Suprascapular Neuropathy
Introduction
In the orchestral composition of the human body, the shoulders play a silent yet crucial symphony, facilitating an intricate dance of movements. However, when a condition like Suprascapular Neuropathy takes center stage, this symphony encounters disruptions, leading to discomfort, weakness, and an array of challenges. Let’s delve into the nuanced world of suprascapular neuropathy, exploring its origins, manifestations, and the strategies employed to restore harmony to the shoulders.
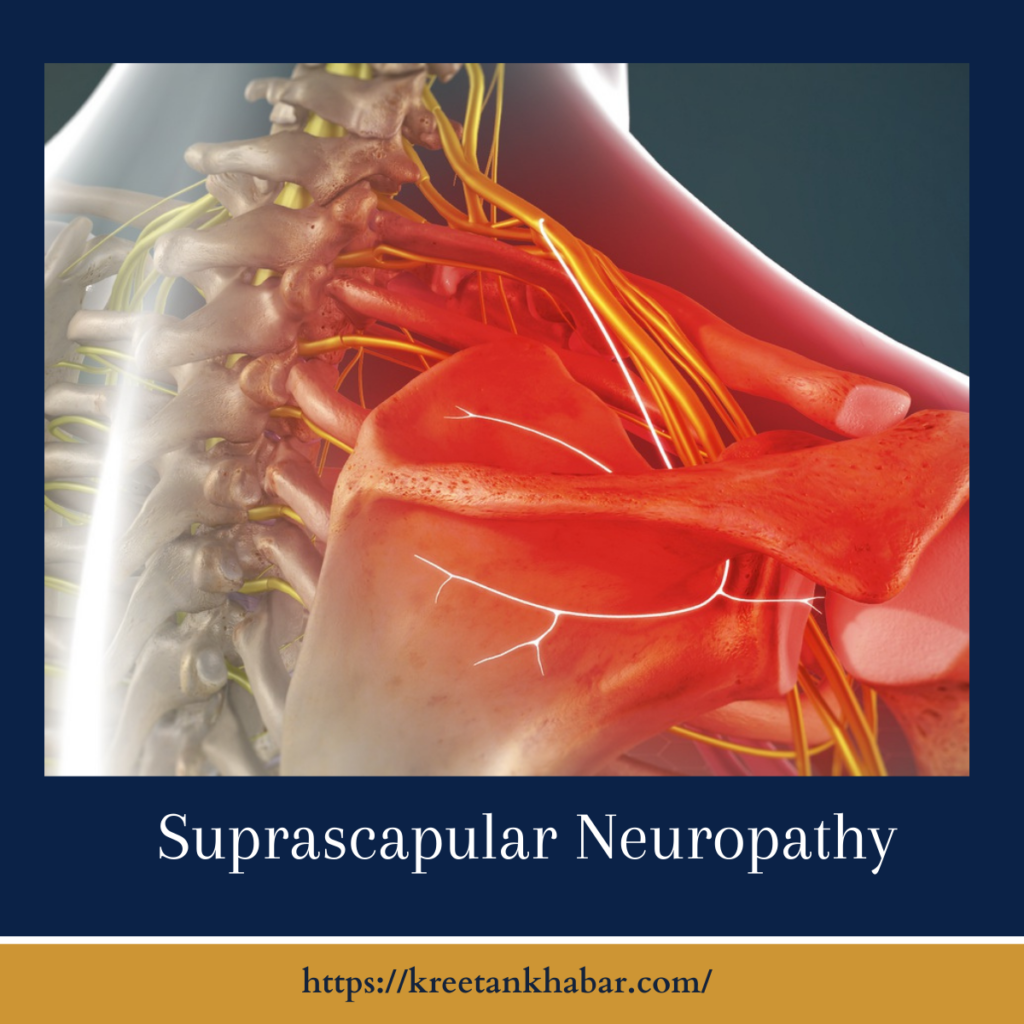
The Anatomy of the Shoulder Symphony
The suprascapular nerve, a key player in the shoulder symphony, arises from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. Its branches intricately weave through the shoulder region, supplying vital motor and sensory functions to the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles. When this nerve encounters entrapment, compression, or injury, the result is a silent yet impactful disruption—Suprascapular Neuropathy.
Origins and Causes
- Entrapment and Compression Ballet:
- Suprascapular neuropathy often emerges from the entrapment or compression of the nerve along its course.
- Causes include anatomical variations, cysts, ganglion compressions, or inflammation within the shoulder’s complex landscape.
- Overhead Movements Overture:
- Overhead athletes, particularly those engaging in repetitive overhead movements, may find themselves susceptible to suprascapular neuropathy.
- This includes athletes in sports like volleyball, tennis, or weightlifting, where the shoulder undergoes frequent and intense use.
- Trauma as a Crescendo:
- Trauma, such as direct impact or shoulder injuries, can serve as a crescendo in the development of suprascapular neuropathy.
- Fractures, dislocations, or repetitive microtrauma can contribute to nerve damage and compromise its function.
Symptoms: The Unheard Melody
Suprascapular neuropathy paints a subtle yet impactful portrait with its array of symptoms, each note resonating in the intricate landscape of the shoulders. Picture the silent melody of shoulder weakness as the leading theme, where individuals find themselves navigating daily tasks with a sense of resistance and difficulty lifting the arm. Shoulder pain, a more nuanced note.
weaves into the composition, manifesting as a subtle ache that often lingers around the shoulder blade or travels down the back of the arm. As the neuropathy progresses, muscle atrophy joins the symphony, introducing a visual element to the performance with a noticeable loss of shoulder muscle mass. Each of these symptoms, though quiet individually, collectively plays a part in this intricate composition, reminding individuals of the delicate dance occurring within their shoulder’s silent symphony.
- Shoulder Weakness Duet:
- One of the primary manifestations of suprascapular neuropathy is weakness in the shoulder muscles it innervates.
- Individuals may experience difficulty lifting the arm or performing overhead movements.
- Shoulder Pain as a Subtle Note:
- Shoulder pain, though subtle, becomes a note in the unheard melody of suprascapular neuropathy.
- The pain may be localized to the shoulder blade region or radiate down the back of the arm.
- Muscle Atrophy Symphony:
- Over time, persistent neuropathy may lead to muscle atrophy in the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles.
- This can contribute to a noticeable loss of shoulder muscle mass and altered shoulder contour.
Diagnosis: Decoding the Silent Symphony
- Clinical Evaluation Pas de Deux:
- Diagnosis involves a clinical evaluation, where healthcare professionals assess the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and perform physical examinations.
- Specific tests may be conducted to evaluate strength, range of motion, and pinpoint areas of discomfort.
- Imaging Harmonies:
- Imaging studies, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound, play a crucial role in visualizing the shoulder’s internal structures.
- These studies aid in identifying potential causes of nerve entrapment or compression.
- Electromyography (EMG) Solo:
- Electromyography may be employed to assess the electrical activity of muscles, helping identify areas of nerve dysfunction.
- This diagnostic tool assists in confirming the presence and extent of suprascapular neuropathy.
Treatment: The Rehabilitation Sonata
Navigating the treatment of suprascapular neuropathy involves orchestrating a comprehensive approach to restore the shoulders’ silent symphony. The initial movements often include conservative measures, where the tempo slows to allow for rest, activity modification, and the careful guidance of physical therapy. Picture a rehabilitation sonata designed by skilled therapists, aimed at strengthening shoulder muscles and improving joint function.
In some instances, anti-inflammatory notes join the composition, providing relief and reducing the swelling that contributes to the neuropathy. When needed, corticosteroid injections emerge as a targeted intermezzo, delicately alleviating localized inflammation. For cases requiring a more pronounced crescendo, surgical interventions take center stage, aiming to release nerve entrapment or decompress the affected nerve. Yet, the true artistry lies in the postoperative coda, where rehabilitation and strengthening exercises become the gentle yet vital concluding notes, guiding individuals toward rediscovering the harmonious movement and strength inherent in the shoulder’s intricate dance.
- Conservative Measures Prelude:
- Initial treatment often involves conservative measures such as rest, activity modification, and physical therapy.
- Physical therapists design rehabilitation programs to strengthen shoulder muscles and improve overall joint function.
- Anti-inflammatory Cadence:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area.
- This helps manage symptoms and contributes to the overall treatment composition.
- Corticosteroid Injections Intermezzo:
- Corticosteroid injections may be considered to address inflammation and provide targeted relief.
- These injections are often administered under imaging guidance to ensure precision.
- Surgical Crescendo:
- In cases resistant to conservative measures, surgical intervention may take center stage.
- The goal is to release nerve entrapment or decompress the nerve through procedures such as arthroscopy or open surgery.
- Rehabilitation and Strengthening Coda:
- Postoperative rehabilitation becomes a critical coda, guiding individuals through exercises to restore strength, flexibility, and functionality.
- The rehabilitation process ensures a seamless transition back into the shoulder’s silent symphony.
Conclusion: Rediscovering Harmony
Suprascapular neuropathy may introduce a temporary dissonance into the shoulder symphony, but with accurate diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, the goal is to rediscover harmony. Whether through conservative measures, medical interventions, or surgical crescendos, the silent symphony of the shoulders can regain its fluidity, allowing individuals to once again move through life with the grace and strength inherent in the intricate dance of the human body.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023