Sinusitis: Unraveling the Mystery of Stuffy Noses and Facial Pain
Introduction
Sinusitis, (also known as swelling)a common ailment that plagues millions of individuals worldwide, is more than just a stuffy nose and facial discomfort. It’s a condition that can disrupt daily life, causing headaches, fatigue, and even difficulty in breathing. In this article, we will delve into the world of swelling, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
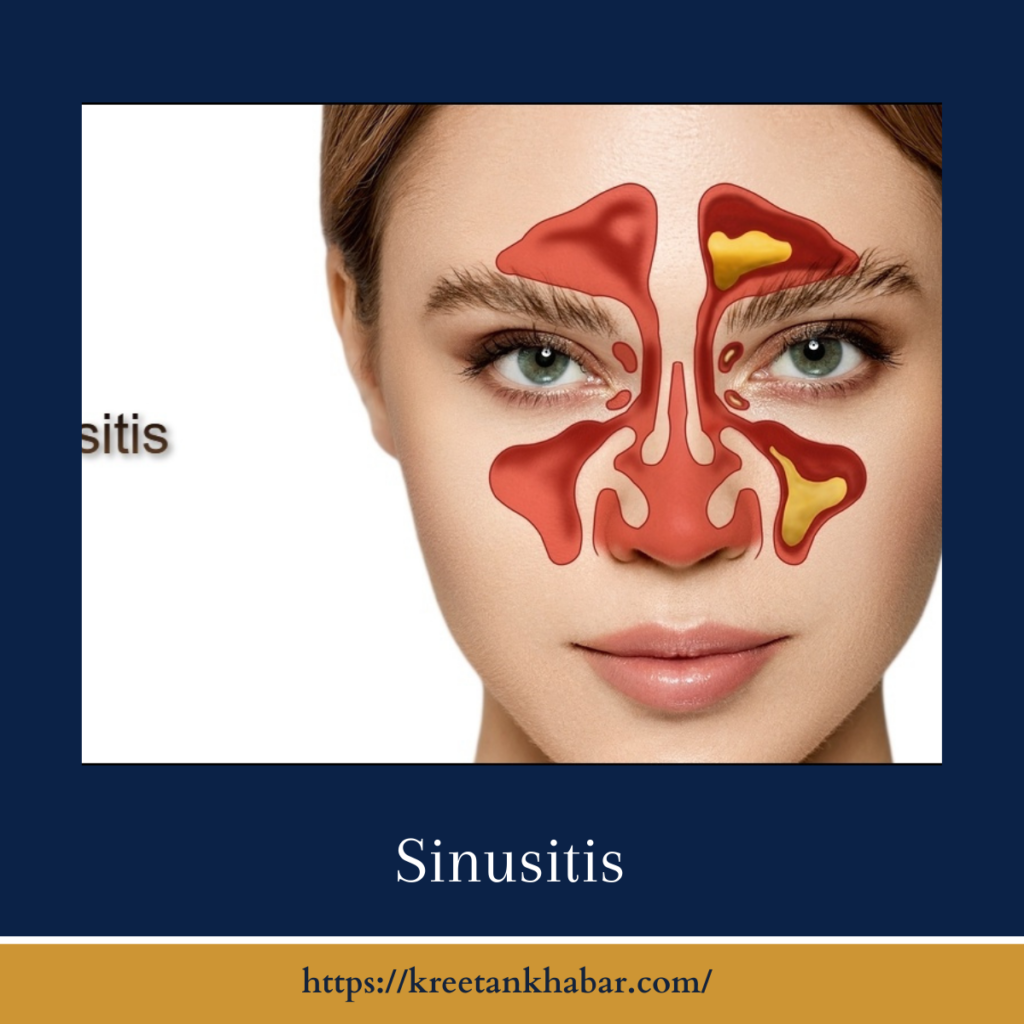
Understanding Sinusitis
Sinusitis, often referred to as a sinus infection, is the inflammation or swelling of the sinus cavities. These air-filled spaces, located in the skull, are lined with a mucus membrane that produces mucus to keep the nasal passages moist and trap potential contaminants like dust and bacteria.
Causes of Sinusitis
- Viral Infections: The common cold or flu viruses are the most frequent culprits behind acute swelling. They can inflame the sinus linings, causing congestion and discomfort.
- Bacterial Infections: Bacterial swelling occurs when bacteria infect the sinus cavities, often following a viral infection that has weakened the immune system.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to airborne allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander, can lead to allergic swelling, characterized by chronic inflammation.
- Nasal Polyps: Noncancerous growths in the nasal passages or sinus cavities can obstruct proper drainage, contributing to chronic swelling.
Symptoms of Sinusitis
Common symptoms of sinusitis include:
- Nasal Congestion: A blocked or stuffy nose is a hallmark symptom.
- Facial Pressure: Discomfort or pressure in the forehead, cheeks, and behind the eyes is a common complaint.
- Nasal Discharge: Thick, discolored mucus may drain from the nose or throat.
- Headaches: Sinus headaches often develop due to the increased pressure in the sinuses.
- Cough: A persistent cough, particularly worse at night, can result from postnasal drip.
- Fatigue: swelling can leave individuals feeling tired and rundown.
- Reduced Sense of Smell: A diminished ability to smell and taste is common.
- Sore Throat: Postnasal drip can irritate the throat, leading to a sore throat.
here are unique points regarding the symptoms of swelling:
- Nasal Congestion: One of the hallmark symptoms of swelling is nasal congestion or a blocked nose, often accompanied by difficulty in breathing through the nostrils.
- Facial Pain or Pressure: Many individuals with swelling experience discomfort or pressure in the facial areas, including the forehead, cheeks, and the area between the eyes.
- Headache: Sinus headaches can be intense and are often felt as a dull, aching pain in the forehead or around the eyes.
- Thick Nasal Discharge: A thick, yellow or green discharge from the nose is common in swelling, especially when it’s bacterial in origin.
- Cough: Postnasal drip can lead to a persistent cough, which may worsen at night.
- Reduced Sense of Smell: swelling can impair the sense of smell, making it difficult to detect odors.
- Sore Throat: Postnasal drip can cause irritation in the throat, resulting in a sore or scratchy throat.
- Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath, also known as halitosis, can occur due to the accumulation of mucus and bacteria in the throat.
- Fatigue: Chronic swelling, in particular, can lead to fatigue and a feeling of general malaise.
- Tooth Pain: swelling affecting the maxillary sinuses (located near the upper back teeth) can lead to toothache or dental discomfort.
- Ear Pressure: Some individuals with swelling may experience ear pressure or fullness due to the close proximity of the sinuses to the ear canals.
- Fever: In cases of bacterial swelling, fever may develop as the body’s immune system responds to the infection.
- Worsened Symptoms at Night: swelling symptoms can often worsen when lying down, making it difficult to sleep restfully.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced taste and smell sensations can lead to a decreased appetite.
- Pain when Bending Forward: Bending forward or sudden movements can intensify facial pain and pressure.
- General Irritability: Discomfort and disrupted sleep can contribute to feelings of irritability and frustration.
- Eye Redness: In severe cases, the eyes may become red and watery due to the proximity of the sinuses to the eye sockets.
- Difficulty Breathing: Severe nasal congestion can make it challenging to breathe through the nose.
- Neck Stiffness: The pressure and discomfort in the facial area can sometimes extend to the neck, causing stiffness.
- Chronic Symptoms: Chronic swelling may lead to long-lasting symptoms, such as persistent nasal congestion, cough, and fatigue.
These points highlight the diverse range of symptoms associated with swelling, which can vary in intensity and duration depending on the underlying cause and individual factors.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing swelling often involves a thorough medical history and physical examination. In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend imaging tests, such as a CT scan, to assess the extent of inflammation.
Treatment options for sinusitis depend on the underlying cause:
- Viral Sinusitis: Typically resolves on its own with rest, hydration, and over-the-counter decongestants or saline nasal sprays to relieve symptoms.
- Bacterial Sinusitis: May require antibiotics to clear the infection and alleviate symptoms.
- Allergic Sinusitis: Management involves identifying and avoiding allergens, as well as using antihistamines or corticosteroid nasal sprays to control inflammation.
- Chronic Sinusitis: For persistent cases, healthcare providers may recommend surgery to remove nasal polyps or improve drainage.
Here are unique points regarding the diagnosis and treatment of swelling:
Diagnosis of Sinusitis:
- Medical History: A comprehensive medical history, including the duration and nature of symptoms, helps in diagnosing swelling. Details of any recent illnesses or allergies are crucial.
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination, including assessing the nasal passages and facial tenderness, to identify signs of swelling.
- Endoscopy: In some cases, an endoscope may be used to examine the nasal passages and sinus openings for signs of inflammation or obstruction.
- Imaging: CT scans or X-rays can provide detailed images of the sinuses, helping to confirm the diagnosis and assess the extent of inflammation.
- Nasal Culture: If bacterial swelling is suspected, a nasal swab may be taken to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection.
Treatment of Sinusitis:
- Rest and Hydration: Adequate rest and staying well-hydrated are fundamental components of treatment for swelling, especially in viral cases.
- Decongestants: Over-the-counter or prescription decongestants can help reduce nasal congestion and relieve pressure in the sinuses.
- Saline Nasal Irrigation: Rinsing the nasal passages with saline solution using a Neti pot or nasal spray can help flush out mucus and improve breathing.
- Nasal Corticosteroids: These prescription or over-the-counter sprays can reduce inflammation in the nasal passages and sinuses.
- Antibiotics: In cases of bacterial swelling, antibiotics are prescribed to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. Amoxicillin is commonly used.
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help manage sinus headaches and facial pain.
- Antihistamines: For allergic swelling, antihistamines can help reduce allergic reactions and relieve symptoms.
- Humidifiers: Using a humidifier in the bedroom can add moisture to the air and alleviate dry nasal passages.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the face can provide relief from facial pain and pressure.
- Surgery: In chronic or severe cases, surgery may be considered. Procedures such as functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) can improve drainage and remove obstructions.
- Allergy Management: For chronic sinusitis related to allergies, identifying and managing allergens is crucial to prevent recurrence.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Lifestyle changes, including avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, can help reduce irritants that exacerbate sinusitis.
- Follow-Up: Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
- Sinus Rinse Kits: Using sinus rinse kits with saline solution can help keep the nasal passages clear of mucus and irritants.
- Preventive Measures: Discussing preventive measures with a healthcare provider, such as flu vaccines or allergy management strategies, can reduce the risk of recurring swelling.
These points highlight the diverse approaches to diagnosing and treating swelling, considering factors like its underlying cause and the severity of symptoms.
Prevention
Preventing swelling often involves minimizing exposure to allergens, practicing good hand hygiene, and staying hydrated. If you have a history of swelling, discussing preventive strategies with a healthcare provider can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Swelling a common condition with various underlying causes, but it is typically manageable with proper diagnosis and treatment. Understanding its symptoms and triggers can help individuals take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort and improve their quality of life.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023