Sjogren’s Syndrome: Unveiling the Challenges of Autoimmunity
Introduction
Sjogren’s syndrome, often pronounced “shuh-gren’s,” is a complex autoimmune disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of Sjogren’s syndrome, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and its impact on the lives of those affected by this chronic condition.
Understanding Sjogren’s Syndrome
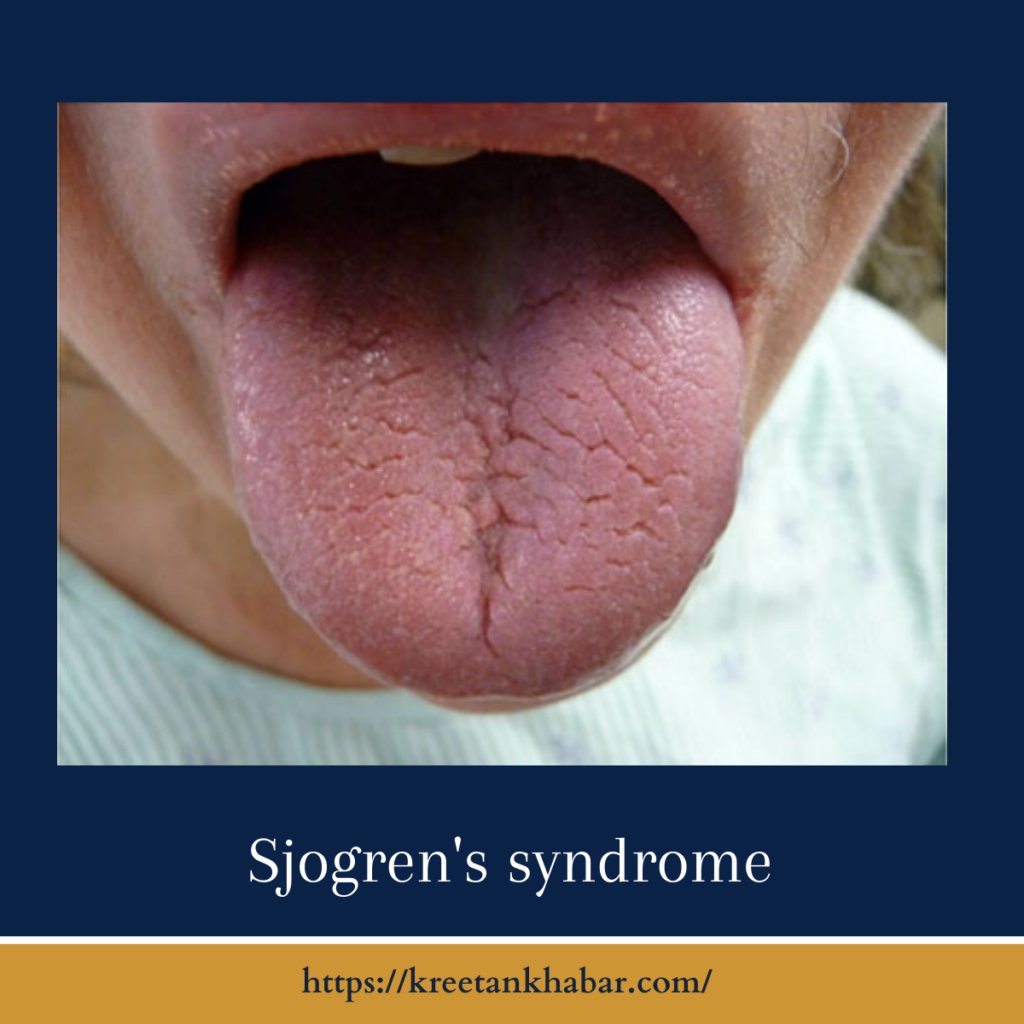
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and damages the exocrine glands, primarily the salivary and lacrimal glands. These glands are responsible for producing saliva and tears, making dryness a hallmark symptom of the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Sjogren’s syndrome remains unknown, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetics: A genetic predisposition may increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Hormones: Hormonal factors, particularly in women, are thought to play a role, as the syndrome predominantly affects females.
- Viral Infections: Some viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus, have been linked to an increased risk of Sjogren’s syndrome.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain environmental factors may trigger the autoimmune response in susceptible individuals.
Common Symptoms
Sjogren’s syndrome is characterized by a range of symptoms that can affect various parts of the body:
- Dry Eyes: Chronic dryness and irritation of the eyes, often described as feeling like sandpaper.
- Dry Mouth: Persistent dryness of the mouth, leading to difficulty in speaking and swallowing.
- Fatigue: Profound and unrelenting fatigue that can interfere with daily activities.
- Joint Pain: Joint pain and stiffness, which can mimic the symptoms of arthritis.
- Dry Skin: Skin dryness and itchiness are common complaints.
- Dental Problems: Increased risk of dental cavities and gum disease due to decreased saliva production.
- Dry or Inflamed Throat: Sore throat and difficulty in swallowing may occur.
- Vaginal Dryness: Women with Sjogren’s syndrome may experience vaginal dryness, which can lead to discomfort.
Here are 30 common symptoms associated with Sjogren’s syndrome:
- Dry Eyes: Persistent dryness, grittiness, and discomfort in the eyes.
- Dry Mouth: Chronic dryness and a sticky feeling in the mouth.
- Fatigue: Profound and unexplained tiredness that can be debilitating.
- Joint Pain: Aching, stiffness, and swelling in the joints, often resembling arthritis.
- Dry Skin: Skin dryness and itching, sometimes leading to rashes or eczema.
- Dry or Inflamed Throat: A persistent sore or scratchy throat that may make swallowing difficult.
- Dental Issues: Increased risk of dental cavities, gum disease, and tooth decay due to reduced saliva production.
- Vaginal Dryness: Women with Sjogren’s syndrome may experience dryness, discomfort, and pain during sexual activity.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Trouble swallowing due to a lack of saliva and dryness in the throat.
- Dry Nose: Dryness inside the nose, which can lead to nosebleeds and discomfort.
- Dry Cough: A chronic, non-productive cough due to dryness in the respiratory tract.
- Change in Taste: An altered or reduced sense of taste, known as dysgeusia.
- Burning or Itching Eyes: A sensation of burning or itching in the eyes, often accompanied by redness.
- Eye Fatigue: Eyes may tire easily, especially when reading or using screens.
- Photosensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light, causing discomfort in bright environments.
- Muscle Pain: Muscular discomfort and pain, similar to fibromyalgia.
- Swollen Salivary Glands: Swelling and tenderness in the salivary glands, particularly around the jawline.
- Difficulty Speaking: Dryness in the mouth and throat can lead to hoarseness and difficulty in articulating words.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes, especially in the neck and under the jaw.
- Oral Sores: Recurrent mouth sores or ulcers, often painful.
- Eye Infections: Increased susceptibility to eye infections due to dryness.
- Skin Sensitivity: Heightened skin sensitivity and discomfort, especially in dry or windy weather.
- Headaches: Frequent headaches or migraines may occur as a symptom.
- Sleep Disturbances: Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep due to discomfort.
- Painful Chewing: Pain or discomfort while eating or chewing, primarily due to dry mouth.
- Blurred Vision: Temporary blurred vision, especially upon waking in the morning.
- Memory Issues: Difficulty concentrating and memory problems.
- Difficulty Wearing Contact Lenses: Discomfort and intolerance to contact lenses due to dry eyes.
- Nasal Congestion: Chronic nasal congestion and dryness.
- Depression and Anxiety: Emotional and psychological symptoms such as depression and anxiety can often accompany the physical symptoms of Sjogren’s syndrome.
These symptoms can vary in severity and may come and go over time. Sjogren’s syndrome is a complex condition, and individuals with the syndrome may experience a combination of these symptoms to varying degrees.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Sjogren’s syndrome is often challenging due to its varied and overlapping symptoms. Key diagnostic steps include:
- Medical History: A comprehensive medical history helps identify symptoms and assess their duration.
- Physical Examination: Physical signs such as dry eyes and mouth are assessed.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests measure specific antibodies (such as anti-SSA and anti-SSB) and markers of inflammation.
- Eye and Mouth Evaluation: Specialized tests like the Schirmer’s test and salivary gland biopsy may be performed to assess eye and mouth dryness.
- Imaging: Imaging studies like ultrasound or scintigraphy can help evaluate the salivary glands.
Treatment Options
Sjogren’s syndrome is a chronic condition with no known cure, but various treatments aim to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Artificial Tears and Saliva Substitutes: These over-the-counter or prescription products help manage dry eyes and mouth.
- Immunosuppressive Drugs: Medications like corticosteroids and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) can help suppress the autoimmune response.
- Prescription Medications: Drugs like pilocarpine and cevimeline stimulate saliva and tear production.
- Hydroxychloroquine: This medication is sometimes used to manage joint and skin symptoms.
- Dental Care: Regular dental check-ups and oral hygiene practices are essential to prevent dental complications.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Staying hydrated, using humidifiers, and avoiding environmental triggers can help manage symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy and gentle exercises can help manage joint pain and stiffness.
- Psychological Support: Living with a chronic condition can be emotionally challenging, and counseling or support groups can provide valuable assistance.
Conclusion
Sjogren’s syndrome is a complex autoimmune disorder that affects multiple aspects of a person’s health and well-being. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment, involving rheumatologists, ophthalmologists, and dentists, are essential in managing this condition. While there is no cure, the right combination of treatments and lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with Sjogren’s syndrome, allowing them to navigate the challenges of autoimmunity with resilience and grace.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023