Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears
Introduction:
The human wrist is a marvel of intricate mechanics, allowing us to perform a myriad of daily tasks with precision. Yet, like any complex machinery, it is susceptible to wear and tear. One common issue that can affect wrist stability is a tear in the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC). In this article, we will explore what the TFCC is, the causes and symptoms of tears, and the various treatment options available for those grappling with this condition.
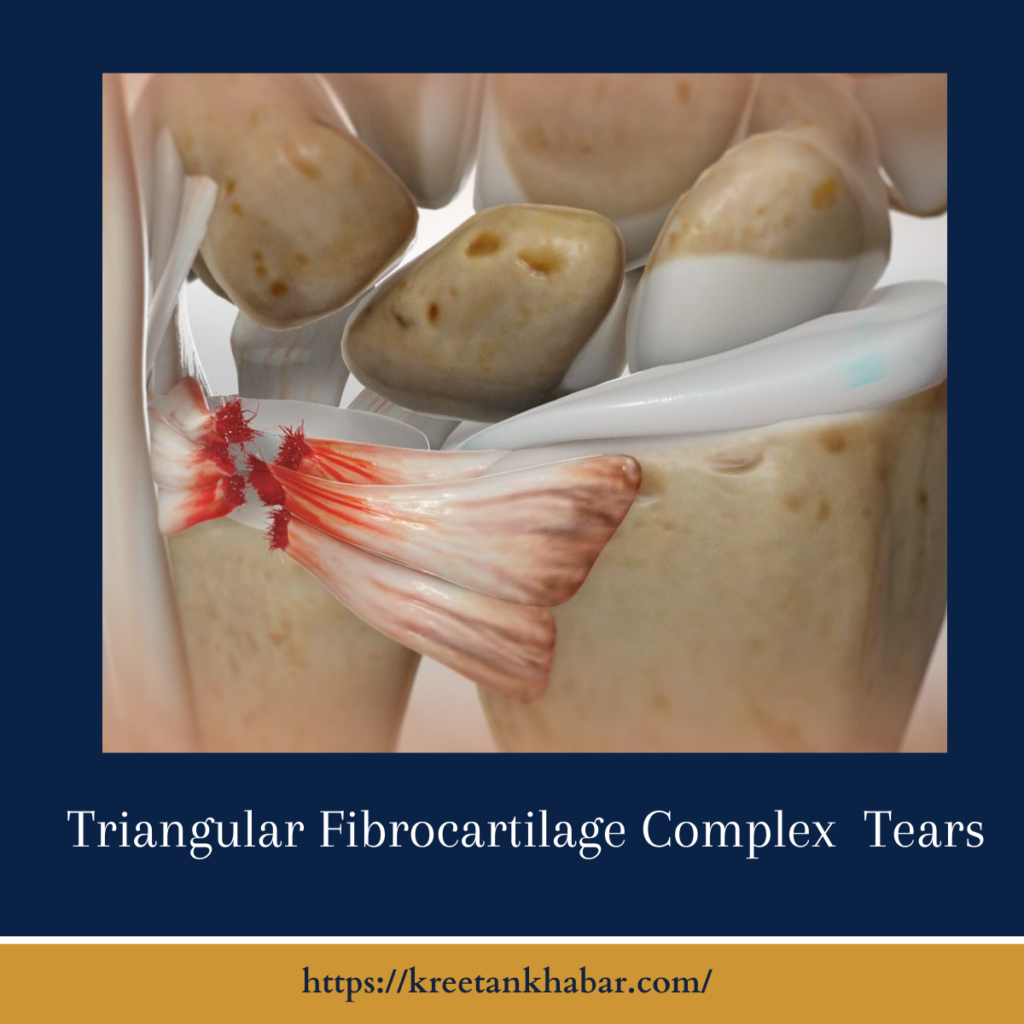
Understanding the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex:
The Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex is a critical structure in the wrist that provides stability and support. Situated on the ulnar side of the wrist, it is a triangular-shaped piece of cartilage and ligaments that cushions and reinforces the joint between the ulna and the carpal bones. The TFCC plays a crucial role in maintaining proper wrist function and distributing forces during gripping and rotational movements.
Causes of TFCC Tears:
- Trauma:
- A sudden, forceful impact on the wrist, such as a fall onto an outstretched hand, can lead to acute TFCC tears.
- Repetitive Stress:
- Engaging in activities that involve repetitive wrist movements or loading, such as certain sports or manual labor, may contribute to gradual wear and tear of the TFCC.
- Aging:
- As individuals age, the TFCC can naturally degenerate, making it more prone to tears. This age-related wear can be exacerbated by other factors like arthritis.
- Ulnar Variance:
- Anatomic variations in the length of the ulna compared to the radius, known as ulnar variance, can increase the risk of TFCC tears.
- Instability:
- Chronic instability in the wrist, often related to ligament injuries, can put additional stress on the TFCC and lead to tears over time.
- Sports Injuries:
- Athletes involved in activities that stress the wrist, such as gymnastics or racket sports, may be more susceptible to TFCC tears.
- Work-Related Factors:
- Certain occupations that involve repetitive or forceful hand movements, such as manual labor or typing, can contribute to TFCC injuries.
Symptoms of TFCC Tears:
Recognizing the symptoms of TFCC tears is crucial for early intervention. Common indicators include:
- Pain on the Ulnar Side of the Wrist:
- Persistent pain on the side of the wrist closest to the little finger, particularly during gripping or rotational movements.
- Swelling and Tenderness:
- Swelling and tenderness in the wrist, especially along the ulnar side, may be present.
- Clicking or Popping Sensation:
- Some individuals may experience a clicking, popping, or grinding sensation during wrist movements.
- Weak Grip Strength:
- Decreased grip strength, particularly when trying to grasp or hold onto objects.
- Limited Range of Motion:
- Difficulty in fully rotating or bending the wrist without pain.
- Pain with Weight-Bearing:
- Pain that intensifies during activities that put weight on the affected wrist, such as push-ups or weightlifting.
More points of symptoms:
Treatment Options for TFCC Tears:
- Rest and Immobilization:
- Temporary cessation of activities that exacerbate symptoms, coupled with the use of a brace or splint to immobilize the wrist.
- Ice and Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
- Applying ice to reduce swelling and using nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy:
- Targeted exercises to strengthen the muscles around the wrist and improve range of motion.
- Corticosteroid Injections:
- In some cases, a healthcare provider may administer corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
- Arthroscopic Surgery:
- Minimally invasive surgery to repair or debride the torn TFCC, often performed using arthroscopy.
- Open Surgery:
- For more severe cases, traditional open surgery may be necessary to address complex Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears.
- Ulnar Shortening Osteotomy:
- A surgical procedure to address ulnar variance by shortening the ulna, reducing strain on the Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears.
- PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) Therapy:
- An emerging treatment option involving the injection of concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood to promote healing.
Conclusion:
TFCC tears can significantly impact wrist function and quality of life, but with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, individuals can often regain stability and alleviate symptoms. If you suspect a TFCC tear or are experiencing persistent wrist pain, seeking the guidance of a healthcare professional is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. From conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to surgical interventions, the array of treatment options reflects the commitment to restoring optimal wrist function for those grappling with Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Tears.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023