Osteonecrosis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction:
Osteonecrosis, a condition also known as avascular necrosis, is a complex and often debilitating disorder affecting the bones. Characterized by the death of bone tissue due to inadequate blood supply, avascular necrosis can occur in various joints, most commonly in the hip, knee, and shoulder. This article delves into the intricacies of osteonecrosis, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the diverse array of treatment options available for individuals grappling with this challenging bone disorder.
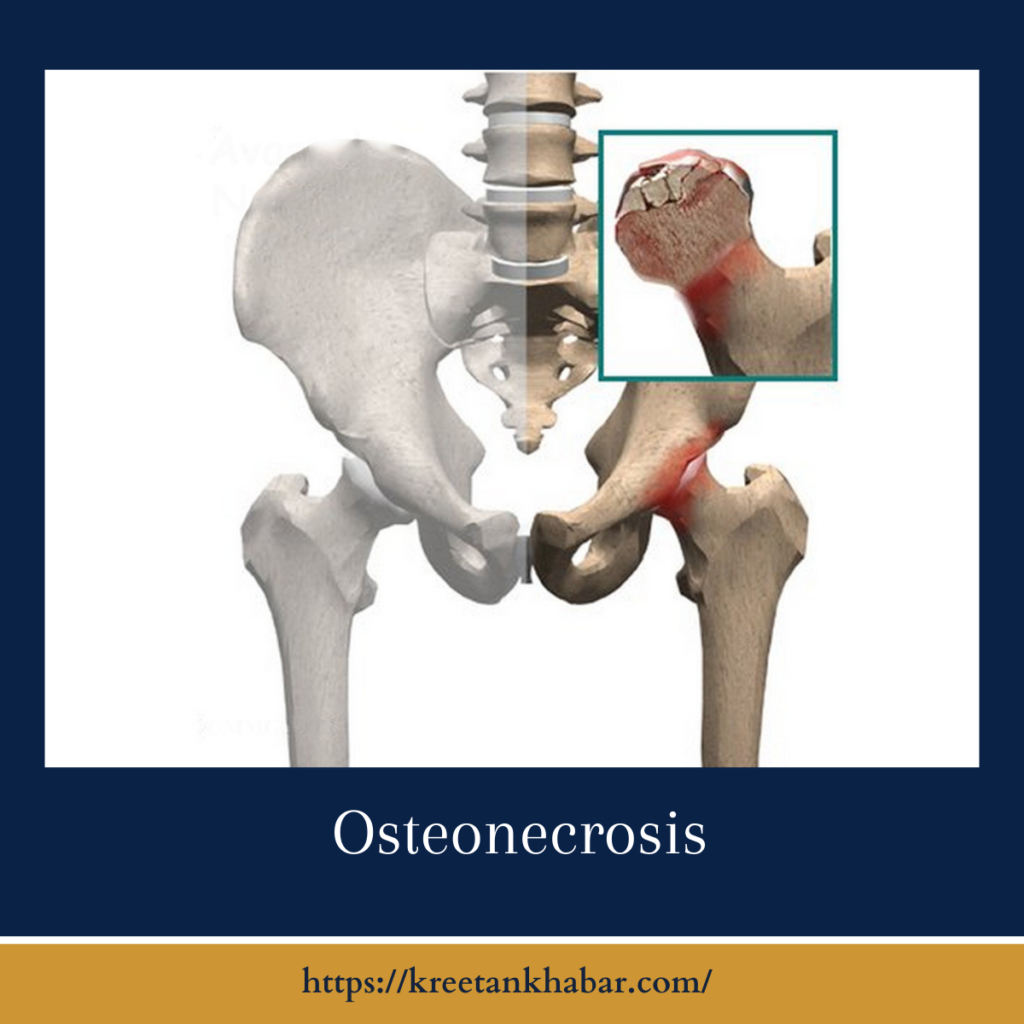
Causes:
The primary cause of avascular necrosis is compromised blood flow to the affected bone. This can result from numerous factors, including trauma, long-term use of corticosteroids, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions such as sickle cell anemia or lupus. The disruption of blood supply starves the bone tissue of oxygen and nutrients, leading to its eventual death.
Causes of Osteonecrosis: Key Points
- Disrupted Blood Supply:
- avascular necrosis, or avascular necrosis, primarily occurs due to a compromised blood supply to the affected bone.
- Insufficient blood flow starves the bone tissue of oxygen and nutrients, leading to its eventual death.
- Trauma:
- Joint trauma, such as fractures or dislocations, can disrupt blood vessels supplying the bone, increasing the risk of avascular necrosis.
- The severity of trauma and the location of the injury contribute to the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Corticosteroid Use:
- Prolonged or high-dose use of corticosteroid medications, commonly prescribed for inflammatory conditions, can impact bone health and increase the risk of avascular necrosis.
- Medical Conditions:
- Certain medical conditions, including sickle cell anemia, lupus, and other autoimmune disorders, may predispose individuals to avascular necrosis.
- These conditions can affect blood vessel health and overall bone metabolism.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption:
- Chronic heavy alcohol consumption is a recognized risk factor for avascular necrosis, particularly affecting the hip joint.
- Alcohol-induced changes in lipid metabolism and blood vessel function contribute to the development of the condition.
- Joint Decompression:
- Certain medical procedures, such as joint decompression, can disrupt blood flow to the bone and potentially lead to avascular necrosis.
- Understanding the risks associated with surgical interventions is crucial in preventing this complication.
- Radiation Therapy:
- Exposure to radiation therapy, often used in cancer treatment, can adversely affect bone health and increase the risk of avascular necrosis in the irradiated area.
- Idiopathic Causes:
- In some cases, the cause of avascular necrosis remains idiopathic, without a clear identifiable factor.
- The spontaneous occurrence of the condition underscores the complexity of its etiology.
- Genetic Predisposition:
- Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to avascular necrosis, making them more susceptible to the condition.
- Understanding family medical history can provide insights into potential genetic factors.
- Blood Clotting Disorders:
- Disorders affecting blood clotting, such as antiphospholipid syndrome, can disrupt blood flow and contribute to the development of avascular necrosis.
Understanding the diverse causes of avascular necrosis is essential for identifying at-risk individuals and implementing preventive measures. By addressing underlying medical conditions, avoiding excessive use of corticosteroids, and adopting lifestyle changes, individuals can potentially mitigate the risk of developing this complex bone disorder.
Symptoms:
Osteonecrosis often manifests with joint pain, which can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating pain. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience limited joint mobility, stiffness, and muscle atrophy. The onset of symptoms can be gradual, making early detection challenging, but as the disease advances, the impact on joint function becomes more apparent.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing osteonecrosis typically involves a combination of imaging studies and clinical evaluation. X-rays can reveal changes in bone structure, while more advanced imaging techniques like magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provide detailed views of the affected bone and surrounding tissues. Blood tests may also be conducted to rule out underlying medical conditions contributing to the development of avascular necrosis.
Treatment:
The approach to treating osteonecrosis depends on several factors, including the stage of the disease, the affected joint, and the underlying cause. Conservative measures may include pain management, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to reduce stress on the affected joint. For advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Core decompression, bone grafting, and joint replacement are among the surgical options aimed at preserving joint function and alleviating pain.
Challenges in Treatment:
Osteonecrosis poses unique challenges in treatment due to the varying factors influencing its development. Successful management often requires a multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic specialists, rheumatologists, and pain management experts. Individualized treatment plans are crafted based on the specific needs and circumstances of each patient, highlighting the complexity of addressing this condition.
Prevention and Lifestyle Considerations:
While not always preventable, certain lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of developing osteonecrosis. Limiting alcohol intake, avoiding excessive use of corticosteroids, and managing underlying health conditions contribute to overall bone health. Timely intervention and adherence to prescribed treatments are essential for mitigating the impact of osteonecrosis and improving long-term outcomes.
Conclusion:
Osteonecrosis presents a multifaceted challenge, requiring a comprehensive and personalized approach to treatment. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring the array of available treatment options are pivotal steps in addressing this complex bone disorder. Ongoing research and advancements in medical science continue to shape the landscape of osteonecrosis management, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for individuals navigating this intricate condition.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023