Tapeworm Infection
Introduction
In the unseen realms of parasitic invaders, the tapeworm stands as a remarkable yet unsettling character in the intricate drama of human health. A tapeworm infection, scientifically known as taeniasis, is a parasitic condition that, though often associated with underdeveloped regions, can transcend geographical boundaries and find its way into unsuspecting hosts. Let’s delve into the complexities of tapeworm infection, exploring its origins, symptoms, and the strategies to navigate the labyrinth of prevention and treatment.
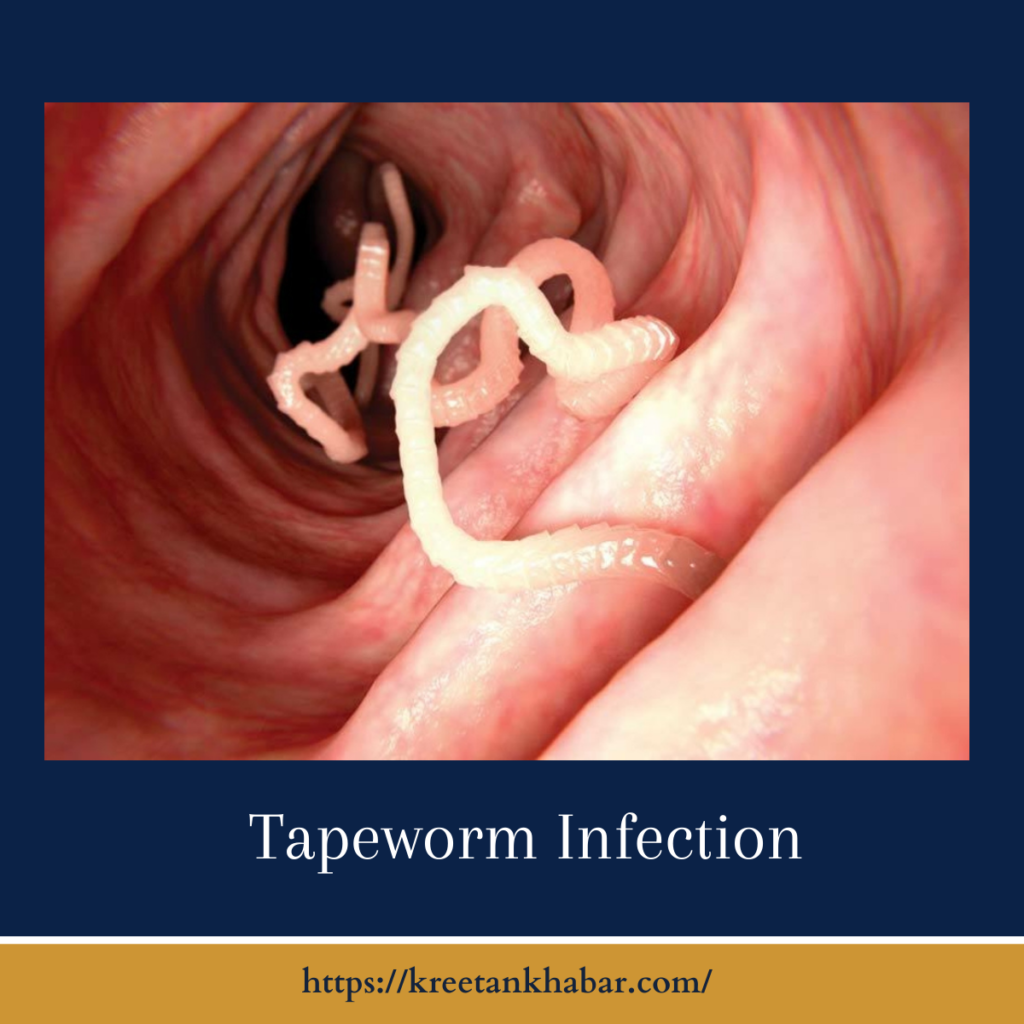
The Life Cycle Unveiled
The tapeworm’s life cycle is a remarkable feat of adaptation, often involving multiple hosts. It begins as eggs are ingested by an intermediate host, typically a grazing animal. Within the host’s digestive system, these eggs hatch into larvae, which then migrate to various tissues. When the intermediate host is consumed by a human or another definitive host, the tapeworm larvae are liberated in the intestines, where they mature into adult tapeworms and attach themselves to the intestinal wall.
Origins and Sources
Tapeworm infections can find their origins in various sources, with contaminated food and water serving as primary conduits. Consuming undercooked or raw meat, particularly pork, beef, and fish, represents a common route of infection. Additionally, inadequate hygiene practices and contact with contaminated surfaces can facilitate the transmission of tapeworm eggs, emphasizing the importance of sanitation in preventing infection.
Symptoms and Silent Invaders
One of the intriguing aspects of tapeworm infections is their often subtle or asymptomatic nature. Individuals infected with tapeworms may not exhibit obvious symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, as the tapeworm grows and matures, some common signs may emerge, including abdominal discomfort, nausea, weight loss, and changes in bowel habits. In more severe cases or specific types of tapeworms, segments of the worm may be visible in the stool.
Prevention: A Shield Against Intruders
Preventing tapeworm infection involves a combination of vigilant hygiene practices and mindful consumption habits. Cooking meat thoroughly, especially pork, beef, and fish, ensures that any potential tapeworm larvae are killed. Adopting stringent hygiene measures, such as washing hands thoroughly before eating and after using the restroom, contributes to breaking the transmission cycle. Additionally, avoiding the consumption of raw or undercooked fish and meats, and treating pets for potential tapeworm infections, adds layers to the defense against these silent invaders.
- Thorough Cooking of Meat: Ensure that meat, especially pork, beef, and fish, is cooked thoroughly before consumption. Proper cooking kills tapeworm larvae that may be present in raw or undercooked meat, acting as a crucial line of defense against infection.
- Safe Food Handling Practices: Adopt safe food handling practices to prevent contamination. This includes using separate cutting boards for raw meat and other food items, washing hands thoroughly after handling raw meat, and avoiding cross-contamination during food preparation.
- Freezing or Curing Fish: If consuming raw or undercooked fish, freezing it beforehand or curing it through methods like smoking or salting can help kill potential tapeworm larvae. These precautions are especially important for dishes like sushi or ceviche.
- Proper Hand Hygiene: Practice proper hand hygiene, particularly before eating and after using the restroom. Thorough handwashing with soap and water helps prevent the transmission of tapeworm eggs from contaminated surfaces to the mouth.
- Avoiding Raw Meat: Minimize the consumption of raw or undercooked meat, especially in regions where tapeworm infections are more prevalent. Cooking meat to the recommended temperatures reduces the risk of ingesting tapeworm larvae.
- Educational Awareness: Stay informed about the regions or areas where tapeworm infections are more common. Being aware of potential risks and understanding preventive measures is crucial, especially for individuals residing in or traveling to areas with a higher prevalence of tapeworm infections.
- Proper Sanitation: Maintain proper sanitation practices in living spaces. This includes ensuring the cleanliness of living areas, practicing safe waste disposal, and avoiding contact with fecal matter that may contain tapeworm eggs.
- Avoiding Raw or Undercooked Animal Products: In addition to meat, be cautious with other animal products like milk and eggs. Ensure that these items are sourced from reputable and sanitary sources to minimize the risk of tapeworm contamination.
- Regular Pet Deworming: If living with pets, ensure they receive regular deworming treatments. Pets, particularly dogs and cats, can harbor tapeworms, and preventing their transmission to humans involves maintaining the health and hygiene of animal companions.
- Seeking Medical Attention: If residing in or traveling to regions with a high prevalence of tapeworm infections, seeking medical attention for any unexplained symptoms is crucial. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing the progression of tapeworm infection and its potential complications.
Treatment: Evicting the Unwanted Guest
In the event of a confirmed tapeworm infection, treatment becomes a priority to evict the unwanted guest from the digestive system. Antiparasitic medications, prescribed by healthcare professionals, are the primary weapons against tapeworms. These medications work by killing the tapeworm or causing it to release its grip on the intestinal wall, allowing the body to expel the parasite naturally.
Conclusion
The tapeworm, a seemingly unassuming yet remarkable creature in the world of parasites, has woven its tale of infection across cultures and continents. Unveiling the realities of tapeworm infection empowers individuals to adopt preventative measures and seek timely treatment when needed. Through the combination of hygiene practices, informed consumption habits, and medical intervention, we can navigate the intricate pathways of tapeworm prevention and treatment, safeguarding our digestive health from these silent invaders.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023