Understanding Penile Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction
Penile cancer, though relatively rare, is a serious condition that can affect men of all ages. It occurs when malignant cells grow in the tissues of the penis. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and available treatment options for penile cancer.
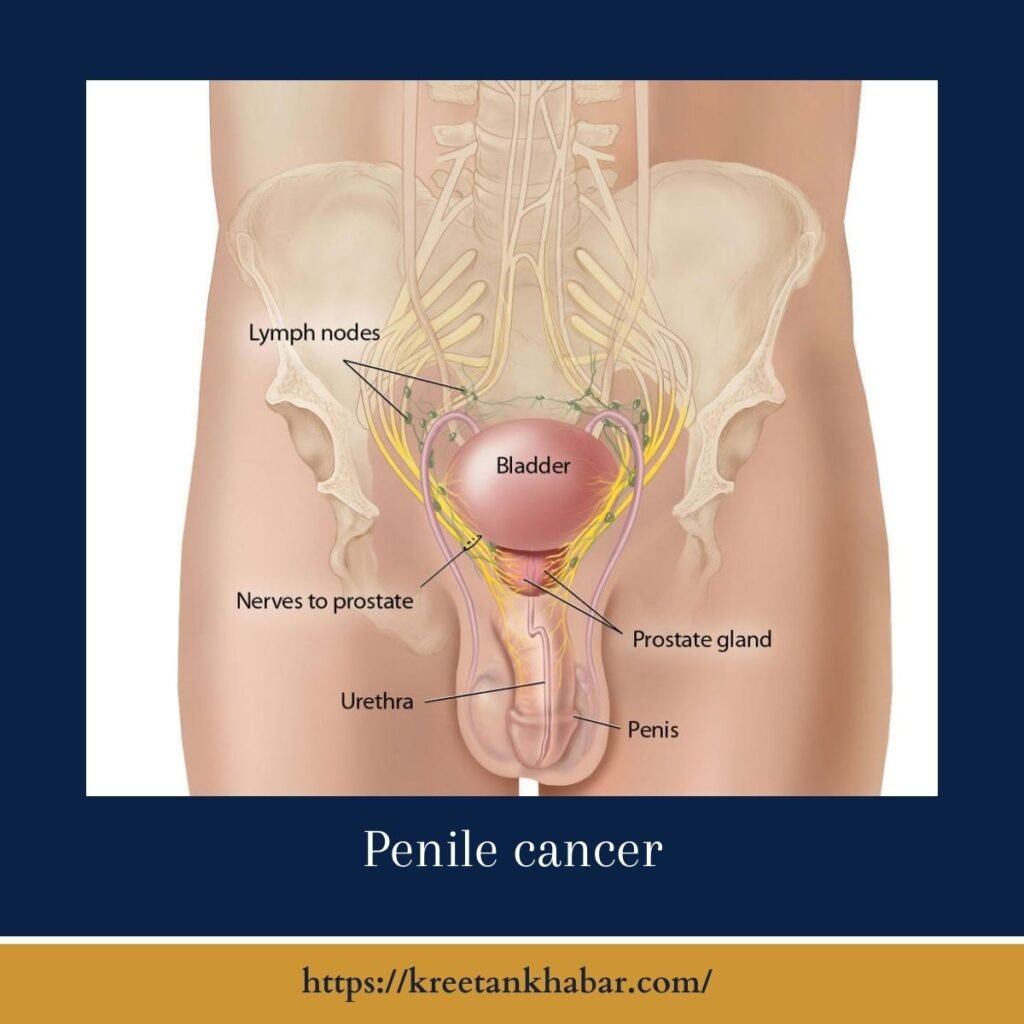
What is Penile Cancer?
Penile cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the penis. It typically starts in the skin or in the tissues that line the internal structures of the penis. Penile cancer can be aggressive, so early detection and treatment are crucial for the best possible outcome.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of penile cancer is not always clear, but several risk factors are associated with an increased likelihood of developing the disease:
- HPV Infection: Infection with certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV) is a significant risk factor for penile cancer. Practicing safe sex and getting the HPV vaccine can reduce this risk.
- Phimosis: Uncircumcised men with a condition called phimosis, where the foreskin cannot be retracted over the glans, have a higher risk.
- Tobacco Use: Smoking cigarettes or using smokeless tobacco products increases the risk of penile cancer.
- Age: Penile cancer is more common in older men, typically occurring in their 60s or 70s.
- Poor Hygiene: Lack of proper hygiene, which can lead to chronic irritation and infection, may contribute to the development of penile cancer.
- Genital Hygiene: Practices such as regular cleaning of the genital area can reduce the risk of infection and inflammation.
Common Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of penile cancer may include:
- A lump or growth on the penis: A painless lump or sore on the penis is often the first noticeable sign.
- Changes in the skin: Discoloration, thickening, or changes in the texture of the penile skin.
- Ulceration or sores: Open sores that may bleed or ooze.
- Redness or irritation: Persistent redness or irritation in the penile area.
- Foul-smelling discharge: A discharge that has an unpleasant odor.
- Bleeding: Bleeding from the penis that is not related to an injury.
Diagnosis
If any of the above symptoms are present, it is important to seek medical evaluation. A healthcare provider will typically perform the following diagnostic tests:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the penis and surrounding areas.
- Biopsy: Removal of a small tissue sample for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of cancer.
- Imaging: Imaging tests such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be conducted to determine the extent of cancer’s spread.
Treatment Options
The choice of treatment for penile cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgery to remove the cancerous tissue is often the primary treatment. This may involve partial or total removal of the penis (penectomy).
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy X-rays or other radiation sources may be used to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Medications are used to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. Chemotherapy may be used in advanced cases or in combination with other treatments.
- Mohs Surgery: A specialized technique to remove skin cancers layer by layer, preserving healthy tissue.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials may be an option for some patients, especially if conventional treatments are not effective.
here are the key treatment options for penile cancer:
- Surgery:
- Partial Penectomy: In cases where the cancer is small and localized, only a part of the penis may be removed.
- Total Penectomy: For more advanced cases, the entire penis may need to be surgically removed. However, reconstructive surgery (penile reconstruction) can often be performed to restore appearance and function.
- Radiation Therapy:
- External Beam Radiation: High-energy X-rays are directed at the cancerous tissue to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors. It may be used as the primary treatment or after surgery to target any remaining cancer cells.
- Brachytherapy: Radioactive implants are placed directly inside the tumor to deliver radiation from within.
- Chemotherapy:
- Systemic Chemotherapy: Medications are administered intravenously or orally to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. Chemotherapy is typically used in advanced cases or when cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Laser Therapy:
- Laser Ablation: High-intensity laser beams are used to target and vaporize cancerous tissue. This minimally invasive procedure may be suitable for early-stage penile cancer.
- Cryotherapy:
- Cryosurgery: Extremely cold gases or liquids are used to freeze and destroy cancer cells. This approach is sometimes considered for small tumors or as palliative care to alleviate symptoms.
- Immunotherapy:
- PD-1 Inhibitors: Drugs like pembrolizumab and nivolumab, which block PD-1 proteins, are being studied for their potential to enhance the body’s immune response against penile cancer cells.
- Clinical Trials:
- Participation in clinical trials may provide access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies that are not yet widely available.
- Adjuvant Therapy:
- Some patients may receive additional treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy after surgery to reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
- Palliative Care:
- In advanced stages where a cure is not possible, palliative care focuses on improving the patient’s quality of life. It may involve pain management, symptom control, and emotional support.
- Follow-Up Care:
- Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential to monitor for any signs of cancer recurrence and to address any potential side effects of treatment.
- Supportive Services:
- Psychological counseling, support groups, and sexual health counseling can be valuable for patients and their partners to cope with the physical and emotional challenges of penile cancer and its treatment.
The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the stage of cancer, the location and size of the tumor, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment plans are often personalized to address the specific needs and goals of each individual diagnosed with penile cancer.
Conclusion
Penile cancer is a rare but serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Early detection, regular check-ups, and adopting healthy lifestyle choices can reduce the risk of developing this disease. If diagnosed and treated in the early stages, the prognosis for penile cancer can be quite positive, emphasizing the importance of awareness and timely medical intervention.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023