Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Knee
Introduction:
In the intricate world of orthopedics, a condition silently affecting the knees known as Osteochondritis Dissecans (OCD) demands our attention. This enigmatic ailment, characterized by the detachment of bone and cartilage fragments within the knee joint, presents both a diagnostic puzzle and a unique challenge for those who grapple with its effects. Join us on a journey through the maze of OCD, shedding light on its origins, symptoms, and the strategies employed to reclaim mobility and well-being.
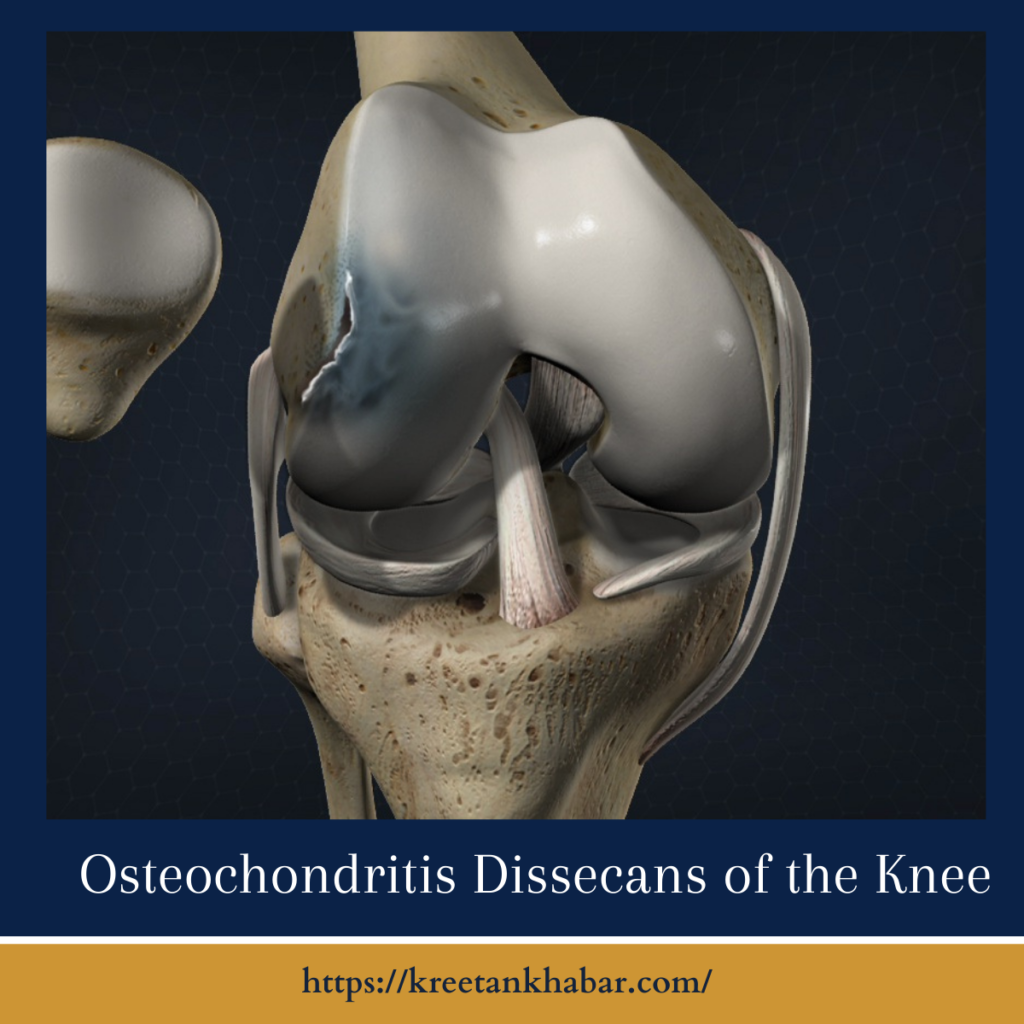
Unraveling the Enigma of Osteochondritis Dissecans:
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the knee is a condition that primarily targets the knee joint, although it can manifest in other joints as well. The term itself provides a clue to its nature, with “osteo” referring to bone and “chondritis” to cartilage. In OCD, a segment of bone and its overlying cartilage, typically at the end of the femur (thigh bone) or the tibia (shin bone), becomes detached. This detachment can lead to the formation of loose bodies within the joint, triggering pain, swelling, and a gradual erosion of joint function.
The Silent Onset:
One of the perplexing aspects of Osteochondritis Dissecans of the knee is its often subtle onset. Initially, individuals may experience vague discomfort or aching in the affected knee, dismissed as mere overuse or strain. As the condition progresses, however, more distinctive symptoms emerge. Persistent pain, swelling, and a noticeable decrease in joint flexibility become telltale signs that something more complex is at play beneath the surface.
Who’s at Risk?
OCD does not discriminate based on age or activity level, yet certain factors may predispose individuals to its development. Adolescents and young adults, particularly those engaged in sports that involve repetitive stress on the knees, are more susceptible. Additionally, genetic predispositions, hormonal imbalances, and anatomical variations may contribute to the emergence of Osteochondritis Dissecans of the knee.
The Diagnostic Dance:
Diagnosing OCD is akin to performing a delicate dance between clinical evaluation and advanced imaging. While X-rays may reveal characteristic changes in the affected joint, MRI scans provide a more detailed look at the status of the bone, cartilage, and any loose fragments within the joint. The diagnostic journey may also involve ruling out other knee conditions that mimic the symptoms of OCD, adding an extra layer of complexity.
Treatment Strategies:
Once the curtain is lifted on the presence of Osteochondritis Dissecans of the knee, a tailored treatment plan takes center stage. The approach varies based on the severity of the condition, the age of the individual, and the specific characteristics of the lesion. Conservative measures, such as rest, physical therapy, and the use of supportive devices, may be sufficient for milder cases. For more advanced stages, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove loose fragments, secure detached cartilage, or stimulate the healing response within the joint.
The Road to Recovery:
Recovery from Osteochondritis Dissecans of the knee is not just about fixing the immediate issue; it’s about restoring the intricate balance within the knee joint. Physical therapy plays a pivotal role, guiding individuals through exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles, improve joint stability, and enhance overall function. Patience becomes a virtue as the joint heals and rehabilitation progresses, gradually paving the way for a return to normal activities.
Prevention as the Best Medicine:
In the realm of OCD, prevention is a powerful ally. Mindful conditioning, proper warm-up routines, and avoiding overuse or excessive stress on the knees can go a long way in reducing the risk of developing this orthopedic conundrum. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers, especially for those engaged in high-impact sports, provide an opportunity for early detection and intervention.
Conclusion:
Osteochondritis Dissecans of the knee is a complex interplay of bone and cartilage, demanding both our attention and understanding. As we navigate through its silent onset, diagnostic intricacies, and tailored treatment strategies, we uncover the resilience of the human body and the collaborative efforts of healthcare professionals. In the face of this knee conundrum, knowledge becomes the compass guiding individuals towards recovery and a renewed appreciation for the delicate balance within their joints.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023