Understanding Bulimia: Unmasking the Hidden Struggle
Introduction
In today’s world, the pressure to conform to society’s unrealistic standards of beauty has left many individuals grappling with various eating disorders. One such disorder is bulimia nervosa (also called hyperphagia), a complex and often misunderstood condition. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of bulimia, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and available treatments, in an effort to raise awareness and promote understanding of this hidden struggle.
Defining Bulimia
Bulimia nervosa, commonly known as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors to rid the body of the consumed calories. These compensatory behaviors often include self-induced vomiting, excessive exercise, fasting, or the misuse of laxatives or diuretics. Individuals with hyperphagia often engage in these behaviors to alleviate the guilt and anxiety associated with overeating.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Bulimia is a multifaceted disorder with no single cause. Several factors can contribute to its development, including:
- Genetics: There is evidence to suggest that genetics may play a role in predisposing some individuals to eating disorders like hyperphagia. A family history of eating disorders or other mental health conditions can increase the risk.
- Psychological Factors: Low self-esteem, perfectionism, and body dissatisfaction are common psychological factors that can contribute to the development of hyperphagia. These feelings may be exacerbated by societal pressure to attain an idealized body image.
- Environmental Influences: Social and environmental factors, such as exposure to thin-ideal media portrayals and peer pressure, can influence the development of hyperphagia. A culture that emphasizes thinness and dieting can contribute to disordered eating behaviors.
- Trauma and Stress: Traumatic experiences, such as childhood abuse or significant life stressors, can increase the vulnerability to hyperphagia. For some individuals, engaging in binge eating and purging may serve as a coping mechanism to deal with emotional pain or stress.
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of bulimia is crucial for early intervention and treatment. Common indicators include:
- Frequent Episodes of Binge Eating: Individuals with hyperphagia often consume large amounts of food in a short period, feeling a lack of control during these episodes.
- Compensatory Behaviors: Following a binge, individuals may engage in purging behaviors, such as vomiting, fasting, or excessive exercise, in an attempt to counteract the consumed calories.
- Concern About Body Weight and Shape: An intense preoccupation with body weight, shape, and appearance is a hallmark of hyperphagia. This obsession can lead to extreme dieting and exercise.
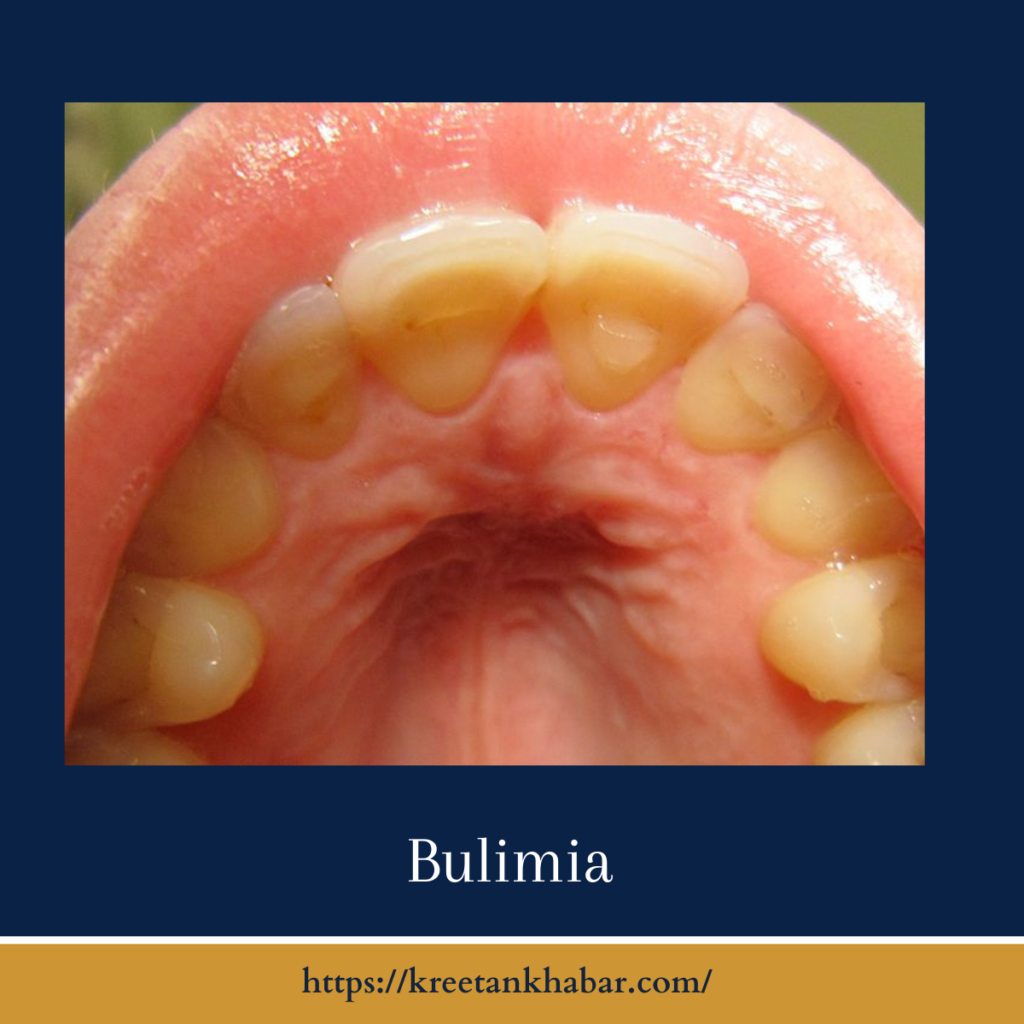
- Physical Signs: Repeated purging can lead to physical consequences, including dental problems, electrolyte imbalances, gastrointestinal issues, and damage to the esophagus.
here are 20 key signs and symptoms of bulimia:
- Recurrent Binge Eating: Individuals with bulimia often engage in episodes of uncontrollable overeating, consuming unusually large amounts of food within a short period.
- Lack of Control: During binge eating episodes, those with hyperphagia feel a marked lack of control over their eating behavior.
- Binge-Food Choices: Binge eating typically involves consuming high-calorie, often unhealthy foods.
- Secretive Eating: People with bulimia may hide their binge eating episodes out of embarrassment or guilt.
- Compensatory Behaviors: Following binge eating, individuals may resort to compensatory behaviors to rid the body of the calories consumed.
- Self-Induced Vomiting: Frequent self-induced vomiting is a common symptom, with individuals using this method to purge after binge eating.
- Fasting: Some individuals with bulimia may engage in prolonged periods of fasting to compensate for binge episodes.
- Excessive Exercise: Over-exercising, even to the point of exhaustion, is another common compensatory behavior.
- Laxative or Diuretic Abuse: The misuse of laxatives or diuretics to expel calories and fluids from the body is a sign of hyperphagia.
- Intense Fear of Weight Gain: A preoccupation with body weight and a persistent fear of gaining weight is a defining feature.
- Body Dissatisfaction: Individuals with bulimia are often highly dissatisfied with their body shape and size.
- Ritualistic Behaviors: Some people may develop rituals or specific routines around binge eating and purging.
- Emotional Distress: Feelings of guilt, shame, anxiety, or depression often accompany bulimia.
- Social Withdrawal: As the disorder progresses, individuals may withdraw from social activities to hide their behaviors.
- Dental Problems: Frequent vomiting can lead to dental issues like tooth decay and enamel erosion.
- Gastrointestinal Problems: Repeated purging can cause digestive problems such as gastritis and esophageal damage.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Vomiting and laxative use can disrupt electrolyte balance, leading to serious health issues.
- Swollen Glands: Enlarged salivary glands, or parotid glands, are a common physical sign of hyperphagia.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: In females, bulimia can lead to irregular or absent menstrual periods.
- Hair and Nail Problems: Nutritional deficiencies can result in brittle hair and nails, which are observable signs of the disorder.
These signs and symptoms may vary in intensity among individuals with hyperphagia, but recognizing them is crucial for early intervention and support. If you or someone you know is struggling with these symptoms, seeking professional help is highly recommended for a path toward recovery.
Treatment and Recovery
Recovery from bulimia is possible with the right support and treatment. The primary goal of treatment is to address the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the disorder. Treatment approaches may include:
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and dialectical-behavior therapy (DBT) are commonly used psychotherapeutic approaches to help individuals with hyperphagia address distorted thoughts and behaviors.
- Nutritional Counseling: Registered dietitians can work with individuals to develop healthier eating patterns and address nutritional deficiencies.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage co-occurring mental health conditions like depression or anxiety.
- Support Groups: Group therapy can provide individuals with a supportive community of peers who understand their struggles.
Conclusion
Bulimia nervosa is a complex and often hidden eating disorder that can have serious physical and psychological consequences if left untreated. Understanding the causes, signs, and available treatments for hyperphagia is essential for raising awareness and providing support to those who are struggling. With the right help and resources, individuals with hyperphagia can embark on a path to recovery and regain control over their lives, free from the grip of this challenging disorder.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023