Posterior Tibial Neuralgia: A Nerve’s Tale of Discomfort
Introduction
In the intricate tapestry of the human body, nerves play the role of silent messengers, orchestrating the symphony of sensations. Yet, within this delicate network, there exists a condition that disrupts the harmony—the tale of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia. As a lesser-known but impactful nerve disorder, this condition takes center stage in the narrative of discomfort. Let us embark on a journey through the complexities of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia, exploring its origins, symptoms, and the strategies that offer a glimmer of relief to those navigating this nerve’s tale of discomfort.
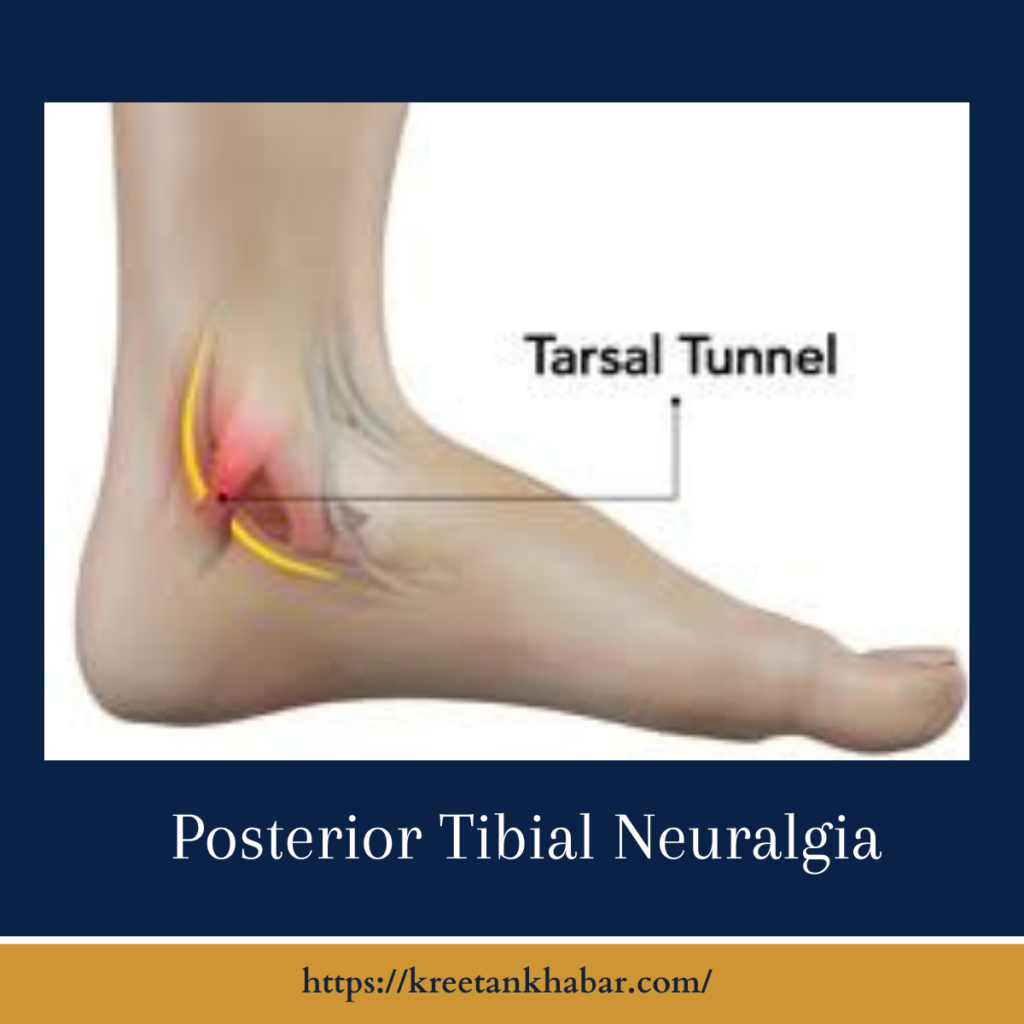
The Anatomy of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia
The posterior tibial nerve, coursing through the lower leg and foot, serves as a vital conduit for sensory and motor signals. Neuralgia, in this context, refers to the pain caused by irritation or damage to a nerve. Posterior Tibial Neuralgia emerges when this crucial nerve becomes entangled in a web of distress, sending signals of discomfort that resonate throughout the lower extremities.
Origins of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia
The origins of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia unravel as a complex tapestry woven from various threads of influence, each contributing to the intricate narrative of nerve discomfort. Within the anatomy of the lower leg and foot, this condition often finds its roots in structural anomalies—a dance of flat feet, overpronation, or the subtle presence of bone spurs that sets the stage for nerve compression. Inflammatory conditions emerge as characters in this tale, with arthritis or tendonitis casting a shadow of swelling and irritation onto the posterior tibial nerve.
Trauma, whether from accidents or the relentless toll of repetitive stress, marks a chapter of injury that can leave the nerve ensnared in a web of discomfort. The plot thickens with the notion of nerve entrapment, where tight anatomical spaces like the tarsal tunnel become the stage for compression and the onset of neuralgia. In understanding the origins of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia, we decipher the intricate script that guides this nerve’s journey from subtle irritation to a symphony of discomfort.
The origins of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia are as diverse as the nerves it affects. Several factors contribute to the irritation or compression of the posterior tibial nerve, including:
- Structural Abnormalities: Anomalies in the structure of the foot, such as flat feet, overpronation, or bone spurs, can create an environment conducive to nerve compression, setting the stage for posterior tibial neuralgia.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Inflammatory conditions like arthritis or tendonitis can lead to swelling and compression of the posterior tibial nerve, initiating the cascade of neuralgia symptoms.
- Trauma or Injury: Trauma or injury to the foot, ankle, or lower leg, whether through accidents or repetitive stress, can cause damage to the nerve and contribute to the onset of neuralgia.
- Nerve Entrapment: Entrapment of the posterior tibial nerve within tight anatomical spaces, such as the tarsal tunnel, can result in compression and subsequent neuralgia.
Symptoms of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia
Posterior Tibial Neuralgia, a condition where the posterior tibial nerve weaves a tapestry of discomfort, unveils its presence through a symphony of symptoms. In the quiet recesses of the lower extremities, pain takes center stage—an orchestra of tingling, burning sensations that dance along the nerve’s path, from the inner ankle to the sole of the foot. Numbness emerges as a silent player, rendering the affected areas insensate to the nuances of touch. This nerve’s tale extends beyond mere sensation;
weakness creeps in, affecting the orchestrated movements of muscles under the nerve’s command, creating a subtle discord in the rhythm of mobility. Swelling and tenderness lend their voices to the narrative, a chorus reflecting the underlying inflammation and the nerve’s plea for respite. In the complex interplay of these symptoms, those grappling with Posterior Tibial Neuralgia navigate a nuanced landscape of discomfort, seeking relief and restoring harmony to the orchestra of sensations.
The symptoms of Posterior Tibial Neuralgia manifest as a repertoire of discomfort, often characterized by:
- Pain and Tingling: Individuals with Posterior Tibial Neuralgia commonly experience pain, tingling, or a burning sensation along the path of the nerve, radiating from the inside of the ankle to the sole of the foot.
- Numbness: Numbness in the inner ankle and the sole of the foot is a prevalent symptom, affecting normal sensation and potentially impacting mobility.
- Weakness: Weakening of the muscles controlled by the posterior tibial nerve may occur, leading to difficulties in walking, maintaining balance, or performing certain movements.
- Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling and tenderness in the affected area may accompany Posterior Tibial Neuralgia, reflecting the underlying inflammation and nerve irritation.
Navigating the Path to Relief
The journey to relief from Posterior Tibial Neuralgia involves a thoughtful approach that addresses the underlying causes and manages the symptoms. Key strategies include:
- Orthotic Support: Custom-made orthotic inserts can help correct foot mechanics, providing support and alleviating pressure on the posterior tibial nerve.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises focused on stretching and strengthening the muscles around the affected nerve can improve flexibility and reduce irritation.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with Posterior Tibial Neuralgia.
- Activity Modification: Modifying activities that exacerbate symptoms, such as avoiding prolonged periods of standing or walking, can help manage neuralgia discomfort.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from symptoms.
- Supportive Footwear: Wearing supportive footwear that accommodates the specific needs of the foot and minimizes stress on the nerve can be beneficial.
Conclusion
Posterior Tibial Neuralgia unfolds as a compelling chapter in the intricate narrative of nerve disorders. Understanding its origins, recognizing the symptoms, and navigating the path to relief require a holistic approach that combines medical expertise with individualized care. In this journey through the nerve’s tale of discomfort, those affected find solace in the pursuit of relief, a testament to the resilience of the human body and spirit in the face of neuralgia’s challenges.
Read also : Exploring the Delightful Boost of the Green Tea Shot 2023