Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever: A Challenging Frontier in Infectious Diseases
Introduction:
Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever (MHF) stands as a formidable and enigmatic member of the viral hemorrhagic fever family, captivating the attention of scientists and health professionals alike. Named after the German town where the virus was first identified in 1967, Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever shares similarities with its notorious cousin, Ebola. In this article, we embark on a journey to understand the intricacies of Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever, exploring its origins, clinical manifestations, and the ongoing efforts to grapple with this highly infectious and often fatal disease.
Origins and Transmission:
- A Filovirus Intruder:
- Marburgvirus, the causative agent of Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever, belongs to the Filoviridae family, placing it in the same category as Ebola virus. The virus is believed to originate from fruit bats, acting as natural hosts, with sporadic transmission to humans through direct or indirect contact.
- Human-to-Human Transmission:
- Human-to-human transmission occurs through close contact with the blood, secretions, organs, or other bodily fluids of infected individuals. This intense transmissibility poses a significant challenge in controlling the spread of the virus, particularly in healthcare settings.
Clinical Manifestations:
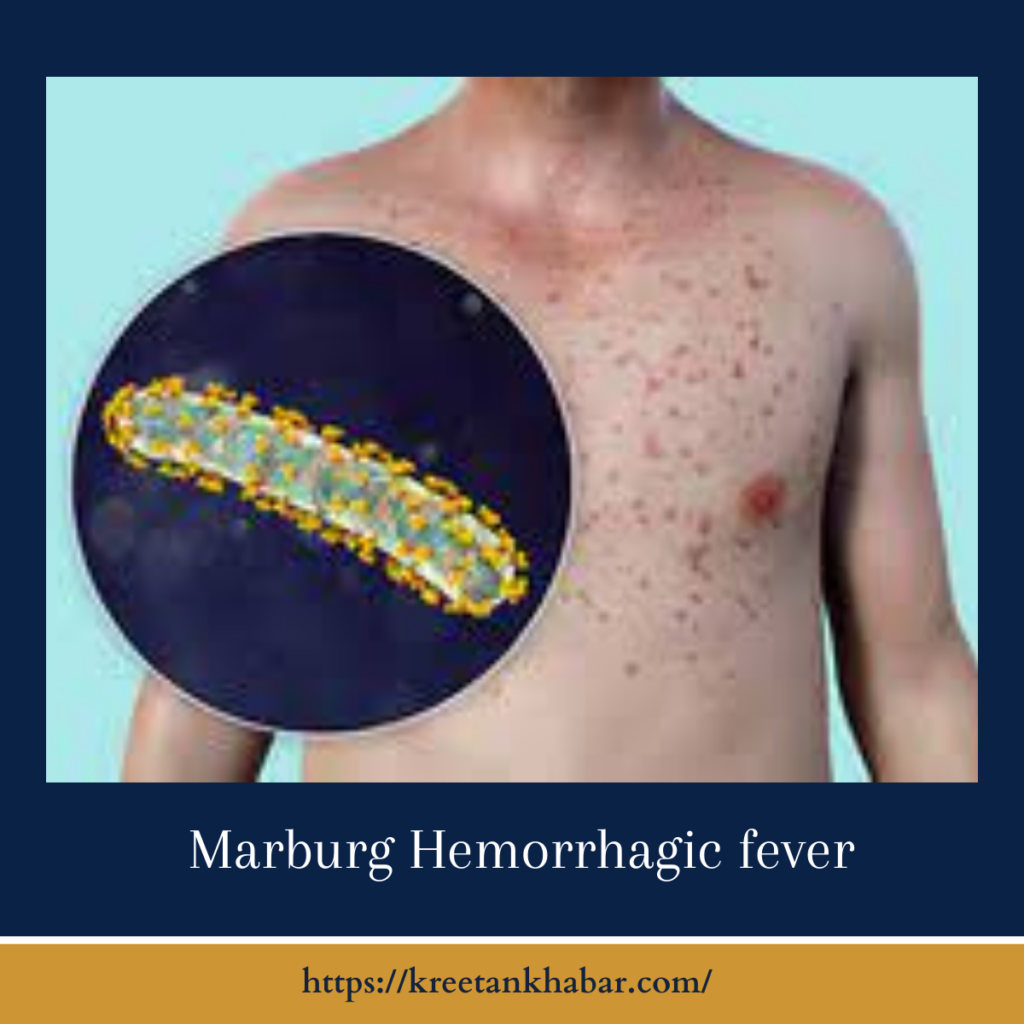
The clinical manifestations of Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever (MHF) unfold like a sinister symphony, reflecting the virus’s relentless assault on the human body. The initial phase is deceptively mild, with symptoms mimicking a common flu-like illness—fever, severe headache, and malaise. However, this tranquility is shattered as the virus progresses, ushering in the hemorrhagic phase. Profuse bleeding, both internally and externally, becomes a harrowing reality.
MHF doesn’t discriminate, involving multiple organs such as the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. The severity of the disease intensifies as it ravages through various bodily systems, contributing to a clinical landscape marked by organ dysfunction and a high risk of complications. The dual nature of Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever, beginning with inconspicuous symptoms and escalating into a hemorrhagic onslaught, adds to the challenge of timely diagnosis and underscores the urgency for effective medical interventions in the face of this formidable viral adversary.
- The Stealthy Incubation Period:
- MHF’s incubation period is marked by a deceptive silence, ranging from 2 to 21 days. The virus then unleashes a cascade of symptoms, including fever, severe headache, and malaise, resembling a flu-like illness. This initial phase is often challenging to distinguish from other common ailments.
- Hemorrhagic Unleashing:
- As the disease progresses, Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever earns its “hemorrhagic” designation. Individuals may experience profuse bleeding, both internally and externally, leading to a range of severe complications. This hemorrhagic phase is characterized by bleeding from multiple organs, posing a grave risk to the patient.
- Multi-Organ Involvement:
- MHF doesn’t confine its assault to a single organ. Instead, it engages in multi-organ involvement, affecting the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes. This widespread attack contributes to the severity of the disease and challenges medical interventions.
Points of Clinical Manifestation:
- Deceptive Onset:
- Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever often begins with a misleadingly mild phase, resembling common flu-like symptoms, including fever, severe headache, and general malaise.
- Stealthy Incubation:
- The virus operates in stealth during an incubation period, lasting from 2 to 21 days, making early detection challenging.
- Hemorrhagic Unleashing:
- As MHF progresses, it transforms into its characteristic hemorrhagic phase, where individuals may experience profuse bleeding, both internally and externally.
- Fluctuating Severity:
- The severity of Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever can fluctuate, with some individuals experiencing more severe manifestations, including widespread organ involvement and dysfunction.
- Organ-Specific Impact:
- MHF doesn’t limit its impact to a single organ; instead, it involves multiple organs, contributing to the complexity of clinical manifestations.
- Complications and Risks:
- The hemorrhagic phase poses a high risk of complications due to extensive bleeding, leading to challenges in managing the disease and an increased risk of mortality.
- Nonspecific Early Signs:
- The initial symptoms are nonspecific, making it challenging to distinguish Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever from other common illnesses in its early stages.
- Lack of Specific Treatment:
- There is no specific antiviral treatment for Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever, emphasizing the importance of supportive care and the challenges in managing the disease effectively.
- Diagnostic Complexity:
- Diagnosing MHF is complex, requiring specialized laboratory tests like PCR and serological assays, and access to these resources can be limited in affected regions.
- Severity Escalation:
- The clinical manifestations of MHF underscore its ability to escalate from seemingly benign symptoms to a severe and life-threatening hemorrhagic condition, emphasizing the need for heightened awareness and prompt medical attention.
Global Challenges and Ongoing Efforts:
Global challenges posed by Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever (MHF) paint a daunting picture, requiring concerted efforts and ongoing initiatives to tackle this infectious menace. Outbreak dynamics, characterized by sporadic occurrences in specific regions of Africa, demand swift identification, containment, and timely medical intervention. The diagnostic conundrum adds to the complexity, as early symptoms mimic other common ailments, making rapid and accurate diagnosis challenging. With no specific antiviral treatment available, managing MHF relies on supportive care, placing a significant burden on healthcare resources.
The impact on vulnerable populations, resource strain, and the ease of transmission within healthcare settings elevate Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever as a significant public health concern. Nevertheless, ongoing efforts encompass preventive measures, collaborative research for therapeutic options, and international cooperation. Surveillance, early detection, and public health education are pivotal in preventing widespread outbreaks. As the global community continues to grapple with MHF, a unified approach, combining scientific advancements, public awareness, and international collaboration, remains the linchpin in addressing the multifaceted challenges presented by Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever.
- Outbreak Dynamics:
- Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever is sporadically reported, with outbreaks occurring in specific regions of Africa. The dynamics of these outbreaks present challenges in terms of swift identification, containment, and provision of timely medical care.
- Diagnostic Conundrum:
- Diagnosing MHF in its early stages is challenging due to the nonspecific nature of initial symptoms. Laboratory tests, including PCR and serological assays, are crucial for confirming the presence of the virus, but access to these resources in affected regions can be limited.
- No Specific Treatment:
- Unfortunately, there is no specific antiviral treatment for Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever. Supportive care, including fluid replacement and management of specific symptoms, remains the mainstay of intervention. The lack of a targeted treatment underscores the urgency for research into therapeutic options.
- Preventive Measures:
- Prevention hinges on public health measures, including strict infection control practices in healthcare settings and community education about the modes of transmission. Surveillance and early detection play pivotal roles in preventing widespread outbreaks.
- Global Collaboration:
- Addressing the challenges posed by MHF requires a concerted global effort. Collaborative initiatives between affected countries, international organizations, and research institutions are crucial for advancing our understanding of the virus and developing effective preventive and therapeutic strategies.
Conclusion:
Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever, with its intricate dance of stealthy incubation and explosive symptoms, remains a poignant challenge in the realm of infectious diseases. As the global community strives to comprehend and combat this enigmatic virus, collaborative research, stringent preventive measures, and international cooperation stand as crucial pillars in the ongoing battle against Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023