Hyperhidrosis: Understanding Excessive Sweating and its Impact
Introduction
Hyperhidrosis (also known as sweating) is a medical condition characterized by excessive sweating that goes beyond what is necessary to regulate body temperature. This condition affects millions of people worldwide and can have a profound impact on a person’s daily life. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and management of sweating to shed light on this often-overlooked health issue.
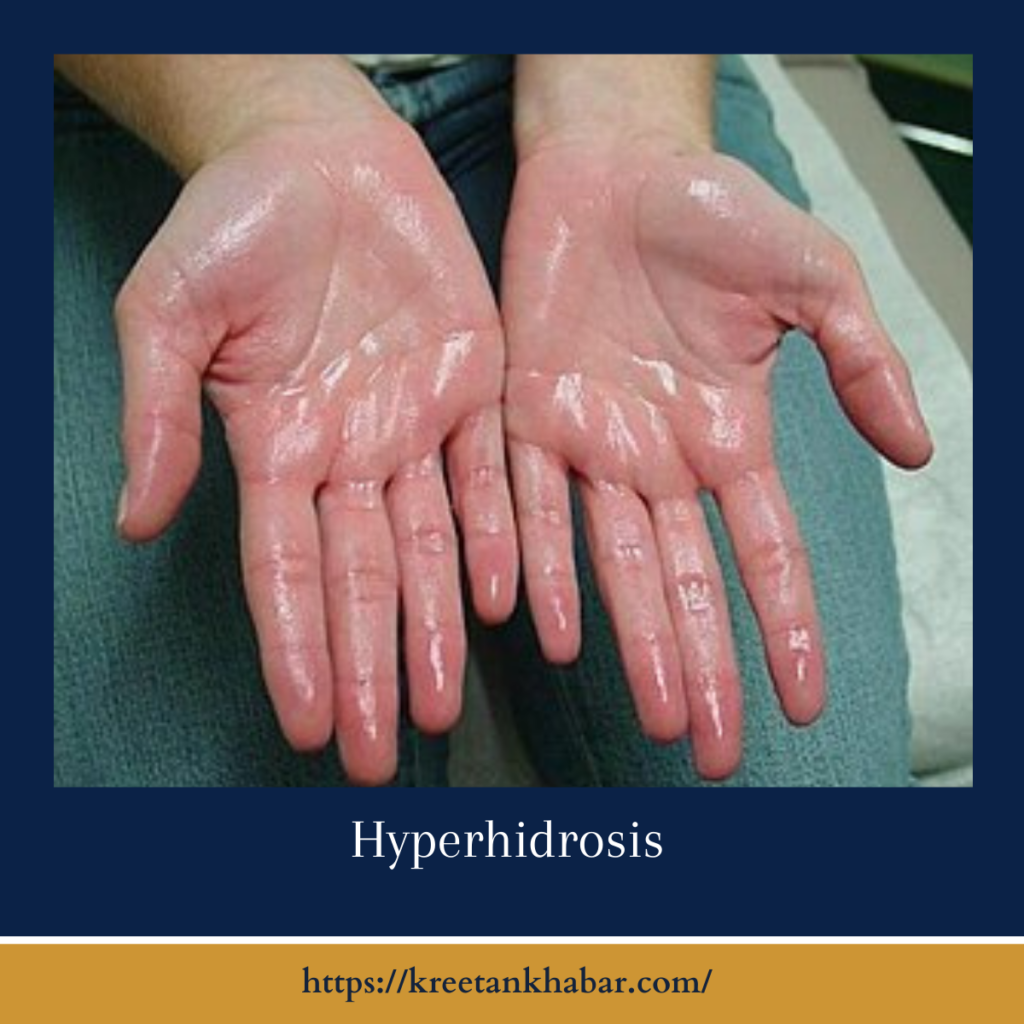
Understanding Hyperhidrosis
- What is Hyperhidrosis?: sweating, also known as diaphoresis, is a condition in which individuals experience excessive sweating, often in specific areas of the body, such as the underarms (axillary hyperhidrosis), palms (palmar hyperhidrosis), or feet (plantar hyperhidrosis).
- Primary vs. Secondary Hyperhidrosis: sweating can be categorized into primary (essential) and secondary forms. Primary hyperhidrosis usually starts in childhood or adolescence and has no underlying medical cause. Secondary hyperhidrosis is associated with an underlying medical condition or medication side effects.
Causes of Hyperhidrosis
- Overactive Sweat Glands: Primary sweating is primarily attributed to overactivity of the sweat glands, which respond excessively to stimuli like heat, emotions, or stress.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Secondary sweating can be caused by medical conditions such as hyperthyroidism, menopause, diabetes, or certain infections.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, and antipyretics, can lead to excessive sweating as a side effect.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menopause, or puberty can trigger excessive sweating in some individuals.
Symptoms of Hyperhidrosis
The symptoms of sweating can vary depending on the severity and affected areas but generally include:
- Visible Sweat Stains: Excessive sweating can result in visible sweat stains on clothing, which can be embarrassing and affect self-confidence.
- Social and Emotional Impact: Individuals with sweating may experience anxiety, embarrassment, and social withdrawal due to their condition.
- Skin Issues: Prolonged moisture can lead to skin problems like fungal infections, rashes, or peeling in the affected areas.
- Odor: The combination of sweat and bacteria can lead to body odor, which can be more pronounced in individuals with sweating.
- Discomfort: Wet or damp hands, feet, or underarms can be uncomfortable and interfere with daily activities.
here are some key points about the symptoms of hyperhidrosis:
- Excessive Sweating: The hallmark symptom of sweating is excessive sweating that goes beyond what is necessary to regulate body temperature.
- Localized Sweating: sweating typically affects specific areas of the body, commonly the:
- Underarms (axillary hyperhidrosis)
- Palms of the hands (palmar hyperhidrosis)
- Soles of the feet (plantar hyperhidrosis)
- Face, particularly the forehead and upper lip (craniofacial hyperhidrosis)
- Persistent Moisture: Individuals with sweating often experience persistent moisture or wetness in the affected areas, even in the absence of heat or physical exertion.
- Visible Sweat Stains: Excessive sweating can lead to noticeable sweat stains on clothing, which can be embarrassing and inconvenient.
- Frequent Skin Issues: Prolonged moisture from sweating can increase the risk of skin problems, including:
- Fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot or jock itch
- Blisters or maceration (softening of the skin due to excessive moisture)
- Peeling or wrinkling of the skin in affected areas
- Odor: The combination of sweat and bacteria can result in body odor, which may be more pronounced in individuals with sweating.
- Social and Emotional Impact: sweating can have a significant emotional and social impact, leading to anxiety, embarrassment, and a reluctance to participate in social activities.
- Discomfort: Wet or damp hands, feet, or underarms can be physically uncomfortable and interfere with daily activities such as writing, gripping objects, or shaking hands.
- Staining of Personal Items: Excessive sweating may lead to the staining or deterioration of personal items like shoes, gloves, or electronics.
- Interference with Daily Life: Hyperhidrosis can interfere with daily tasks and personal interactions, making it challenging to maintain comfort and confidence.
- Symptom Triggers: Sweating episodes can be triggered or exacerbated by various factors, including heat, stress, anxiety, spicy foods, caffeine, or physical activity.
- Nocturnal Symptoms: Some individuals with sweating may experience excessive sweating during sleep, leading to damp bedding and disrupted sleep patterns.
Recognizing the symptoms of sweating is essential for diagnosis and effective management. If you suspect you have sweating or experience any of these symptoms, consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the underlying cause and explore appropriate treatment options to improve your quality of life.
Management of Hyperhidrosis
- Topical Antiperspirants: Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can help reduce sweating when applied to the affected areas.
- Iontophoresis: This non-invasive treatment involves applying a low electrical current to the affected area, usually the hands or feet, to block sweat gland activity.
- Oral Medications: In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications like anticholinergics or antiperspirant pills to reduce sweating.
- Botox Injections: Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections can temporarily block the nerves that stimulate sweat glands, providing relief for several months.
- Surgical Options: For severe cases, surgical interventions like sympathectomy (nerve surgery) or sweat gland removal may be considered.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Wearing breathable clothing, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and avoiding triggers can help manage sweating.
- Alternative Therapies: Some individuals explore alternative therapies such as acupuncture or herbal remedies, but their effectiveness varies.
- Emotional Support: Seeking emotional support through counseling or support groups can help individuals cope with the social and emotional aspects of hyperhidrosis.
here are some key points about the management of hyperhidrosis:
- Topical Antiperspirants:
- Over-the-counter or prescription-strength antiperspirants containing aluminum chloride can be applied to the affected areas (e.g., underarms, hands, feet) to reduce sweat production.
- Iontophoresis:
- This non-invasive treatment involves using a device to pass a low electrical current through the skin’s surface in affected areas (typically hands or feet). It temporarily blocks sweat gland activity and can be performed at home.
- Oral Medications:
- In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe anticholinergic medications like glycopyrrolate to reduce sweating. These medications are usually considered when other treatments are ineffective or cause side effects.
- Botox Injections:
- Botulinum toxin (Botox) injections are a common treatment for axillary hyperhidrosis (excessive underarm sweating). Botox blocks the nerves that stimulate sweat glands and provides relief for several months before requiring re-treatment.
- Prescription Medications:
- Medications like antiperspirant pills (e.g., glycopyrrolate) can be prescribed for generalized hyperhidrosis. They work by reducing overall sweat production but may have side effects.
- Surgical Options:
- For severe cases or when other treatments fail, surgical interventions may be considered:
- Sympathectomy: A surgical procedure that involves cutting or clamping the sympathetic nerves responsible for excessive sweating.
- Sweat Gland Removal: Surgical removal of sweat glands in the affected area (e.g., axillary sweat gland removal) can provide long-lasting relief but may result in scarring.
- For severe cases or when other treatments fail, surgical interventions may be considered:
- Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Wearing moisture-wicking clothing made of breathable fabrics can help manage sweat and reduce discomfort.
- Avoiding triggers such as spicy foods, caffeine, and stressful situations can minimize sweating episodes.
- Emotional Support:
- Coping with hyperhidrosis may require emotional support through counseling or participation in support groups. Sharing experiences and strategies with others facing similar challenges can be empowering.
- Alternative Therapies:
- Some individuals explore alternative therapies like acupuncture, biofeedback, or hypnotherapy as complementary approaches to manage stress and reduce sweating. Results vary, and these methods may not be effective for everyone.
- Maintaining Good Hygiene:
- Practicing good personal hygiene, including frequent washing and using antibacterial soaps, can help manage odor associated with excessive sweating.
- Regular Follow-Up:
- Individuals receiving medical treatments for hyperhidrosis should have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare providers to assess treatment effectiveness and address any concerns or side effects.
- Combination Therapies:
- In some cases, a combination of treatments may be the most effective approach to managing hyperhidrosis. This can be tailored to the individual’s specific needs and preferences.
Effective management of hyperhidrosis often requires a personalized approach based on the type and severity of the condition. Consulting with a healthcare provider or dermatologist is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan for individuals experiencing excessive sweating, allowing them to regain comfort and confidence in their daily lives.
Conclusion
Hyperhidrosis is a challenging condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Fortunately, various treatment options are available to help manage excessive sweating, allowing individuals to regain confidence and comfort in their daily lives. If you suspect you have hyperhidrosis, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023