ptomaine poisoning: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
ptomaine poisoning (also known as Botulism), a rare but potentially life-threatening illness, is often associated with foodborne toxins and can lead to severe muscle weakness, respiratory failure, and even death. In this article, we will delve into the world of botulism, understanding its causes, symptoms, and the critical importance of prompt treatment.
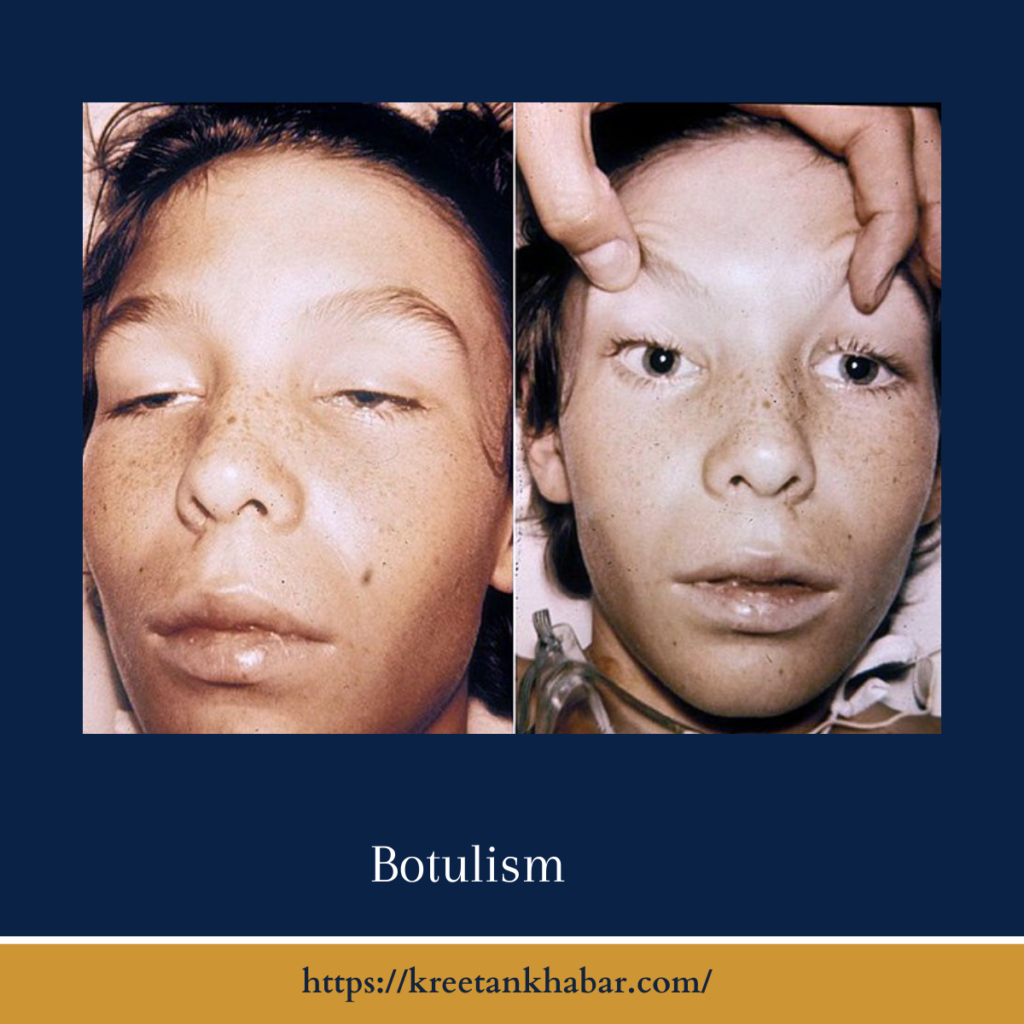
What is Botulism?
Botulism is a rare and serious illness caused by a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. This toxin, known as botulinum toxin, is among the most potent neurotoxins known to science. It attacks the body’s nerves, leading to muscle paralysis. There are several types of botulism, including foodborne, infant, wound, and inhalation botulism.
Causes of Botulism
- Foodborne Botulism: This is the most common form and occurs when people ingest food contaminated with the botulinum toxin. Improperly canned or preserved foods, particularly low-acid foods, are common culprits.
- Infant Botulism: This occurs when infants ingest the spores of Clostridium botulinum, which then multiply in the baby’s intestines and produce the toxin. Honey is a known source of infant ptomaine poisoning.
- Wound Botulism: In rare cases, the botulinum toxin can develop in wounds infected with Clostridium botulinum. This form is often linked to injection drug use.
- Inhalation Botulism: This is extremely rare and happens when the botulinum toxin is inhaled, leading to symptoms resembling those of foodborne ptomaine poisoning.
Symptoms of Botulism
The symptoms of botulism typically begin within 12 to 36 hours of exposure to the toxin. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Muscle Weakness: Botulinum toxin causes progressive muscle weakness, starting with the head and neck muscles and moving downward. Speech and swallowing difficulties often occur.
- Double Vision: Affected individuals may experience double vision or difficulty focusing their eyes.
- Dry Mouth: Dry mouth and difficulty speaking due to muscle weakness can be observed.
- Dizziness and Nausea: Botulism can cause dizziness, nausea, and general malaise.
- Respiratory Distress: Severe cases of ptomaine poisoning can lead to respiratory distress and breathing difficulties, potentially requiring mechanical ventilation.
- Paralysis: In advanced stages, individuals may experience full-body paralysis, including the muscles used for breathing, which can be life-threatening.
here are key points about the symptoms of botulism:
- Muscle Weakness: One of the primary symptoms of ptomaine poisoning is muscle weakness. It often starts in the head and neck area, affecting muscles responsible for facial expressions, swallowing, and speaking.
- Double Vision: Botulism can cause double vision or difficulty in focusing the eyes. This symptom typically arises due to the weakness of the eye muscles.
- Dry Mouth: Dry mouth and difficulty speaking may be experienced as the muscles controlling these functions become weak.
- Dizziness and Nausea: Individuals with ptomaine poisoning may feel dizzy and nauseous, leading to general discomfort.
- Respiratory Distress: Severe ptomaine poisoning cases can result in respiratory distress, making it difficult to breathe. This is a critical symptom that requires immediate medical attention.
- Paralysis: In advanced stages of ptomaine poisoning, individuals can experience full-body paralysis, including the muscles needed for breathing. This can be life-threatening and is considered a medical emergency.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Swallowing difficulties, also known as dysphagia, are common and can lead to choking or aspiration of food or fluids.
- Slurred Speech: Weakened muscles in the face and throat can cause slurred speech or difficulty in articulating words.
- Weakness Spreading: The muscle weakness caused by botulinum toxin tends to progress from the head and neck downwards, affecting the trunk and limbs as well.
- Fatigue: Individuals with ptomaine poisoning often experience extreme fatigue and muscle tiredness due to the weakening of the muscles.
- Vision Problems: Blurred or impaired vision can occur, making it difficult to focus on objects.
- Sensory Disturbances: Some people may report sensory disturbances, such as tingling or numbness in the extremities.
It’s important to note that ptomaine poisoning symptoms can vary in severity, and not all individuals will experience all of these symptoms. Early diagnosis and prompt medical treatment are crucial to managing botulism effectively and preventing life-threatening complications.
Diagnosis of Botulism
Diagnosing botulism is often based on a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Clinical Assessment: Healthcare providers assess symptoms and medical history to identify potential exposure sources.
- Laboratory Testing: Samples of blood, stool, or vomit may be analyzed for the presence of the botulinum toxin.
- Nerve Conduction Tests: Electromyography (EMG) can help confirm the diagnosis by evaluating nerve and muscle function.
Treatment of Botulism
Early treatment of botulism is crucial, as the condition can be life-threatening. Treatment measures include:
- Antitoxin Administration: The mainstay of ptomaine poisoning treatment is the administration of antitoxin. Botulism antitoxin can help neutralize the toxin and prevent its further effects. It is most effective when given as early as possible.
- Supportive Care: Patients with severe ptomaine poisoning may require intensive medical care, including mechanical ventilation to assist with breathing.
- Wound Care: In cases of wound ptomaine poisoning, proper wound care and, if necessary, surgical intervention may be essential.
- Gastric Lavage: In some cases, gastric lavage (stomach pumping) can help remove unabsorbed toxin from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Rehabilitation: Individuals recovering from ptomaine poisoning may require physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain muscle strength and function.
here are key points about the treatment of ptomaine poisoning:
- Antitoxin Administration: The primary treatment for ptomaine poisoning is the prompt administration of antitoxin. Botulism antitoxin helps neutralize the botulinum toxin circulating in the body, preventing further damage to nerve cells and muscles. It’s most effective when given as early as possible.
- Supportive Care: Patients with severe ptomaine poisoning may require intensive medical care. This includes close monitoring of vital signs and providing supportive measures to maintain bodily functions. In some cases, individuals may need mechanical ventilation to assist with breathing if respiratory muscles are affected.
- Wound Care: In cases of wound botulism, proper wound care is essential. Cleaning and, if necessary, surgical intervention to address the infected wound can help prevent the production of more toxin and further progression of the disease.
- Gastric Lavage: In some instances, gastric lavage, which is the process of washing out the stomach, may be performed to remove unabsorbed toxin from the gastrointestinal tract. This is often considered when botulism is suspected to result from ingesting contaminated food.
- Rehabilitation: Individuals recovering from botulism may require physical therapy and rehabilitation to regain muscle strength and function. Rehabilitation programs can help them relearn and practice movements and regain independence in daily activities.
- IV Fluids and Nutrition: Maintaining proper hydration and nutrition is essential during the recovery phase. Intravenous (IV) fluids and nutrition may be provided if swallowing difficulties persist.
- Monitoring: Patients with botulism require careful monitoring to assess their progress and ensure that the botulinum toxin is gradually eliminated from their system. This may involve regular checks of muscle strength, respiratory function, and vital signs.
- Preventing Complications: Efforts are made to prevent complications associated with prolonged immobility and muscle weakness. Preventive measures, such as turning and repositioning bedridden patients, are implemented to avoid bedsores.
- Early Recognition and Treatment: The key to successful botulism treatment is early recognition and immediate medical intervention. The sooner antitoxin is administered, the better the chances of preventing the progression of the disease and its potentially life-threatening complications.
It’s important to emphasize that botulism is a medical emergency, and treatment should not be delayed. Timely diagnosis and appropriate therapeutic measures are essential to ensure the best possible outcome and recovery for individuals affected by this rare but serious condition.
Botulism is a rare but serious condition that demands prompt medical attention. Preventing botulism involves proper food preparation and preservation techniques, avoiding the consumption of honey by infants, and practicing safe wound care. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are critical to a successful recovery from this potentially life-threatening illness.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023