Rhabdomyosarcoma: Unveiling the Rare Pediatric Cancer
Introduction
Rhabdomyosarcoma, often abbreviated as RMS, is a rare and aggressive form of pediatric cancer that arises from the soft tissues, primarily in skeletal muscles. This cancer is a daunting adversary, affecting children and adolescents, and understanding its nature is vital for early detection and effective treatment. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of rhabdomyosarcoma, exploring its characteristics, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of ongoing research.
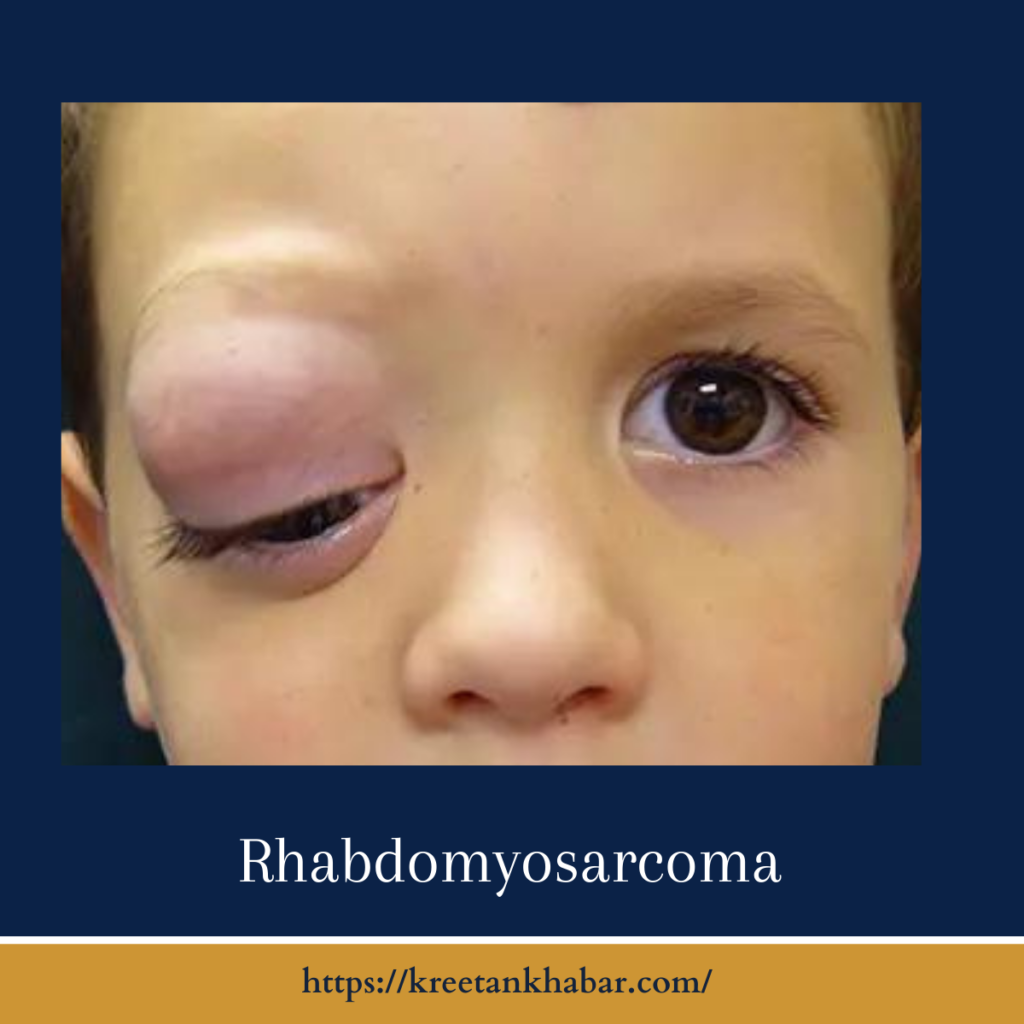
Understanding Rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a cancer that develops in the body’s soft tissues, with a strong predilection for skeletal muscles, which control voluntary movements. It accounts for a small fraction of childhood cancers, representing approximately 3-4% of all cases. RMS typically occurs in children and young adults under the age of 20, although it can occasionally affect adults.
Types of Rhabdomyosarcoma
There are two primary types of rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma: This is the most common form, comprising about 60-70% of all RMS cases. It often occurs in the head and neck region, urinary and reproductive organs, and the trunk.
- Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma: This type accounts for approximately 20-30% of RMS cases and is typically found in the limbs, chest, or abdominal wall. Alveolar RMS is generally more aggressive and harder to treat than embryonal RMS.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of rhabdomyosarcoma remains unknown. However, there are some recognized risk factors:
- Genetic Predisposition: Some genetic conditions, such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome and neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), increase the risk of developing RMS.
- Age: RMS primarily affects children and young adults, with the highest incidence in those under 20 years old.
- Gender: It occurs slightly more often in males than in females.
Symptoms
The symptoms of rhabdomyosarcoma can vary depending on the tumor’s location. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Swelling or Lump: A painless lump or swelling in the affected area, which may increase in size over time.
- Pain: Pain or discomfort in the area where the tumor is located.
- Difficulty Moving: If the tumor affects muscles, it may lead to difficulty in moving or using the affected body part.
- Bladder or Bowel Issues: Tumors in the pelvic area can cause problems with urination or bowel movements.
- Respiratory Problems: Tumors in the chest can lead to breathing difficulties, coughing, or chest pain.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing rhabdomyosarcoma typically involves a combination of tests and procedures:
- Physical Examination: The doctor examines the affected area to check for lumps or abnormalities.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound are commonly used to visualize the tumor’s location and extent.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample (biopsy) is taken from the tumor to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of RMS.
- Bone Marrow Aspiration: In some cases, a bone marrow aspiration may be performed to check if the cancer has spread to the bone marrow.
Treatment Options
Treatment for rhabdomyosarcoma typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is often the initial step if possible.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation may be used to target and shrink the tumor or as a preventive measure to eliminate any remaining cancer cells after surgery.
- Chemotherapy: Powerful medications are used to kill cancer cells throughout the body, making it particularly valuable when the cancer has spread or is inoperable.
- Targeted Therapy: Some patients may receive targeted therapy drugs that specifically target cancer cells with certain genetic mutations.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may offer innovative treatments and therapies under investigation.
Here are some unique points about the treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma:
- Multimodal Approach: The treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma typically involves a multimodal approach that combines surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. The specific treatment plan depends on factors such as the tumor’s location, size, and stage, as well as the patient’s age and overall health.
- Surgery: Whenever possible, the primary treatment goal is to surgically remove the tumor. Surgeons aim to achieve complete tumor resection while preserving surrounding healthy tissue. However, the location of the tumor may make complete removal challenging.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is commonly used in cases where the tumor cannot be entirely removed through surgery or to shrink the tumor before surgery. It is also employed as adjuvant therapy to eradicate any remaining cancer cells. Specialized techniques like proton therapy may be used to minimize radiation exposure to healthy tissues.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a cornerstone of rhabdomyosarcoma treatment. It involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Chemotherapy is often administered before surgery to shrink the tumor, making it more manageable for surgical removal. It may also be used after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells or in cases where radiation therapy is not feasible.
- Targeted Therapies: Ongoing research is exploring targeted therapies that specifically target cancer cells with certain genetic mutations. While not yet standard treatment, these therapies hold promise for more precise and effective rhabdomyosarcoma treatments in the future.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials is an option for some rhabdomyosarcoma patients. These trials investigate innovative treatments and therapies that are under investigation, offering potential access to cutting-edge approaches.
- Rehabilitation and Supportive Care: Rhabdomyosarcoma and its treatments can have significant physical and emotional impacts on patients. Rehabilitation, physical therapy, and supportive care services are essential components of treatment to help patients cope with the side effects and improve their quality of life.
- Long-Term Follow-Up: After completing the primary treatment, patients typically undergo long-term follow-up care to monitor for any signs of recurrence or late effects from treatment. This follow-up care may include regular medical check-ups, imaging tests, and ongoing support.
- Pediatric vs. Adult Treatment: The treatment approach for rhabdomyosarcoma may differ between pediatric and adult patients. Pediatric cases often involve more aggressive treatments due to the age and resilience of the patients, while treatment for adults may consider the overall health and tolerance of the individual.
- Emotional Support: Rhabdomyosarcoma treatment can be physically and emotionally challenging, especially for children and their families. Emotional support, counseling, and involvement in support groups can help patients and their loved ones navigate the emotional aspects of the journey.
- Second Opinions: Seeking a second opinion from a specialist in pediatric oncology or sarcoma is a prudent step, as treatment decisions can be complex and may benefit from the expertise of multiple healthcare professionals.
In conclusion, the treatment of rhabdomyosarcoma is a comprehensive and multidisciplinary effort that aims to achieve complete tumor removal, eradicate cancer cells, and minimize side effects. Ongoing research and advancements in targeted therapies hold promise for improving outcomes and reducing the impact of this rare and challenging cancer.
The Importance of Research
Given its rarity and complexity, ongoing research into rhabdomyosarcoma is crucial. Research efforts focus on understanding the genetic basis of the disease, developing more effective treatments with fewer side effects, and improving the long-term outcomes for patients.
Conclusion
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a challenging and rare pediatric cancer that demands early detection and a comprehensive treatment approach. While advancements in treatment have improved the prognosis for many patients, ongoing research and increased awareness are vital to enhance our understanding and management of this formidable adversary.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023