Lymphoedema: Understanding the Condition and Managing its Impact
Introduction
Lymphoedema (also known as lymphatic edema) is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the lymphatic system, which is responsible for draining excess fluids from the body, becomes impaired, leading to the accumulation of lymphatic fluid and swelling in various body parts. In this article, we will delve into what lymphoedema is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and strategies for managing and living with this condition.
Understanding Lymphoedema
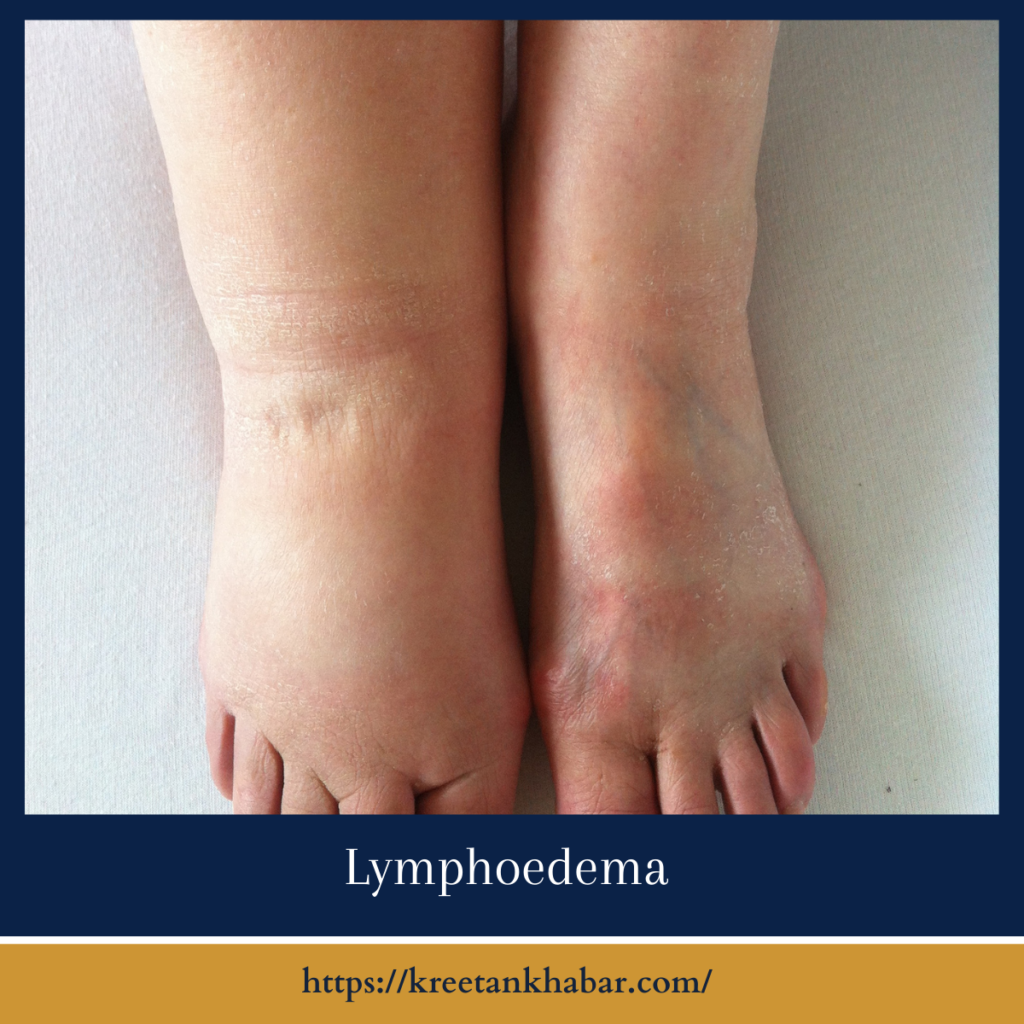
What is Lymphoedema? lymphatic edema is a chronic and progressive condition characterized by the accumulation of lymphatic fluid in the interstitial tissues, resulting in localized swelling. It typically affects the arms and legs, although it can occur in other body parts as well. lymphatic edema is categorized into two primary types:
- Primary Lymphoedema: This type is rare and often hereditary, resulting from congenital malformation or dysfunction of the lymphatic system.
- Secondary Lymphoedema: Secondary lymphatic edema is more common and occurs as a result of damage to the lymphatic system due to surgery, radiation therapy, infection, trauma, or other medical conditions like cancer.
Causes of Lymphoedema
Causes of Secondary lymphatic edema:
- Cancer Treatment: Surgery to remove lymph nodes, radiation therapy, or the presence of tumors can disrupt the lymphatic system, leading to secondary lymphatic edema.
- Infection: Conditions like cellulitis or filariasis can damage lymphatic vessels and cause lymphatic edema.
- Trauma: Physical injuries or accidents that damage the lymphatic system can result in lymphatic edema.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can place pressure on the lymphatic system and contribute to the development of lymphatic edema.
- Venous Insufficiency: Chronic venous insufficiency can increase the risk of lymphatic edema in the legs.
Symptoms of lymphatic edema
Common Symptoms of lymphatic edema:
- Swelling: Persistent swelling in the affected limb or body part is the hallmark symptom of lymphatic edema.
- Heaviness or Discomfort: Individuals with lymphatic edema often report a feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the affected area.
- Decreased Range of Motion: Swelling can limit the range of motion in joints near the affected area.
- Skin Changes: The skin over the affected area may become thickened, hardened, or develop folds and indentations.
- Recurrent Infections: lymphatic edema increases the risk of skin infections, such as cellulitis, due to compromised immune function in the affected tissue.
here are the key points regarding the symptoms of Lymphoedema:
Symptoms of Lymphoedema:
- Swelling: The most common and noticeable symptom of lymphoedema is persistent swelling in the affected limb or body part. This swelling may range from mild to severe and can be uncomfortable or painful.
- Heaviness and Discomfort: Many individuals with lymphoedema describe a feeling of heaviness or fullness in the affected area. This sensation can be bothersome and affect daily activities.
- Limited Range of Motion: Swelling in the affected limb can lead to decreased flexibility and range of motion, making it challenging to move the limb freely.
- Skin Changes: Over time, the skin in the affected area may undergo changes. It can become thickened, hardened, or fibrotic. Additionally, the skin may develop folds, creases, or indentations.
- Recurrent Infections: Lymphoedema impairs the immune function in the affected tissue, making it more susceptible to infections. Individuals with lymphoedema are at higher risk for skin infections like cellulitis, which can cause redness, warmth, pain, and fever.
- Frequent Swelling: Lymphoedema swelling tends to be persistent but may fluctuate in severity. It often worsens after prolonged standing or sitting.
- Clothing and Jewelry Tightness: Individuals with lymphoedema may notice that clothing, shoes, or jewelry feel tighter on the affected limb due to the swelling.
- Fibrotic Tissue Formation: In advanced cases, the accumulation of lymphatic fluid and chronic inflammation can lead to the development of fibrotic tissue, further restricting movement and causing discomfort.
- Psychological Impact: Lymphoedema can have psychological effects, including body image concerns, self-esteem issues, and feelings of frustration or anxiety due to its impact on daily life.
It’s important to note that lymphoedema symptoms can vary in severity and progression, and they may develop gradually over time. Early recognition and diagnosis are essential for managing lymphoedema effectively and preventing complications. Individuals experiencing any of these symptoms should seek medical evaluation and consult with a healthcare professional, such as a lymphoedema therapist, for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis:
- Diagnosis of lymphatic edema typically involves a physical examination and medical history.
- Imaging tests, such as lymphoscintigraphy, can help visualize the lymphatic system and confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
- lymphatic edema is a chronic condition with no cure, but treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Common treatment options include:
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): A specialized massage technique to encourage the flow of lymphatic fluid.
- Compression Therapy: The use of compression garments or bandaging to reduce swelling.
- Exercise: Customized exercise programs to improve lymphatic flow and muscle function.
- Skin Care: Proper skin hygiene to prevent infections.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to reduce swelling and manage symptoms.
- Surgery: Surgical options may be considered in severe cases.
Living with Lymphoedema
Living with lymphatic edema requires ongoing self-care and management. Individuals can take several steps to improve their quality of life:
- Adherence to Treatment: Consistently follow the recommended treatment plan provided by healthcare professionals.
- Skin Care: Keep the skin clean and moisturized, and promptly address any cuts or infections to prevent complications.
- Compression Garments: Wear compression garments as prescribed to maintain reduced swelling.
- Exercise: Engage in regular, gentle exercise routines recommended by a lymphatic edema therapist or physical therapist.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy weight and lifestyle to reduce the risk of exacerbating lymphatic edema.
Conclusion
Lymphoedema is a chronic condition that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life. While there is no cure, proper management, early intervention, and a commitment to self-care can help individuals with lymphatic edema maintain a good quality of life. Working closely with healthcare professionals and lymphoedema therapists is crucial in managing the condition effectively and preventing complications.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023