Kneecap Bursitis and Easing the Discomfort
Introduction:
In the intricate machinery of our bodies, joints play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless movement. However, every now and then, these joints may experience issues, causing discomfort and hindering our day-to-day activities. One such ailment that often flies under the radar is kneecap bursitis.
The Silent Disruptor:
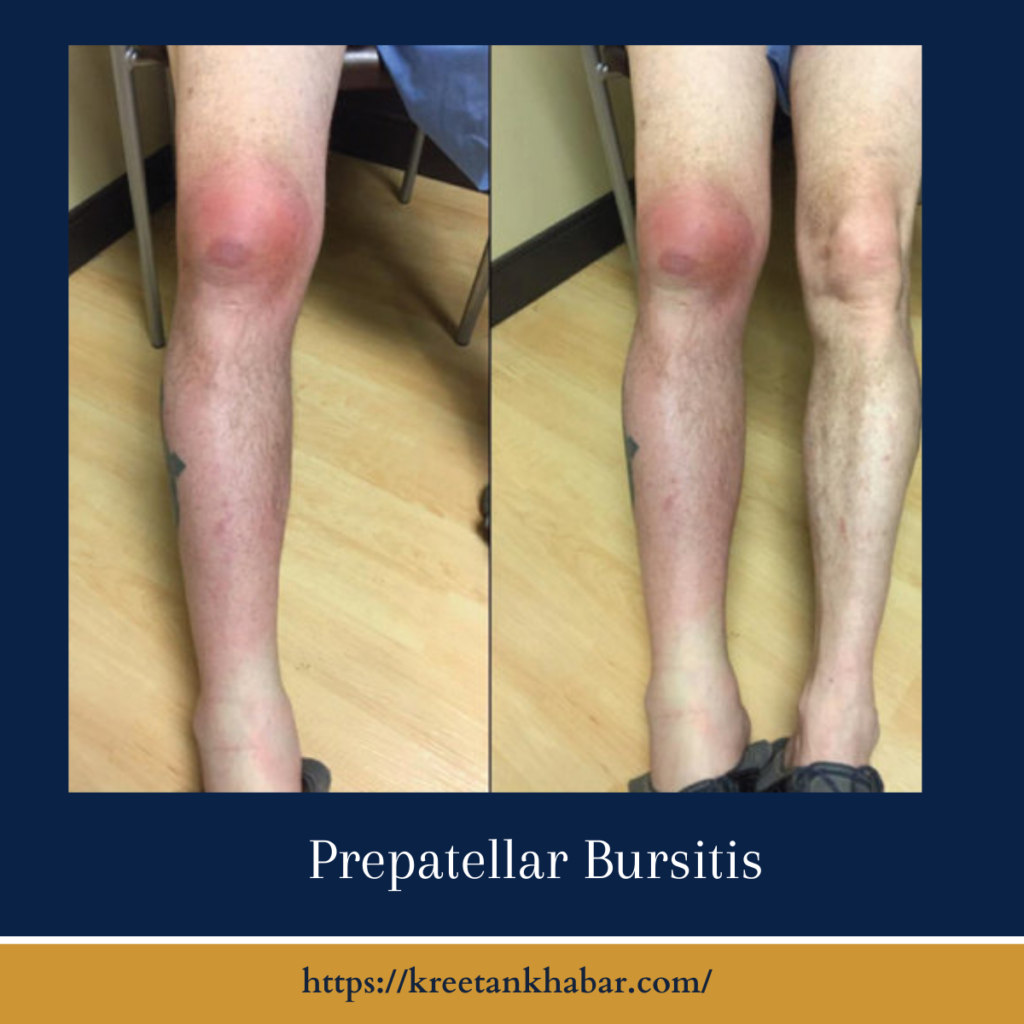
Kneecap bursitis, also known as prepatellar bursitis, is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the bursa located just in front of the kneecap. The bursa, a small fluid-filled sac, acts as a cushion between the bones and tendons, reducing friction and allowing smooth movement of the knee.
Causes:
Several factors can trigger kneecap bursitis, with repetitive pressure or trauma to the knee being primary culprits. Occupations or activities that involve frequent kneeling, such as flooring installation or gardening, may increase the risk of developing this condition. Additionally, direct blows to the knee, infection, or underlying medical conditions like arthritis can also contribute to the inflammation of the bursa.
- Repetitive Kneeling: One of the primary causes of kneecap bursitis is repetitive kneeling. Occupations or activities that involve prolonged periods of kneeling, such as carpet installation, gardening, or certain sports, can lead to increased pressure on the knee joint, triggering inflammation of the bursa.
- Direct Trauma or Blows to the Knee: Accidents happen, and a direct blow to the knee can result in trauma to the bursa, leading to inflammation. Whether it’s a fall, a collision, or any impact that targets the knee, these incidents can be a catalyst for the development of kneecap bursitis.
- Infection: In some cases, infection can infiltrate the bursa, causing inflammation and leading to kneecap bursitis. This can occur if bacteria enter the bursa through a cut or abrasion on the knee or as a secondary complication of another infection in the body.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or gout, can contribute to the development of kneecap bursitis. These conditions affect joint health and increase the susceptibility of the bursa to inflammation.
- Overuse or Strain: Overusing the knee joint or placing excessive strain on it can also be a contributing factor. This may be seen in athletes or individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive motion of the knee, leading to irritation and inflammation of the bursa.
- Improper Footwear or Knee Protection: Wearing inadequate footwear or lacking proper knee protection during activities that involve kneeling can increase the risk of developing bursitis. The absence of proper support puts additional stress on the knee joint, making it more vulnerable to inflammation.
- Excess Weight: Carrying excess body weight places additional stress on the knee joints. This increased pressure can contribute to the development of kneecap bursitis, especially if the individual engages in activities that involve kneeling or repetitive knee movement.
- Age-Related Changes: As we age, the structure and function of joints naturally undergo changes. The wear and tear on the knee joint over time can make the bursa more susceptible to inflammation, increasing the likelihood of kneecap bursitis in older individuals.
Understanding these various causes is crucial for both prevention and effective management of kneecap bursitis. Whether it’s adjusting daily activities, using protective gear, or seeking medical attention for underlying conditions, addressing the root causes can significantly reduce the risk of developing this painful condition.
Symptoms:
Recognizing the signs of kneecap bursitis is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include swelling in the front of the knee, localized pain, and tenderness. The affected area may also appear red and feel warm to the touch. In severe cases, individuals may experience difficulty in fully extending or bending the knee.
Treatment Options:
Fortunately, managing kneecap bursitis often involves non-invasive measures that can be implemented at home. Rest is paramount, allowing the body time to heal and the inflammation to subside. Applying ice packs to the affected area and taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications can help alleviate pain and swelling.
For persistent cases, a healthcare professional may recommend physical therapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee, providing additional support. In some instances, the excess fluid in the bursa may need to be drained through a minor procedure.
- Rest and Activity Modification: The cornerstone of treating kneecap bursitis is giving the affected knee ample time to rest. Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as kneeling or excessive bending, allows the inflamed bursa to heal. Modification of daily activities can be crucial in preventing further irritation.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected knee helps reduce swelling and provides relief from pain. Cold therapy can be applied for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the initial stages of bursitis. It’s a simple yet effective way to manage inflammation.
- Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter NSAIDs, like ibuprofen or naproxen, can be instrumental in alleviating pain and reducing inflammation associated with kneecap bursitis. However, it’s essential to use these medications under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in both the treatment and prevention of kneecap bursitis. Therapists can design exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving joint stability and reducing the risk of recurrence. Techniques such as ultrasound or gentle massage may also be employed to aid healing.
- Knee Aspiration (Fluid Removal): In cases where the bursa becomes significantly swollen and painful, a healthcare professional may perform a minimally invasive procedure known as aspiration. This involves removing excess fluid from the bursa, providing immediate relief and facilitating a quicker recovery.
- Protective Padding or Knee Braces: For individuals whose occupations involve frequent kneeling, wearing protective padding or knee braces can help distribute pressure more evenly across the knee joint. This added support reduces the strain on the bursa, aiding in the healing process.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some instances, healthcare providers may recommend corticosteroid injections directly into the affected bursa to alleviate inflammation and pain. While these injections can provide rapid relief, they are typically reserved for more severe cases due to potential side effects.
- Antibiotics (If Infection is Present): If the kneecap bursitis is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the underlying bacterial source. Combining antibiotics with other treatment modalities is crucial for a comprehensive approach to healing.
- Lifestyle Changes: Individuals with recurrent kneecap bursitis may benefit from making lifestyle changes. This could include maintaining a healthy weight to reduce stress on the knee joint and adopting ergonomic practices to minimize repetitive strain.
- Surgical Intervention (Rare Cases): In very rare and severe cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be considered. This could involve removing the inflamed bursa or addressing any underlying structural issues contributing to the condition.
It’s important to note that the appropriate treatment for kneecap bursitis may vary based on individual circumstances. Seeking professional medical advice ensures a tailored approach to managing and resolving this condition effectively.
Prevention:
Preventing kneecap bursitis revolves around adopting proactive measures, especially for individuals whose daily activities involve kneeling or significant stress on the knees. Wearing knee pads or using cushions when kneeling for extended periods can help reduce the impact on the joint. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that place undue stress on the knees can contribute to overall joint health.
Conclusion:
While kneecap bursitis may not be a household name, its impact on daily life can be profound. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for timely and effective intervention. By prioritizing joint health and adopting preventive measures, individuals can navigate the discomfort associated with kneecap bursitis and continue to move through life with ease.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023