Kidney Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Introduction
Kidney infections,(also known as pyelonephritis) medically known as pyelonephritis, are a serious type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that can affect one or both kidneys. While kidney infections are less common than lower UTIs like bladder infections, they can cause severe complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for kidney infections.
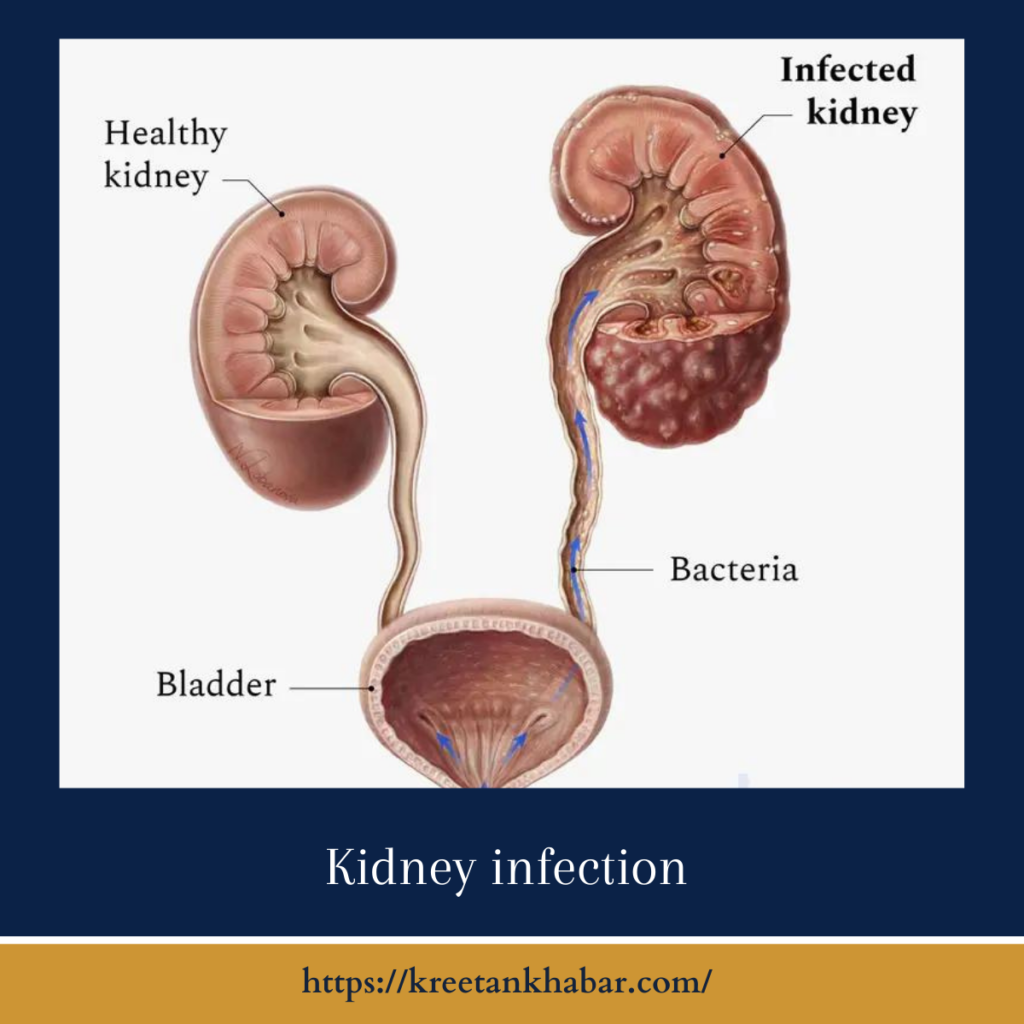
Causes of Kidney Infections
pyelonephritis typically occur when bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urinary tract and travel up to the kidneys. Several factors can increase the risk of kidney infections:
- Untreated UTIs: A urinary tract infection that is not promptly treated can progress to a kidney infection.
- Urinary Tract Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract, such as kidney stones or urinary obstructions, can create conditions favorable for infection.
- Catheter Use: Using a urinary catheter increases the risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract, potentially leading to a kidney infection.
- Gender: Women are more prone to UTIs due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
- Age: Infants, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk of pyelonephritis.
Symptoms of Kidney Infections
Recognizing the symptoms of a kidney infection is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Fever and Chills: A high fever is a hallmark sign of a kidney infection, often accompanied by chills.
- Pain in the Flank: Dull, aching pain on one side of the lower back or in the flank region is common.
- Frequent Urination: A strong, persistent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty.
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation or pain during urination.
- Cloudy or Bloody Urine: Urine may appear cloudy, dark, or contain blood.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and vomiting can occur.
- Fatigue: Generalized weakness, fatigue, and malaise may be present.
- Mental Confusion: In severe cases, pyelonephritis can cause confusion and altered mental status.
Treatment for Kidney Infections
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications associated with pyelonephritis. Treatment options typically include:
- Antibiotics: Oral or intravenous antibiotics are prescribed to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescription medications can help manage pain and reduce fever.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial to flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for intravenous antibiotics and supportive care.
- Surgical Intervention: Surgery may be required to treat underlying urinary tract abnormalities or complications like abscesses.
here are key points about the treatment of kidney infections:
Treatment for Kidney Infections
- Antibiotics: The cornerstone of kidney infection treatment is antibiotics. A healthcare provider will prescribe antibiotics to target and eliminate the bacteria causing the infection.
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, or if there is a risk of complications, hospitalization may be necessary. Intravenous (IV) antibiotics can be administered more effectively in a hospital setting.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescription medications can help manage pain and reduce fever associated with pyelonephritis.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is crucial during treatment. Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Urinary Catheter Removal: If a urinary catheter was used, its removal is typically recommended as soon as possible to minimize the risk of introducing more bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Surgical Intervention: In rare cases, surgery may be necessary to address underlying urinary tract abnormalities or complications like abscesses.
- Reevaluation: After several days of antibiotic treatment, a healthcare provider will reevaluate to ensure the infection is responding to treatment. If necessary, the antibiotic regimen may be adjusted.
- Complete Antibiotic Course: It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished.
- Follow-Up: After treatment, follow-up appointments may be scheduled to ensure the infection is completely resolved and to address any lingering issues.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining good hygiene practices and practicing safe sex, may be recommended to prevent future pyelonephritis.
It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a kidney infection, as early treatment is crucial to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery. pyelonephritis can be serious, but with proper medical care, most individuals recover fully and do not experience long-term kidney damage.
Prevention of Kidney Infections
Taking preventive measures can help reduce the risk of kidney infections:
- Hygiene: Maintain good personal hygiene, including regular handwashing and proper wiping after using the toilet.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to promote frequent urination and flush out potential bacteria.
- Urinate Promptly: Don’t delay urination when you feel the need, and empty your bladder completely.
- Wipe Front to Back: Women should wipe from front to back to prevent the spread of bacteria from the anal area to the urinary tract.
- Empty Bladder Before and After Intercourse: Urinating before and after sexual activity can help flush out bacteria.
- Avoid Harsh Feminine Hygiene Products: Perfumed products can irritate the urethra and potentially lead to infection.
- Treat UTIs Promptly: If you experience UTI symptoms, seek treatment promptly to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys.
here are key points about the prevention of kidney infections:
Prevention of Kidney Infections
- Good Hygiene: Maintain good personal hygiene practices, including regular handwashing with soap and water. Proper hygiene reduces the risk of introducing bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water daily to help flush bacteria out of the urinary tract. Proper hydration is essential for kidney health.
- Urinate Promptly: Don’t delay urination when you feel the need. Emptying your bladder promptly can help prevent the growth of bacteria in the urinary tract.
- Wipe Front to Back: Women should always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent the spread of bacteria from the anal area to the urinary tract.
- Empty Bladder Before and After Intercourse: Urinating before and after sexual activity can help flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sex.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use barrier methods like condoms to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections that can lead to pyelonephritis.
- Cranberry Juice or Supplements: Some individuals find that consuming cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent UTIs, which can progress to pyelonephritis.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid harsh feminine hygiene products and perfumed bath products that can irritate the urethra and potentially lead to infection.
- Manage Underlying Conditions: If you have conditions like diabetes or kidney stones that increase the risk of kidney infections, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage these conditions effectively.
- Regular Check-Ups: Attend regular healthcare check-ups and screenings to monitor your kidney health and detect any potential issues early.
- Prompt UTI Treatment: If you experience symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI), seek prompt medical treatment. UTIs can progress to kidney infections if left untreated.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Make necessary lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol and tobacco use, to minimize the risk factors associated with kidney infections.
By adopting these preventive measures and maintaining good urinary tract health, you can significantly reduce the risk of kidney infections. If you are prone to recurrent kidney infections or have underlying health conditions that make you more susceptible, consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice on prevention and management.
Conclusion
Kidney infections are a serious medical condition that demands prompt attention. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and adopting preventive measures are essential for kidney health. With proper care and medical intervention, most kidney infections can be effectively treated, reducing the risk of complications and ensuring a full recovery.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023