Patellar Tendinitis
Introduction:
Our knees are remarkable joints, allowing us to walk, run, and engage in various activities. However, with great mobility comes the risk of wear and tear, and one common ailment that afflicts many is patellar tendinitis. This condition, often referred to as “jumper’s knee,” can be a persistent source of discomfort, affecting individuals across different age groups and activity levels.
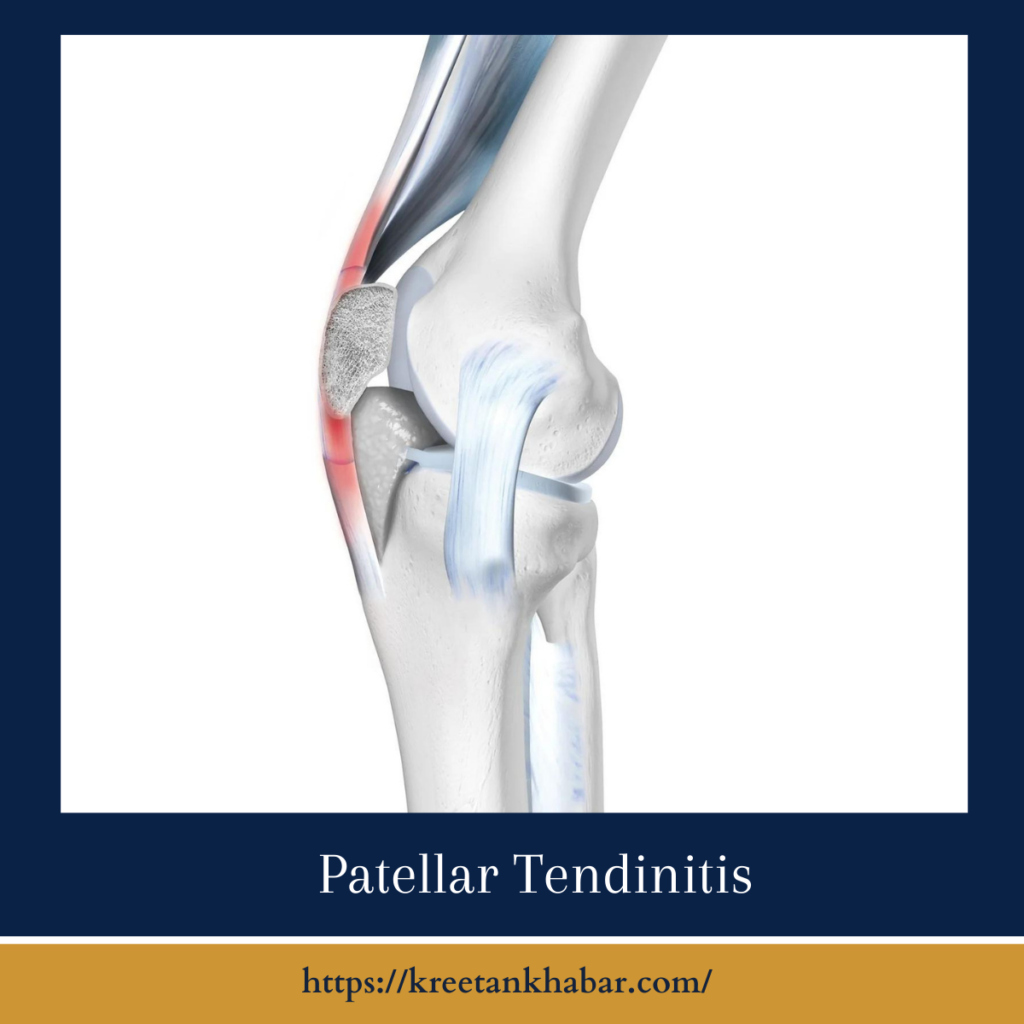
Understanding Patellar Tendinitis:
Patellar tendinitis is the inflammation of the patellar tendon, the robust band of tissue that connects the kneecap (patella) to the shinbone (tibia). This crucial tendon plays a pivotal role in the extension of the knee, allowing us to perform activities that involve kicking, jumping, and straightening the leg. When the tendon becomes inflamed, it can result in pain and stiffness around the kneecap, particularly just below it.
Causes of Patellar Tendinitis:
Patellar tendinitis, often known as the vexing “jumper’s knee,” finds its roots in a convergence of factors that challenge the resilience of our knee’s patellar tendon. The primary culprit is often overuse, as activities involving repetitive jumping or running place undue stress on the tendon without affording it sufficient time to recover. This overexertion can lead to microscopic tears, triggering inflammation and the onset of tendinitis.
Muscle imbalances, where the harmonious interplay between quadriceps and hamstrings falters, contribute to the problem. Poor biomechanics, encompassing irregularities in leg alignment or issues like flat feet, add another layer of vulnerability to the patellar tendon. Skipping the essential preamble of warm-ups and stretches before physical endeavors sets the stage for trouble, leaving the tendon less equipped to handle the demands placed upon it. In essence, the causes of patellar tendinitis weave a complex narrative, emphasizing the importance of balanced activity, biomechanical awareness, and proper care for our knee’s vital components.
- Overuse and Repetitive Stress:
- Engaging in activities that involve frequent jumping or running, such as in sports like basketball or volleyball, can lead to overuse of the patellar tendon. The repetitive stress on the tendon without adequate rest can trigger inflammation and the onset of tendinitis.
- Muscle Imbalances:
- Imbalances in the strength and flexibility of the muscles surrounding the knee, particularly the quadriceps and hamstrings, can contribute to patellar tendinitis. Weakness or tightness in these muscles alters the forces acting on the patellar tendon, increasing the risk of inflammation.
- Poor Biomechanics:
- Irregularities in the alignment or mechanics of the lower extremities can place uneven stress on the patellar tendon, leading to inflammation. Factors such as flat feet, high arches, or issues with leg alignment may contribute to the development of tendinitis.
- Inadequate Warm-Up or Stretching:
- Skipping proper warm-up routines before physical activities or neglecting stretching exercises can leave the patellar tendon vulnerable to injury. A warmed-up and well-stretched tendon is better equipped to handle the stresses of movement.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
The hallmark symptom of patellar tendinitis is pain, often felt as a dull ache around the lower part of the kneecap. This discomfort may be exacerbated during activities that involve jumping or bending the knee, and individuals with patellar tendinitis may experience stiffness and swelling. Diagnosis typically involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional, including a discussion of symptoms, physical tests, and sometimes imaging studies such as an ultrasound or MRI.
Treatment Strategies:
Embarking on the journey of treating patellar tendinitis is akin to conducting a personalized symphony of care, tailored to the nuances of each individual’s condition. A fundamental cadence in this treatment composition is the temporary respite of rest, allowing the beleaguered patellar tendon the opportunity to heal. Physical therapy emerges as a virtuoso, guiding patients through a repertoire of exercises that strengthen the supportive muscles, improve flexibility, and address any biomechanical irregularities.
The cool, soothing notes of ice application help in alleviating inflammation, harmonizing with the accompaniment of anti-inflammatory medications when necessary. A crescendo in the recovery process involves the gradual reintroduction of activities, a carefully orchestrated return that prevents a dissonant recurrence of tendinitis. Bracing and support may play a supporting role, providing a stabilizing harmony for the healing tendon. Each treatment plan is a unique composition, conducted with the aim of restoring the knee to its full symphonic potential, ensuring that individuals can once again move through life’s movements with grace and comfort.
- Rest and Activity Modification:
- The first line of defense against patellar tendinitis is often rest. Giving the tendon time to heal by avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms is crucial. Modification of activities and a temporary break from high-impact sports can aid in recovery.
- Physical Therapy:
- Targeted exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can help strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and address any biomechanical issues contributing to tendinitis. A well-designed rehabilitation program is essential for long-term recovery.
- Ice and Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
- Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may also be recommended to manage pain and swelling.
- Bracing and Support:
- In some cases, wearing a knee brace or strap just below the kneecap can provide support and alleviate stress on the patellar tendon during activities. This can be particularly beneficial during the recovery phase.
- Gradual Return to Activity:
- As symptoms subside, a gradual return to activity is recommended. Rushing back into intense physical activity too soon can increase the risk of recurrent tendinitis.
Prevention:
Preventing the unwelcome arrival of patellar tendinitis is akin to orchestrating a symphony of proactive measures aimed at safeguarding the well-being of our knee’s vital patellar tendon. Fundamental to this prevention ensemble is the implementation of thorough warm-up rituals, a prelude that prepares the tendon for the impending physical demands by promoting flexibility and blood flow.
Gradual progression in the intensity and duration of activities is another key note, allowing the body the luxury of adapting without subjecting the patellar tendon to abrupt stress. Maintaining a harmonious balance in the strength and flexibility of the muscles surrounding the knee emerges as a central theme, dissuading the discord that could lead to tendinitis. Listening to the body’s subtle cues and promptly addressing any signs of discomfort serves as a vigilant refrain in this preventive melody. With these orchestrated efforts, individuals can cultivate a resilient defense against the onset of patellar tendinitis, preserving the knee’s intricate symphony of movement and resilience.
Preventing patellar tendinitis involves a proactive approach, including:
- Incorporating proper warm-up and stretching routines before physical activities.
- Gradually increasing the intensity and duration of exercise to allow the body to adapt.
- Ensuring balanced strength and flexibility in the muscles around the knee.
- Listening to the body and addressing any signs of discomfort early on.
Conclusion:
Patellar tendinitis may be a common ailment, but with the right approach to treatment and prevention, individuals can overcome the challenges it presents. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective strategies for recovery are essential steps in navigating the ache of patellar tendinitis and restoring optimal knee function.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023