Axillary Nerve Disorders: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction:
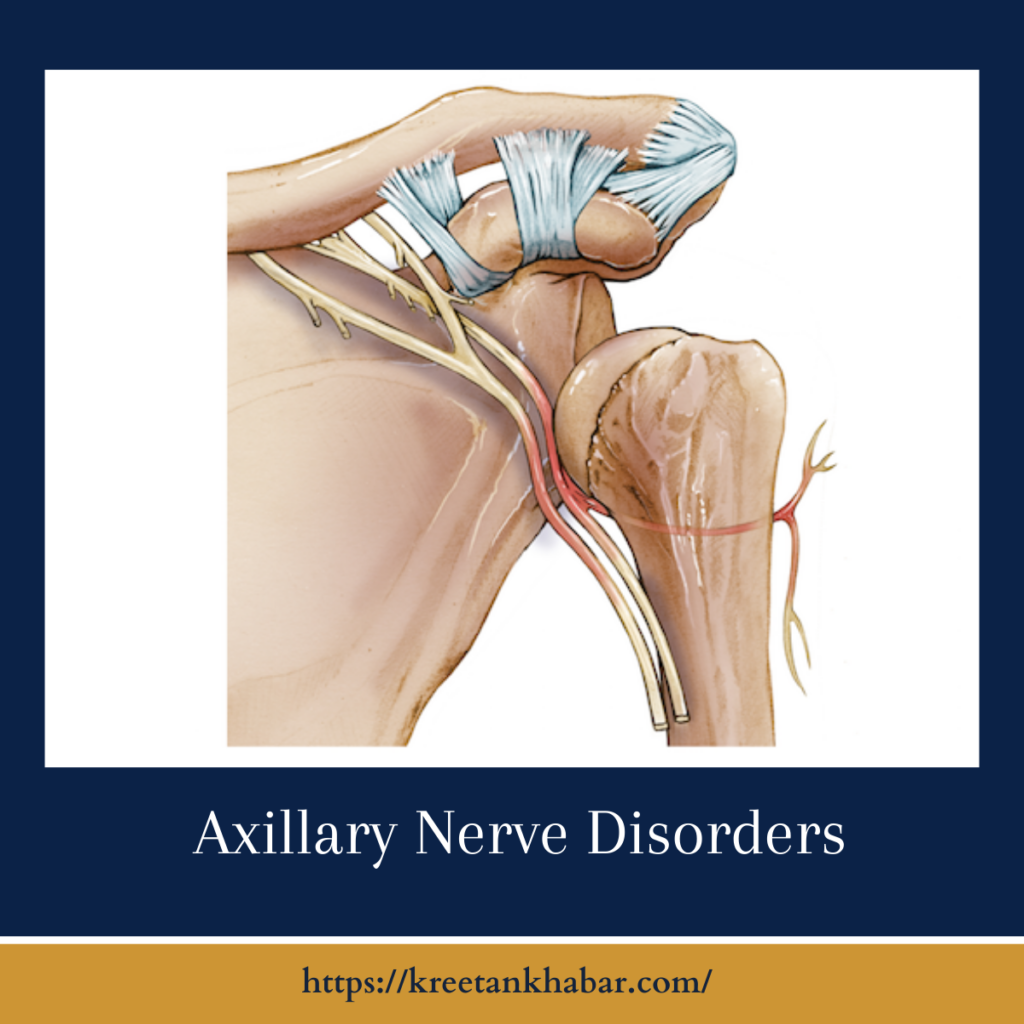
The axillary nerve, a crucial component of the brachial plexus, plays a significant role in shoulder and arm functionality. Disorders affecting the axillary nerve can disrupt the intricate network of signals essential for proper muscle movement and sensation in the shoulder region. This article delves into the complexities of axillary nerve disorders, exploring their causes, symptoms, and potential treatment options to shed light on this often overlooked aspect of neuro-musculoskeletal health.
Causes:
Axillary nerve disorders can arise from various factors, with the most common cause being trauma or injury, particularly in the context of shoulder dislocations or fractures. Additionally, compression or entrapment of the nerve, often referred to as neuropathy, can occur due to prolonged pressure on the shoulder or surrounding tissues. Other potential causes include surgical complications, inflammation, or underlying medical conditions affecting the nerves, such as neuropathies associated with diabetes.
Axillary nerve disorders can stem from various causes, predominantly centering around trauma or injury to the shoulder region. One primary cause is direct trauma, such as a shoulder dislocation or fractures, which can lead to compression or stretching of the axillary nerve. Sports injuries, falls, or accidents involving impact to the shoulder contribute to the risk of axillary nerve disorders. Additionally, surgical procedures around the shoulder area, particularly those involving the placement of implants or joint replacement, may inadvertently damage the axillary nerve.
Prolonged pressure on the shoulder, as seen in individuals who habitually rest their arm on hard surfaces, can result in nerve compression and subsequent dysfunction. Certain medical conditions, including neuropathies associated with diabetes or inflammatory conditions affecting the nerves, also pose a risk for axillary nerve disorders. Understanding these diverse factors is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approaches aimed at addressing the root cause of the disorder.
Symptoms:
The hallmark symptoms of axillary nerve disorders include pain, weakness, and numbness in the shoulder and upper arm. Individuals may experience difficulty lifting the arm, particularly in activities involving overhead motion. Shoulder instability and muscle atrophy are also common indicators of axillary nerve dysfunction. The onset of symptoms may be gradual or sudden, depending on the underlying cause, making early recognition crucial for effective management.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing axillary nerve disorders involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. This may include a detailed medical history, a thorough physical examination to assess muscle strength and sensation, and imaging studies such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or nerve conduction studies. These diagnostic tools aid in pinpointing the location and extent of nerve damage, guiding appropriate treatment strategies.
Treatment:
The approach to treating axillary nerve disorders depends on the underlying cause and the severity of symptoms. Conservative measures may include rest, physical therapy to improve strength and range of motion, and pain management. In cases of nerve compression or entrapment, addressing the root cause, such as correcting shoulder mechanics or relieving pressure on the nerve, is crucial. Surgical interventions may be recommended for severe injuries or cases where conservative measures prove insufficient. Surgical options include nerve decompression, grafting, or, in extreme cases, nerve transfer procedures.
Treatment of Axillary Nerve Disorders: Key Points
- Conservative Measures:
- Initial treatment often involves conservative measures, including rest, activity modification, and physical therapy.
- Physical therapy aims to improve shoulder mechanics, enhance muscle strength, and promote optimal range of motion.
- Pain Management:
- Pain management strategies, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain medications, may be prescribed to alleviate discomfort associated with axillary nerve disorders.
- Nerve Decompression:
- In cases of nerve compression or entrapment, addressing the root cause, such as releasing tight structures or correcting shoulder mechanics, is a primary focus.
- Surgical nerve decompression may be considered to relieve pressure on the axillary nerve.
- Nerve Grafting:
- For severe nerve injuries, nerve grafting procedures may be employed to bridge the gap in damaged nerve tissue, facilitating regeneration.
- Autografts or allografts may be used depending on the specific circumstances.
- Nerve Transfer:
- Nerve transfer procedures involve redirecting a healthy nerve to take over the function of the damaged axillary nerve.
- This approach is considered in cases where direct repair or grafting may not be feasible.
- Rehabilitation:
- Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the treatment process, aiming to restore optimal function and prevent complications.
- A tailored rehabilitation program may include exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and coordination.
- Orthopedic Interventions:
- Orthopedic interventions, such as joint stabilization procedures or addressing structural issues contributing to nerve compression, may be considered for comprehensive treatment.
- Bracing and Assistive Devices:
- Bracing and assistive devices may be recommended to support the affected arm and shoulder during the healing process.
- These aids help prevent excessive stress on the injured nerve and surrounding structures.
- Patient Education:
- Patient education is integral to the treatment plan, emphasizing the importance of adherence to prescribed therapies, lifestyle modifications, and follow-up care.
- Multidisciplinary Approach:
- A multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic specialists, neurologists, physical therapists, and pain management experts is essential for comprehensive and personalized care.
- Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan based on individual responses contribute to optimal outcomes.
- Long-Term Management:
- Long-term management involves ongoing monitoring, periodic evaluations, and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
- Patients are encouraged to actively participate in their care, reporting any changes or concerns promptly to facilitate timely interventions.
Understanding the diverse treatment options and tailoring interventions to the specific needs of individuals with axillary nerve disorders are pivotal in optimizing outcomes and restoring functionality. The collaborative efforts of healthcare professionals and engaged patient participation are key elements in achieving successful treatment results.
Challenges in Treatment:
Axillary nerve disorders pose challenges in treatment, particularly in cases where the cause is multifactorial or involves underlying medical conditions. Nerve regeneration is a slow process, and the extent of recovery can vary widely among individuals. Rehabilitation and ongoing monitoring are essential components of the treatment plan to optimize functional outcomes and prevent complications.
Conclusion:
Axillary nerve disorders underscore the intricate interplay between nerves, muscles, and the shoulder joint. Timely recognition of symptoms, a thorough diagnostic approach, and personalized treatment strategies are paramount for addressing these disorders effectively. As medical knowledge advances, the potential for innovative therapies and rehabilitation techniques offers hope for improved outcomes, emphasizing the importance of a collaborative effort between healthcare professionals and individuals navigating the complexities of axillary nerve disorders.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023