Introduction:
Prostate cancer, a pervasive ailment that impacts men across the globe, continues to pose a significant health challenge. As the second most common cancer in men, it is crucial to be aware of its symptoms to ensure early detection and prompt treatment. In this article, we will explore the various signs and symptoms of prostate cancer, empowering men with knowledge to take charge of their health.
Prostate cancer, like any other form of cancer, can progress to advanced stages if not detected and treated early. While not all men diagnosed with prostate cancer will reach the end stage, it is important to be aware of the potential signs and symptoms that may indicate advanced disease. In this article, we will discuss some of the signs that could suggest a person is in the later stages of prostate cancer. It is crucial to note that these symptoms do not automatically imply a terminal prognosis, but they do warrant immediate medical attention.
Recognizing Signs of Advanced Prostate Cancer: Understanding the Potential prostate cancer symptoms
Changes in Urination:
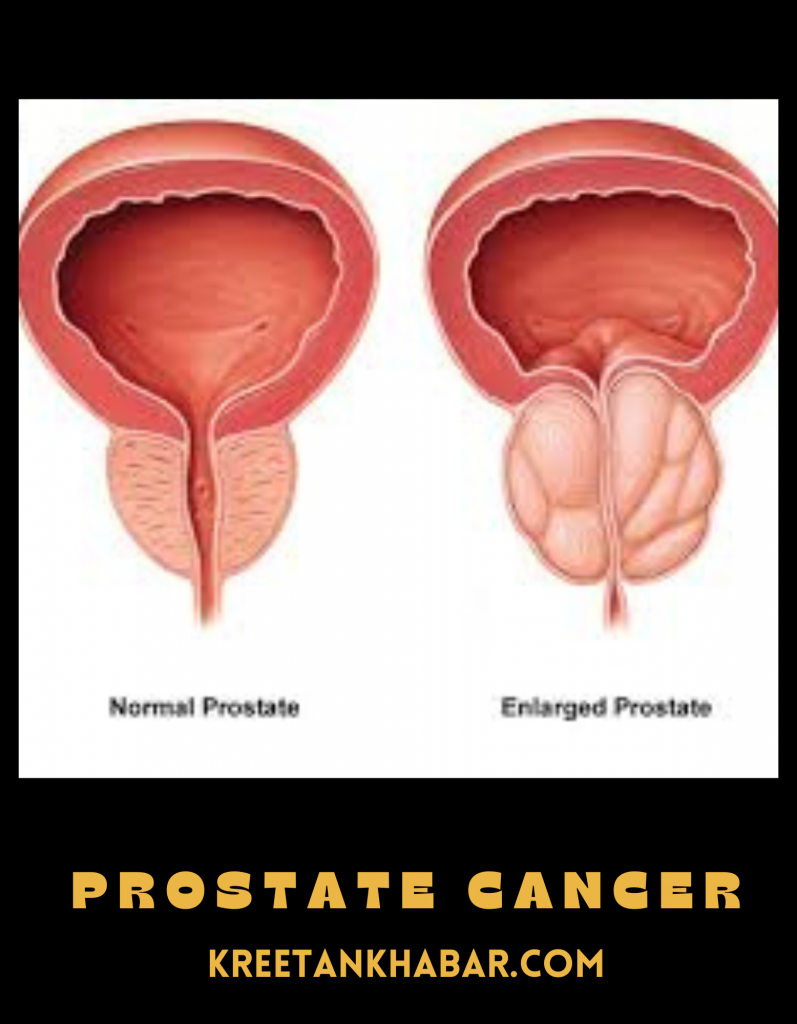
One of the primary symptoms of prostate cancer is changes in urinary patterns. Men may experience increased frequency of urination, particularly during the night (nocturia). They may also notice a sense of urgency or a need to strain while urinating. Additionally, a weak or interrupted urine flow and difficulty initiating or stopping urination can indicate the presence of prostate cancer.
Blood in Urine or Semen:
The presence of blood in urine or semen, medically known as hematuria and hematospermia, respectively, can be alarming and should never be ignored. Although these symptoms can have various causes, they can also be a warning sign of this cancer. If you notice blood in your urine or semen, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation.
Erectile Dysfunction:
Prostate cancer can affect sexual function, leading to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection, commonly known as erectile dysfunction. While many factors can contribute to this condition, it is worth considering prostate cancer as a possible cause, especially if accompanied by other prostate-related symptoms.
Pelvic Pain and Discomfort:
Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic area, lower back, hips, or thighs can be an indication of advanced prostate cancer. These symptoms may arise due to the spread of cancer cells to nearby tissues and bones. If you experience ongoing pain or discomfort in these areas, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Fatigue and Weight Loss:
In some cases, This cancer may lead to unexplained fatigue and weight loss. Cancer cells can disrupt the normal functioning of the body, leading to a general feeling of tiredness and a decrease in appetite. If you notice a significant and unexplained weight loss accompanied by persistent fatigue, it is important to seek medical attention.
Worsening Bone Pain:
As prostate cancer progresses, it may spread (metastasize) to the bones, particularly in the spine, hips, and pelvis. This can cause persistent and severe bone pain that may not respond to conventional pain management strategies. The pain might worsen over time, limiting mobility and affecting the overall quality of life.
Urinary and Bowel Dysfunction:
Advanced prostate cancer can exert pressure on the urinary tract and rectum, leading to urinary and bowel dysfunction. Symptoms may include urinary incontinence, increased urinary frequency, urgency, difficulty in urination, and the sensation of incomplete emptying of the bladder. Bowel changes such as constipation, diarrhea, or rectal bleeding can also occur due to the tumor’s proximity to the rectum.
Fatigue and Weakness:
Fatigue is a common symptom experienced by individuals with advanced prostate cancer. The cancer cells can disrupt normal bodily functions, leading to profound tiredness and weakness. Fatigue may be persistent and not alleviated by rest or sleep. It can significantly impact daily activities and diminish overall quality of life.
Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss:
As the cancer progresses, individuals may experience a loss of appetite, leading to unintentional weight loss. The tumor’s metabolic demands, as well as the body’s response to cancer, can result in a decreased desire to eat. Significant and unexplained weight loss, along with a lack of appetite, should be brought to the attention of a healthcare professional.
Mental and Emotional Changes:
Advanced prostate cancer can also affect a person’s mental and emotional well-being. Some individuals may experience depression, anxiety, or feelings of hopelessness. Cognitive changes such as confusion, memory problems, or difficulty concentrating may also arise due to the spread of cancer to the brain or as a consequence of the overall burden of the disease.
Note:
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of advanced prostate cancer is crucial for timely medical intervention and appropriate supportive care. Worsening bone pain, urinary and bowel dysfunction, fatigue and weakness, loss of appetite and weight loss, as well as mental and emotional changes, can indicate progression to advanced stages. It is important to remember that these symptoms do not automatically mean a terminal prognosis, as treatment options and outcomes can vary from person to person. Prompt consultation with healthcare professionals and engaging in open discussions about symptoms and concerns is vital for effective management and the best possible quality of life.
What causes prostate cancer ?
The exact cause of prostate cancer is not fully understood, but researchers have identified several factors that can contribute to its development. Age is considered one of the most significant risk factors, as the likelihood of developing prostate cancer increases with age. The intricate interplay of familial heritage and genetic factors further contributes to the susceptibility of men, heightening the risk of prostate cancer in individuals with a family history of this prevalent disease.
Ethnicity has been found to influence the incidence rates, with African-American men being more prone to the disease. Hormonal imbalances, specifically higher levels of testosterone and other male hormones, are believed to promote the growth of prostate cancer cells. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as a poor diet high in saturated fats, obesity, and lack of physical activity may contribute to an increased risk.
While these factors may influence the development of prostate cancer, it’s important to note that many cases occur in individuals with no identifiable risk factors, highlighting the complex nature of the disease. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the causes and mechanisms behind prostate cancer.
In addition to the factors mentioned earlier, researchers have been exploring other potential causes and associations related to prostate cancer. Environmental exposures, such as exposure to certain chemicals or toxins, have been investigated for their possible role in prostate cancer development. However, the evidence regarding specific environmental factors remains inconclusive and requires further study.
Chronic inflammation of the prostate gland, known as prostatitis, has also been proposed as a potential risk factor. Some studies suggest that long-term inflammation may contribute to the development of prostate cancer, but the exact relationship between the two is still under investigation.
Furthermore, there have been ongoing studies examining the role of dietary factors and nutritional choices in prostate cancer. Although no definitive conclusions have been reached, some research suggests that a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and certain nutrients like lycopene (found in tomatoes) may have a protective effect against prostate cancer.
Conversely, diets high in processed foods, red meat, or calcium supplements may potentially increase the risk. However, more research is needed to establish clear associations between specific dietary components and prostate cancer.
It is important to emphasize that while these factors have been implicated in prostate cancer development, they do not guarantee the development of the disease. Many men with one or more risk factors do not develop prostate cancer, while others without identifiable risk factors may still develop the disease. The interplay of various genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors is complex and requires further investigation to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Overall, the exact causes of prostate cancer are multifactorial and likely involve a combination of genetic predisposition, hormonal influences, environmental factors, inflammation, and dietary choices. Continued research efforts are necessary to uncover the underlying mechanisms and develop targeted prevention strategies and treatment approaches to combat this disease effectively.
Prostate cancer survival rate
Prostate cancer survival rates vary depending on several factors, including the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the age and overall health of the individual, and the treatment received. Generally, the prognosis for prostate cancer is favorable, with a high survival rate. According to the American Cancer Society, the five-year relative survival rate for localized prostate cancer (cancer that has not spread beyond the prostate gland) is nearly 100%.
This means that almost all men diagnosed with localized prostate cancer can expect to live at least five years after their diagnosis. For regional prostate cancer (cancer that has spread to nearby structures or lymph nodes), the five-year relative survival rate is around 100% as well. However, for distant or metastatic prostate cancer (cancer that has spread to distant organs), the five-year relative survival rate drops to around 30%.
It is important to note that survival rates are statistical estimates and cannot predict an individual’s specific outcome. Advances in screening, early detection, and treatment options continue to improve survival rates and overall outcomes for men with prostate cancer. Regular medical check-ups, early detection, and timely intervention remain crucial for achieving the best possible prognosis.
Prostate cancer treatment
Certainly! Here are some unique points about this cancer treatment:
Active Surveillance: For men with low-risk prostate cancer, active surveillance may be recommended. This approach involves closely monitoring the cancer’s progression through regular check-ups, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, and periodic biopsies. Active surveillance allows men to delay or avoid immediate treatment while maintaining a proactive approach to monitor any potential changes in the cancer.
Surgery: Surgical removal of the prostate gland, known as a radical prostatectomy, is a common treatment option for localized prostate cancer. The surgery can be performed using different techniques, including open surgery, laparoscopic surgery, or robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery (da Vinci system). The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous prostate gland and surrounding tissues to achieve complete cancer removal.
Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and kill cancer cells in the prostate. External beam radiation therapy (EBRT) delivers radiation from outside the body, while brachytherapy involves implanting radioactive seeds directly into the prostate. Radiation therapy can be used as a primary treatment for localized prostate cancer or as an adjuvant therapy following surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Hormone Therapy: Prostate cancer cells often rely on male hormones (androgens) to grow. Hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), aims to lower the levels of testosterone and other androgens in the body. This can be achieved through medications that either block the production of androgens or inhibit their action. Hormone therapy is used in various settings, including as an initial treatment, in combination with radiation therapy, or for advanced or recurrent prostate cancer.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs can be employed to treat prostate cancer that has spread to other parts of the body (metastatic prostate cancer). Chemotherapy aims to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth. It is typically used when hormone therapy is no longer effective or when the cancer has progressed to an advanced stage. Newer targeted therapies, such as immunotherapy and precision medicines, may also be used in specific cases.
Supportive Care: In addition to the specific treatments, supportive care plays a crucial role in managing prostate cancer. This includes managing symptoms, such as pain or urinary problems, and addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of the disease. Supportive care may involve working with a multidisciplinary team, including oncologists, urologists, nurses, psychologists, nutritionists, and physical therapists, to provide comprehensive care and enhance the quality of life.
It’s important to note that treatment decisions for this cancer are highly individualized and depend on factors such as the stage of the cancer, the aggressiveness of the tumor, the patient’s overall health, and personal preferences. Consulting with a healthcare team experienced in prostate cancer management is vital to determine the most suitable treatment approach for each individual case.
Conclusion:
Recognizing the symptoms of prostate cancer is crucial for early detection and timely treatment. It is important for men to be vigilant and pay attention to any changes in urinary patterns, the presence of blood in urine or semen, erectile dysfunction, pelvic pain, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and guide you through the necessary steps for treatment and care.
Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to prostate cancer, and being proactive about your health can significantly impact the outcome. Regular screenings and discussions with healthcare providers can help identify any potential issues at the earliest stages when treatment options are most effective.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023