Lumbar Radiculopathy
Introduction:
In the intricate tapestry of spine health, lumbar radiculopathy emerges as a common yet intricate thread. This condition, often referred to as sciatica, sends ripples of discomfort and pain along the nerve roots of the lower back, affecting the legs and sometimes challenging our everyday movements. In this exploration, we delve into the nuances of lumbar radiculopathy, unraveling its origins, manifestations, and avenues for relief.
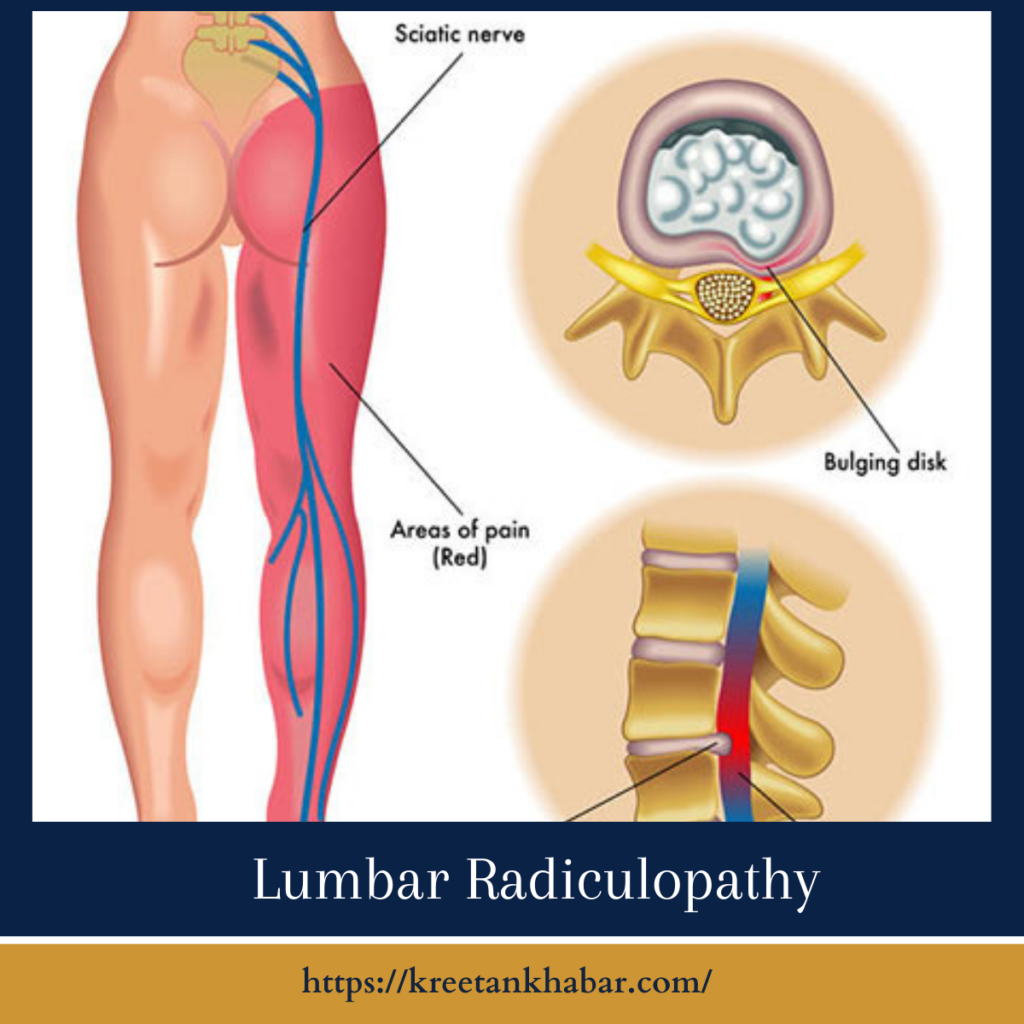
The Lumbar Radiculopathy Tapestry:
Lumbar radiculopathy is not a singular ailment but a manifestation of nerve compression or irritation in the lumbar spine. This compression typically occurs at the point where nerve roots exit the spine, leading to a distinctive set of symptoms that can range from mild discomfort to sharp, shooting pain.
Understanding the Underlying Causes:
At the core of lumbar radiculopathy lies a variety of underlying causes. The most prevalent culprit is herniated discs, where the gel-like center of a spinal disc protrudes, exerting pressure on nearby nerve roots. Other causes include spinal stenosis, narrowing of the spinal canal, and spondylolisthesis, a condition where one vertebra slips forward over another. In rare cases, tumors or infections may contribute to lumbar radiculopathy.
Manifestations of Lumbar Radiculopathy:
The hallmark of lumbar radiculopathy is pain that radiates along the path of the affected nerve. This pain may be accompanied by tingling, numbness, or weakness in the leg. The specific symptoms depend on the location and severity of the nerve compression. Individuals often describe sensations like electric shocks or a burning sensation, creating a distinctive tapestry of discomfort.
Diagnosis: Untangling the Threads:
Diagnosing lumbar radiculopathy involves a meticulous process of untangling the threads of symptoms, clinical assessments, and diagnostic imaging. Physicians employ a comprehensive approach, conducting physical examinations, assessing medical history, and often employing imaging studies like MRIs or CT scans to pinpoint the exact location and cause of nerve compression.
- Clinical Evaluation: Diagnosis of lumbar radiculopathy often begins with a comprehensive clinical evaluation. Healthcare providers gather information about the patient’s medical history, including the onset and nature of symptoms, previous injuries, and any relevant family history.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is a crucial step in diagnosing lumbar radiculopathy. Healthcare professionals assess muscle strength, reflexes, and sensation in the affected areas. Specific maneuvers, such as the straight leg raise test, help identify characteristic signs of nerve compression.
- Neurological Examination: A neurological examination is integral to evaluating the extent of nerve involvement. This includes assessing coordination, balance, and reflexes, providing insights into the specific nerves affected and the severity of the condition.
- Imaging Studies: Diagnostic imaging plays a pivotal role in confirming the diagnosis and identifying the underlying cause of lumbar radiculopathy. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is commonly used to visualize the spine and detect herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or other structural abnormalities.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: In some cases, a CT scan may be employed to provide detailed images of the spine. CT scans can offer additional information about bony structures and are particularly useful in identifying conditions such as spondylolisthesis.
- Electrodiagnostic Tests: Electrodiagnostic tests, including electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies, can help assess the electrical activity of muscles and nerves. These tests aid in pinpointing the location and severity of nerve compression.
- X-rays: X-rays may be used to assess the overall structure of the spine, highlighting any abnormalities such as fractures, degenerative changes, or alignment issues. While X-rays may not directly visualize nerve compression, they provide valuable context.
- Discography: In some cases, discography may be recommended to evaluate the condition of intervertebral discs. This involves injecting contrast dye into the discs and observing any abnormal response, helping to identify damaged or degenerated discs.
- Selective Nerve Root Block: Selective nerve root block is a diagnostic procedure where a local anesthetic and corticosteroid are injected near the affected nerve. If pain relief occurs following the injection, it can help confirm the specific nerve involved and guide further treatment decisions.
- Blood Tests: While not the primary diagnostic tool, blood tests may be conducted to rule out other potential causes of symptoms, such as infections or inflammatory conditions. These tests complement the overall diagnostic process.
- Patient Feedback: Patient feedback is a valuable component of the diagnostic process. Descriptions of symptoms, including the nature of pain, its location, and any factors that exacerbate or alleviate it, contribute essential information to the overall diagnostic picture.
- Rule Out Differential Diagnoses: Lumbar radiculopathy shares symptoms with various other spinal conditions. The diagnostic process includes a careful evaluation to rule out differential diagnoses, ensuring an accurate understanding of the specific nature of the patient’s symptoms.
The diagnosis of lumbar radiculopathy is a collaborative effort, involving the expertise of healthcare professionals and active participation from the patient. Through a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies, and targeted tests, healthcare providers aim to unravel the complexities of lumbar radiculopathy, guiding the path toward effective and individualized treatment.
Treatment Threads: Weaving Relief:
The treatment of lumbar radiculopathy is a nuanced process, with the goal of alleviating symptoms and improving the quality of life. Here are some threads in the tapestry of lumbar radiculopathy treatment:
- Pain Management: Pain relief often involves over-the-counter or prescription medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or muscle relaxants. For severe pain, short-term use of opioids may be considered under careful supervision.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in managing lumbar radiculopathy. Targeted exercises and stretches aim to improve flexibility, strengthen core muscles, and alleviate pressure on the affected nerves.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: In cases of persistent pain, epidural steroid injections may be recommended. These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly to the affected area, providing temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
- Surgical Intervention: For cases resistant to conservative measures, surgical intervention may be considered. Procedures like discectomy (removal of part of a herniated disc) or laminectomy (removal of a portion of the vertebral bone) aim to decompress the affected nerves and provide lasting relief.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Simple lifestyle adjustments can contribute to symptom relief. Maintaining a healthy weight, adopting proper posture, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing can help mitigate the impact of lumbar radiculopathy.
- Alternative Therapies: Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and yoga are threads in the tapestry of alternative approaches to managing lumbar radiculopathy. While individual responses vary, some find relief and improved mobility through these modalities.
The Road to Recovery:
Recovery from lumbar radiculopathy is often a journey rather than a destination. Patience, persistence, and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers are essential in navigating this road. The threads of understanding the condition, exploring treatment options, and making lifestyle adjustments all contribute to the intricate tapestry of recovery.
Conclusion:
Lumbar radiculopathy, with its intricate blend of pain, tingling, and weakness, weaves a complex story that extends beyond the physical realm. It impacts daily activities, challenges resilience, and underscores the importance of a comprehensive approach to spine health. As we unravel the threads of lumbar radiculopathy, we not only gain insights into its origins and manifestations but also discover the diverse avenues available for relief, promising a brighter and more comfortable tapestry for those affected by this condition.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023