Introduction
Liver cirrhosis is a serious medical condition that affects the liver, resulting in progressive damage and scarring. This condition impairs the liver’s ability to function properly and can lead to severe complications. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for liver cirrhosis.
Causes of Liver Cirrhosis
1. Alcohol Abuse: Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption is a leading cause of liver cirrhosis. As the years pass, the consistent consumption of alcohol inflicts harm upon liver cells, causing an inflammatory response and subsequent formation of scar tissue.
2. Chronic Viral Hepatitis: Hepatitis B and C infections can cause long-term liver damage, eventually leading to cirrhosis. These viral infections are transmitted through contaminated blood or body fluids.
3. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, often associated with obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, or metabolic syndrome. In some cases, NAFLD can progress to liver cirrhosis.
4. Autoimmune Hepatitis: This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells, leading to inflammation and liver damage. With the passing of time, the cumulative effects can eventually culminate in the development of cirrhosis, a condition characterized by extensive liver scarring and compromised function.
5. Genetic Disorders: Certain genetic conditions, such as hemochromatosis (excessive iron buildup) and Wilson’s disease (copper accumulation), can cause liver cirrhosis if left untreated.
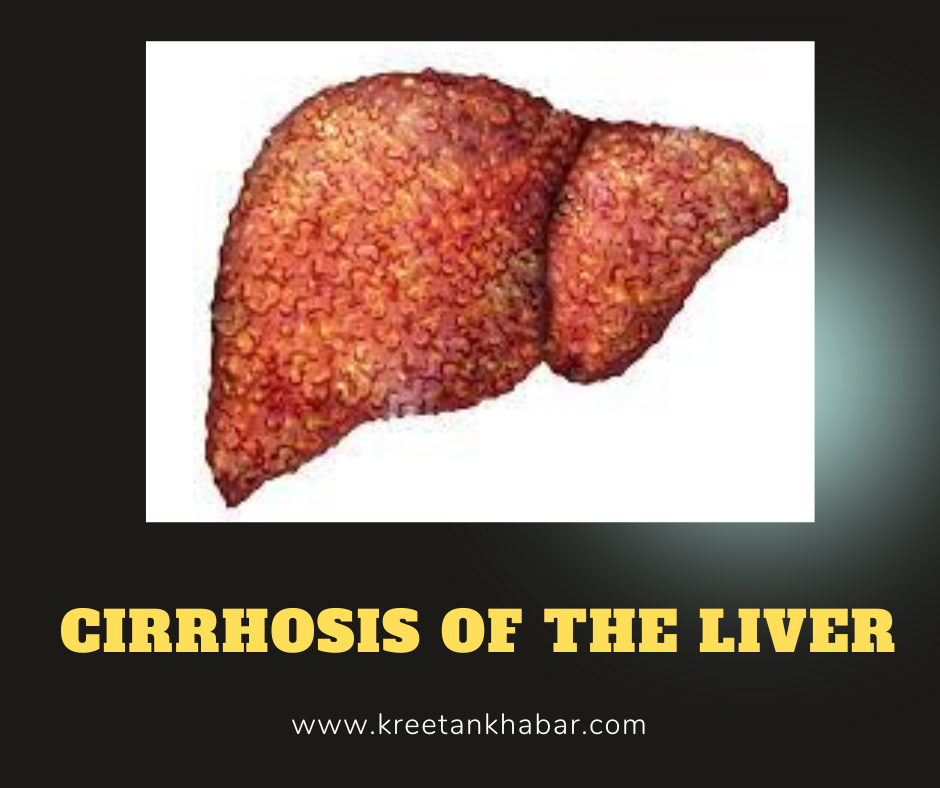
Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis
The symptoms of liver cirrhosis may vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. Some common signs and symptoms include:
1. Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak, even after ample rest, is a common symptom of liver cirrhosis.
2. Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes occurs due to the liver’s impaired ability to process bilirubin, a pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells.
3. Fluid Retention: Cirrhosis can lead to fluid accumulation in the abdomen (ascites) and legs (edema). This occurs when the liver fails to produce enough proteins necessary for maintaining fluid balance.
4. Digestive Issues: Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, and weight loss can occur as a result of cirrhosis.
5. Mental Confusion: As liver function declines, toxins can accumulate in the blood, affecting brain function and causing confusion, forgetfulness, and difficulty concentrating (hepatic encephalopathy).
Treatment Options for Liver Cirrhosis
1. Lifestyle Changes: For individuals with alcohol-related cirrhosis, the most important step is to cease alcohol consumption. Adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
2. Medications: Certain medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms, control complications, or slow down the progression of liver cirrhosis. These can include diuretics, antibiotics, and medications to reduce liver inflammation.
3. Liver Transplant: In advanced cases of cirrhosis, where the liver is severely damaged and no longer functional, a liver transplant may be necessary. To rectify the impaired liver function, the procedure entails surgically replacing the diseased liver with a fully functional liver generously donated by a compatible individual.
4. Management of Complications: Various complications associated with cirrhosis, such as portal hypertension, liver cancer, and hepatic encephalopathy, require specific treatment approaches to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Improving their overall prognosis and maintaining optimal liver health. Regular monitoring of liver function through blood tests and imaging studies is essential for early detection and intervention. It is also important to receive vaccinations for hepatitis A and B to prevent further liver damage.
In addition to medical interventions, individuals with liver cirrhosis can take certain steps to support liver health and minimize complications:
1. Follow a Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing liver cirrhosis. It is important to consume foods that are low in salt to reduce fluid retention and limit the intake of processed and fatty foods. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can provide the necessary nutrients for liver health.
2. Limit Sodium Intake: Sodium can contribute to fluid retention, so it is important to reduce salt intake. This includes avoiding high-sodium processed foods and seasoning meals with herbs and spices instead of salt.
3. Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water helps maintain overall health and supports liver function. However, individuals with cirrhosis should consult their healthcare provider for personalized recommendations regarding fluid intake, as excessive fluid consumption can exacerbate fluid retention.
4. Avoid Alcohol and Substance Abuse: Completely abstaining from alcohol is crucial for individuals with alcohol-related liver cirrhosis. Additionally, avoiding the use of illicit drugs and practicing safe medication use can prevent further liver damage and complications.
5. Engage in Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can help improve overall health, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce the risk of fatty liver disease. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any exercise regimen to ensure it is safe and suitable for individual circumstances.
6. Manage Coexisting Conditions: Individuals with liver cirrhosis often have other medical conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol. Proper management of these conditions through medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular medical check-ups is crucial for overall well-being.
7. Seek Emotional Support: Living with a chronic condition like liver cirrhosis can be emotionally challenging. It is important to seek support from loved ones, join support groups, or consider counseling to cope with the emotional aspects of the condition.
8. Regularly Take Prescribed Medications: If your healthcare provider has prescribed medications to manage your liver cirrhosis or its associated complications, it is crucial to take them as instructed. Be sure to understand the dosage, frequency, and any potential side effects. Inform your healthcare provider about any other medications, supplements, or herbal remedies you are taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
9. Vaccinations: Immunization plays a vital role in preventing additional liver damage. Ensure that you are up to date on vaccinations for hepatitis A and B, as these infections can further harm the liver. Vaccination can protect against these viruses and reduce the risk of complications.
10. Monitor and Manage Ascites: Ascites, the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen, is a common complication of liver cirrhosis. Your healthcare provider may prescribe diuretics to help remove excess fluid and recommend dietary modifications, such as reducing salt intake. In severe cases, paracentesis (fluid drainage) or other procedures may be necessary to alleviate symptoms.
11. Screen for Liver Cancer: Liver cirrhosis increases the risk of developing liver cancer. Regular screening with imaging tests, such as ultrasounds or MRIs, can help detect any early signs of liver cancer. The timely identification of the condition significantly enhances the prospects of effective treatment, maximizing the likelihood of positive outcomes and favorable response to interventions.
12. Hepatic Encephalopathy Management: Hepatic encephalopathy is a condition characterized by cognitive impairment and altered mental function due to liver dysfunction. To manage this condition, your healthcare provider may recommend medications to reduce ammonia levels in the blood, dietary changes to limit protein intake, and close monitoring of symptoms.
13. Supportive Care: Managing liver cirrhosis involves a multidisciplinary approach. Your healthcare team may include hepatologists, nutritionists, social workers, and mental health professionals who can provide valuable support, education, and guidance throughout your journey.
14. Liver Cirrhosis Support Groups: Connecting with others who are experiencing or have experienced liver cirrhosis can be immensely helpful. Joining support groups or online communities allows you to share experiences, gain insights, and find emotional support from individuals who understand the challenges associated with the condition.
15. Stay Informed: Educate yourself about liver cirrhosis, its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. Stay updated on the latest advancements in liver disease management. However, always consult with your healthcare provider for accurate information and guidance tailored to your specific needs.
Foods that helps in cirrhosis
While there is no specific diet that can cure or reverse liver cirrhosis, a well-balanced and nutritious diet can support liver health and overall well-being. Here are some foods that may be beneficial for individuals with cirrhosis:
1. Enrich your diet with an assortment of fresh fruits and vegetables, as their diverse array of nutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants contribute to overall well-being and support optimal liver health.These are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber, which can support overall health and aid digestion. Choose colorful options like berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, carrots, and broccoli.
2. Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat bread, and oats. These provide essential nutrients and dietary fiber while promoting satiety and stable blood sugar levels.
3. Lean Protein Sources: Incorporate lean protein sources into your diet, such as skinless poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and legumes. Protein is important for tissue repair and supports liver function. However, individuals with advanced cirrhosis may need to limit protein intake based on their specific medical recommendations.
4. Healthy Fats: Include healthy fats in moderation, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These provide essential fatty acids that support cell function and reduce inflammation.
5. Low-Sodium Foods: Limit your sodium intake, as excessive sodium can contribute to fluid retention and worsen symptoms like ascites. It is advisable to steer clear of processed and packaged food options due to their tendency to contain excessive amounts of sodium, which can have detrimental effects on health, particularly for individuals managing conditions like liver cirrhosis. Instead, focus on fresh, homemade meals seasoned with herbs and spices.
6. Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and may help reduce liver inflammation. Good sources include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds.
7. Small, Frequent Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day can ease the burden on the liver and aid digestion. This approach can help manage symptoms like bloating and nausea.
8. Adequate Fluid Intake: Stay hydrated by drinking enough fluids, such as water, herbal teas, and diluted fruit juices. However, if you have fluid retention (ascites), consult your healthcare provider for personalized fluid intake recommendations.
It is important to note that dietary needs may vary based on individual circumstances and the severity of liver cirrhosis. It is recommended to work with a registered dietitian or nutritionist who can provide personalized dietary guidance and tailor recommendations to your specific needs and medical condition.
Additionally, it is essential to follow any dietary restrictions or guidelines provided by your healthcare provider, as these may be specific to your situation and medical history.
Conclusion
Liver cirrhosis is a complex condition that requires ongoing management and care. By following a comprehensive treatment plan, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and engaging in regular medical follow-ups, individuals with liver cirrhosis can minimize complications, slow down disease progression, and improve their overall well-being.
Remember, each person’s experience with liver cirrhosis is unique, and treatment approaches may vary. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare team to develop a personalized care plan that suits your specific needs. With proper care and support, individuals with liver cirrhosis can lead fulfilling lives and maintain optimal liver health.
Liver cirrhosis is a serious condition that can have life-threatening consequences if left untreated. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking medical intervention are crucial for managing this condition effectively. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, following prescribed treatments, and regularly consulting healthcare professionals, individuals with liver cirrhosis can enhance their chances of leading a fulfilling life.
Read also : Include corn in your diet for weight loss and know benefits of eating it.