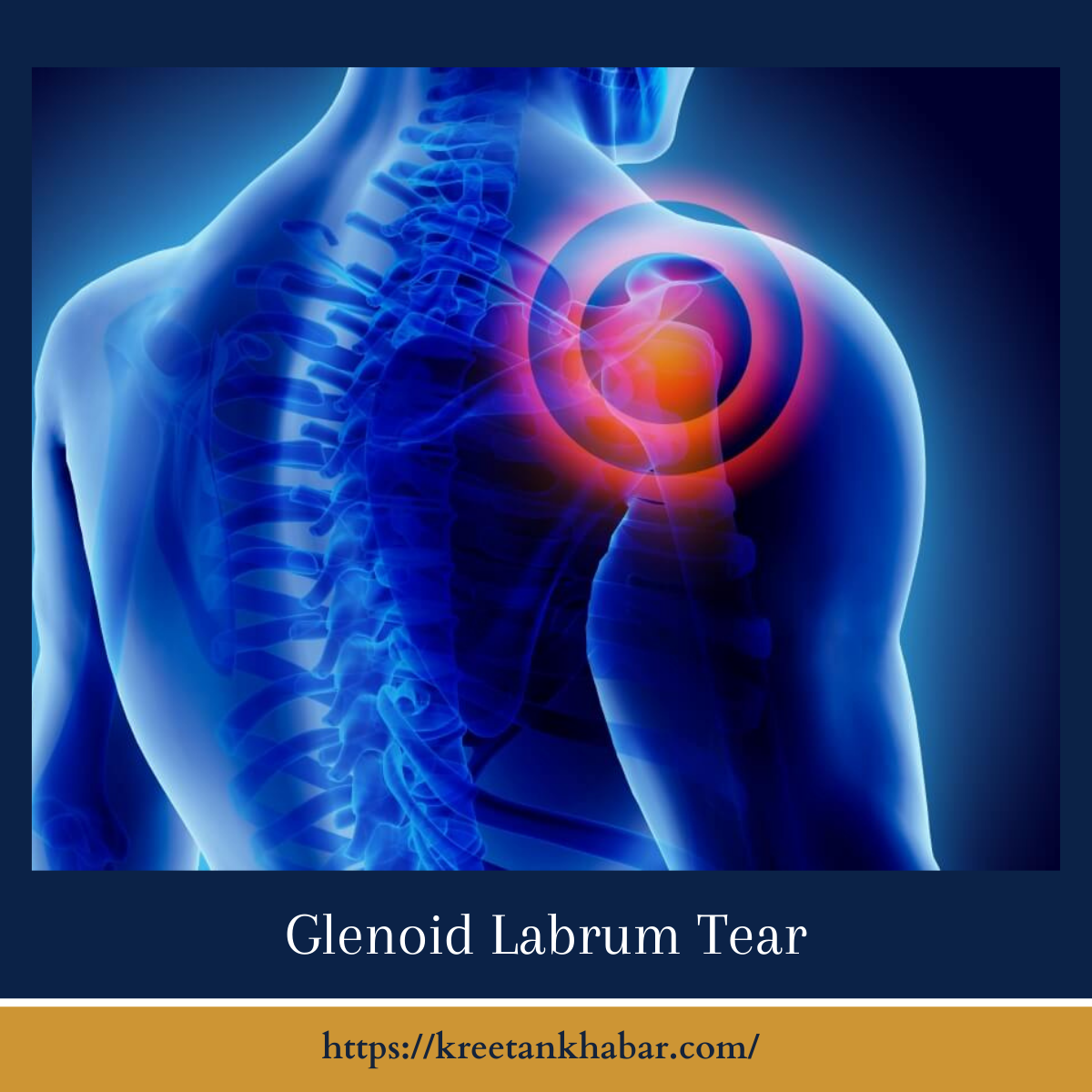
Understanding Glenoid Labrum Tears
The glenoid labrum tears is a ring of fibrous cartilage that surrounds the shallow socket of the shoulder joint, known as the glenoid labrum tears. Its main function is to deepen the socket, providing stability to the joint and enhancing the fit of the humeral head (the ball of the upper arm bone) within the shoulder socket. A tear in the glenoid labrum can occur due to various factors, including:
- Traumatic Injury: Direct trauma to the shoulder, such as a fall onto an outstretched arm or a forceful impact, can lead to a tear in the glenoid labrum tears. This type of injury is common among athletes involved in contact sports or activities that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as baseball, volleyball, or swimming.
- Repetitive Stress: Overuse or repetitive stress on the shoulder joint, particularly in activities that involve overhead motions or lifting heavy objects, can gradually wear down the glenoid labrum tears over time, increasing the risk of glenoid labrum tears. This is often seen in athletes or individuals with physically demanding occupations.
- Anatomical Abnormalities: Some individuals may have anatomical variations in the shape or structure of the shoulder joint, predisposing them to glenoid labrum tears. Conditions such as shoulder instability or shoulder dysplasia can contribute to increased strain on the glenoid labrum tears and make it more susceptible to injury.
Recognizing Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. Individuals with this condition often experience persistent shoulder pain, which may worsen with certain movements or activities. Alongside pain, there’s often a noticeable decrease in the range of motion of the shoulder joint, making tasks like reaching overhead or behind the back challenging and uncomfortable.
Some individuals also report sensations of catching, locking, or popping in the shoulder joint, accompanied by discomfort or instability. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and quality of life, prompting individuals to seek medical evaluation and intervention. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if experiencing persistent shoulder pain or any of these symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage and facilitate effective rehabilitation.
The symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear can vary depending on the severity and location of the tear. Common signs and symptoms may include:
- Shoulder Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the shoulder joint, particularly with certain movements or activities.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Difficulty or stiffness when moving the shoulder, especially when reaching overhead or behind the back.
- Catching or Popping Sensation: Sensations of catching, locking, or popping in the shoulder joint, often accompanied by discomfort.
- Shoulder Instability: Feeling of looseness or instability in the shoulder, as if it may “pop out” of place, especially during certain movements or positions.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent shoulder pain or any of these symptoms, as prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing further damage and restoring shoulder function.
- Shoulder Pain: One of the hallmark symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear is persistent shoulder pain. This pain may vary in intensity and can be felt deep within the shoulder joint. It often worsens with specific movements or activities that involve the shoulder, such as lifting objects overhead or reaching behind the back.
- Clicking or Popping Sensation: Individuals with a glenoid labrum tear may experience a clicking, popping, or catching sensation in the shoulder joint, particularly during certain movements. This sensation is often accompanied by discomfort and may indicate instability or impingement within the joint.
- Decreased Range of Motion: A glenoid labrum tear can lead to a noticeable decrease in the range of motion of the affected shoulder. Individuals may find it challenging to perform tasks that require full shoulder movement, such as reaching overhead, rotating the arm, or lifting objects.
- Shoulder Instability: Some individuals may experience feelings of shoulder instability or a sensation that the shoulder may “give way” or dislocate. This sensation is often more pronounced during activities that place stress on the shoulder joint, such as throwing or swinging motions.
- Shoulder Weakness: In addition to pain and instability, individuals with a glenoid labrum tear may notice weakness in the affected shoulder. This weakness can affect the ability to perform daily activities and may be particularly noticeable during tasks that require lifting or carrying objects.
- Discomfort with Specific Movements: Certain movements or positions of the shoulder joint may exacerbate symptoms of a glenoid labrum tear. For example, individuals may experience increased pain or discomfort when raising the arm overhead, reaching across the body, or performing rotational movements.
- Night Pain: Some individuals with a glenoid labrum tear may experience increased shoulder pain at night, particularly when lying on the affected side. This nocturnal pain can disrupt sleep and may contribute to overall discomfort and decreased quality of life.
- Grinding Sensation: In some cases, individuals with a glenoid labrum tear may experience a grinding sensation within the shoulder joint, particularly during movements that involve rotation or abduction of the arm. This sensation may indicate friction or impingement within the joint due to the tear.
- Tenderness to Touch: The area around the shoulder joint may be tender to the touch in individuals with a glenoid labrum tear. Palpation of the shoulder may elicit pain or discomfort, particularly over the front or top of the shoulder where the tear is located.
- Functional Limitations: Overall, a glenoid labrum tear can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and participate in sports or recreational pursuits. The combination of pain, instability, weakness, and decreased range of motion can lead to functional limitations and may require intervention to restore shoulder health and function.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for a glenoid labrum tear depends on several factors, including the severity of the tear, the individual’s age, activity level, and overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Conservative Management: In cases of mild to moderate glenoid labrum tears, conservative treatments such as rest, activity modification, physical therapy, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be sufficient to relieve symptoms and improve shoulder function.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids into the shoulder joint can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with a glenoid labrum tear. However, these injections are typically used as a temporary measure and may not provide long-term relief.
- Surgical Intervention: For more severe or symptomatic glenoid labrum tears that do not respond to conservative measures, surgical intervention may be necessary. Arthroscopic surgery, a minimally invasive procedure, is often performed to repair or reconstruct the torn glenoid labrum tears, restore stability to the shoulder joint, and alleviate symptoms.
- Rehabilitation and Recovery: Following surgical repair, rehabilitation plays a critical role in restoring shoulder strength, flexibility, and function. Physical therapy exercises aimed at improving range of motion, strengthening the surrounding muscles, and enhancing shoulder stability are typically prescribed to aid in recovery.
Conclusion
Glenoid labrum tears can significantly impact shoulder function and quality of life, particularly in individuals involved in sports or occupations that place repetitive stress on the shoulder joint. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent injury, seek timely medical attention if symptoms arise, and undergo appropriate treatment to restore shoulder health and function. Working closely with healthcare professionals, including orthopedic surgeons and physical therapists, can help individuals navigate the journey toward recovery and regain confidence in their shoulder’s strength and stability.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023