Otitis Externa: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Swimmer’s Ear
Otitis externa, commonly known as swimmer’s ear, is a painful and uncomfortable ear infection that affects the outer ear canal. While it can occur at any age, it is particularly prevalent among children and individuals who frequently engage in water-related activities. In this article, we’ll explore otitis externa, its causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment to help you understand and manage this common ear condition.
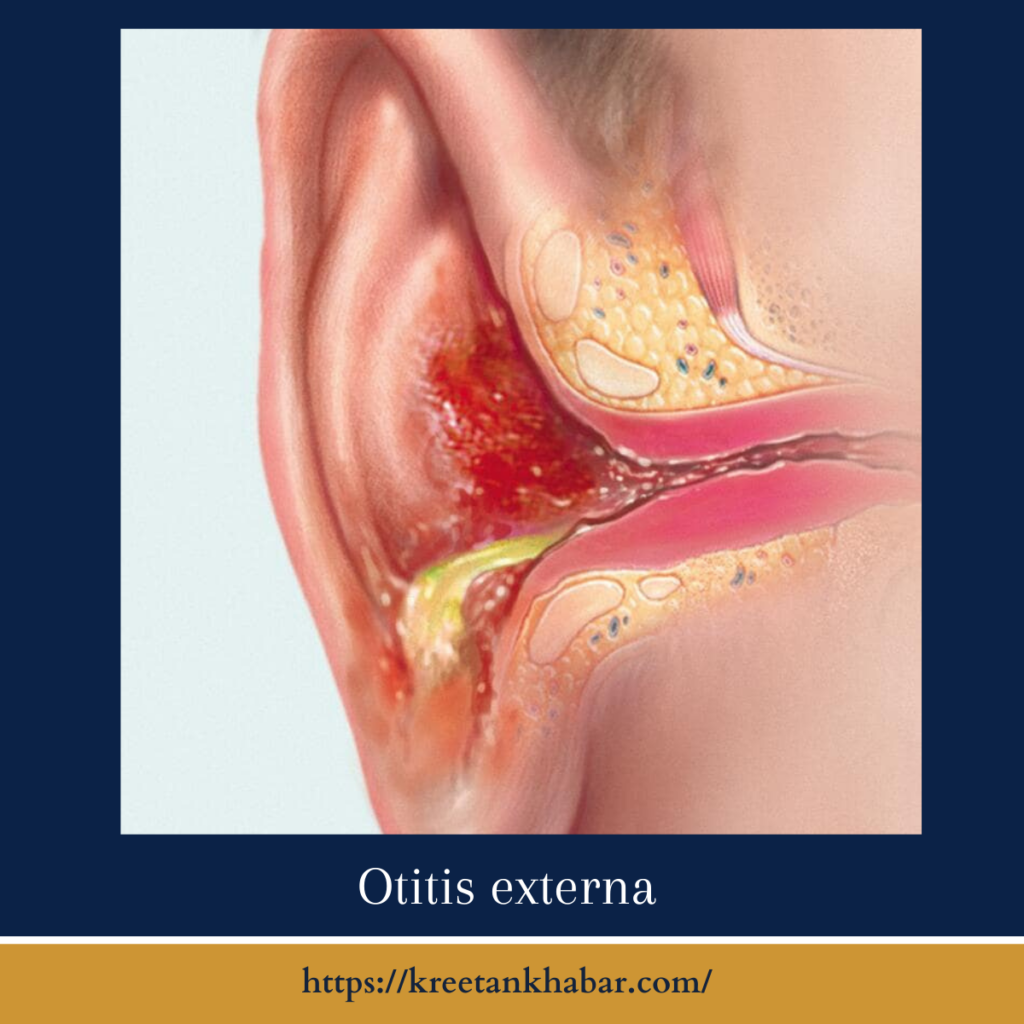
What Is Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear)?
Otitis externa is an infection or inflammation of the external ear canal, the tube that runs from the outer ear to the eardrum. It is often referred to as swimmer’s ear because it can result from exposure to water, which softens the ear canal, making it more susceptible to infection. However, otitis externa can also develop without water exposure.
Common Causes of Otitis Externa:
- Excessive Moisture: Prolonged exposure to water, such as swimming or frequent showering, can create a moist environment in the ear canal conducive to bacterial or fungal growth.
- Injury: Scratches or irritation of the ear canal from foreign objects like cotton swabs or hairpins can increase the risk of infection.
- Bacterial or Fungal Infection: Bacteria like Pseudomonas or Staphylococcus aureus, as well as fungi like Candida, can cause otitis externa.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to substances like hair products or earplugs may lead to inflammation.
Common Symptoms of Otitis Externa:
- Ear Pain: The most prevalent symptom is ear pain, which can range from mild discomfort to severe, sharp pain.
- Itching: The ear canal may become itchy, and scratching can worsen the condition.
- Redness and Swelling: The ear canal may appear red and swollen.
- Discharge: Otitis externa can lead to a watery discharge, often foul-smelling.
- Hearing Loss: Hearing may be temporarily affected due to the ear canal’s inflammation and blockage.
Treatment of Otitis Externa:
- Ear Drops: Prescription or over-the-counter ear drops containing antibiotics and steroids are commonly used to treat otitis externa. These drops help clear the infection and reduce inflammation.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can provide relief from ear pain.
- Keep Ears Dry: Avoid further water exposure to the affected ear. Use earplugs or a cotton ball coated with petroleum jelly when showering or swimming.
- Avoid Inserting Objects: Do not insert cotton swabs, fingers, or any objects into the ear canal, as this can worsen the condition or cause injury.
- Rest and Elevation: Resting with the affected ear elevated can help reduce swelling and alleviate discomfort.
Preventing Otitis Externa:
- Dry Ears After Water Exposure: After swimming or showering, gently dry the ears with a clean towel or tilt the head to allow excess water to drain.
- Avoid Ear Trauma: Be cautious when cleaning the ears and avoid inserting objects into the ear canal.
- Ear Protection: Use earplugs when swimming in contaminated water or when engaging in water activities for extended periods.
- Keep Earbuds and Earphones Clean: Regularly clean and disinfect earbuds and earphones to prevent the introduction of bacteria into the ear canal.
Preventing Otitis Externa (Swimmer’s Ear): Key Points to Consider
- Keep Ears Dry: After swimming, showering, or any water-related activity, ensure that you dry your ears thoroughly using a clean towel. Gently tilt your head to allow any trapped water to drain out.
- Use Earplugs: When swimming in contaminated water or engaging in water activities for extended periods, use earplugs to prevent water from entering the ear canal.
- Avoid Inserting Objects: Never insert cotton swabs, fingers, or any objects into the ear canal. This can damage the delicate ear tissue and increase the risk of infection.
- Clean and Disinfect Earbuds: If you use earbuds or earphones, regularly clean and disinfect them to prevent the introduction of bacteria into the ear canal.
- Use Ear Drops: Consider using preventive ear drops designed to help maintain a healthy ear environment when swimming frequently or in challenging conditions.
- Limit Earphone Usage: Avoid using earphones or earbuds for extended periods, as they can trap moisture and promote bacterial growth in the ear canal.
- Dry Ears After Rain: After exposure to heavy rain, dry your ears as you would after swimming to prevent moisture buildup.
- Avoid Allergenic Substances: If you have known allergies to hair products or earplugs, avoid using them to prevent allergic reactions and inflammation in the ear canal.
- Maintain Good Ear Hygiene: Clean the external part of the ear gently with a washcloth or tissue, but avoid inserting anything into the ear canal.
- Regular Checkups: If you are prone to ear infections or have a history of otitis externa, consider regular checkups with an ear, nose, and throat specialist for preventive guidance.
- Protect Ears During Bathing: In young children, use earplugs or place a soft, clean cloth over the ears to prevent water from entering the ear canal during baths.
- Be Mindful of Water Quality: When swimming in pools or natural bodies of water, be aware of water quality and cleanliness to minimize the risk of infection.
- Educate Children: Teach children about the importance of ear hygiene and proper drying of the ears after swimming or bathing.
- Prompt Treatment: If you experience any ear discomfort, pain, or itching, seek prompt medical attention. Early treatment can prevent the worsening of symptoms and complications.
- Avoid Sharing Earbuds: Refrain from sharing earbuds or earphones, as this can transfer bacteria and increase the risk of infection.
By following these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing otitis externa or swimmer’s ear. Keeping the ears clean, dry, and free from irritants is essential in maintaining ear health and preventing this common ear condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
If symptoms of otitis externa persist, worsen, or if there is any discharge of pus from the ear, it’s crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Untreated otitis externa can lead to complications, including the spread of infection to nearby tissues or the middle ear.
In conclusion
otitis externa, or swimmer’s ear, is a common ear condition that can cause pain and discomfort but is typically treatable with ear drops and proper care. By understanding its causes, symptoms, prevention measures, and timely treatment, individuals can effectively manage this condition and prevent complications. If you suspect otitis externa or experience persistent ear pain or discomfort, consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and guidance on treatment.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023